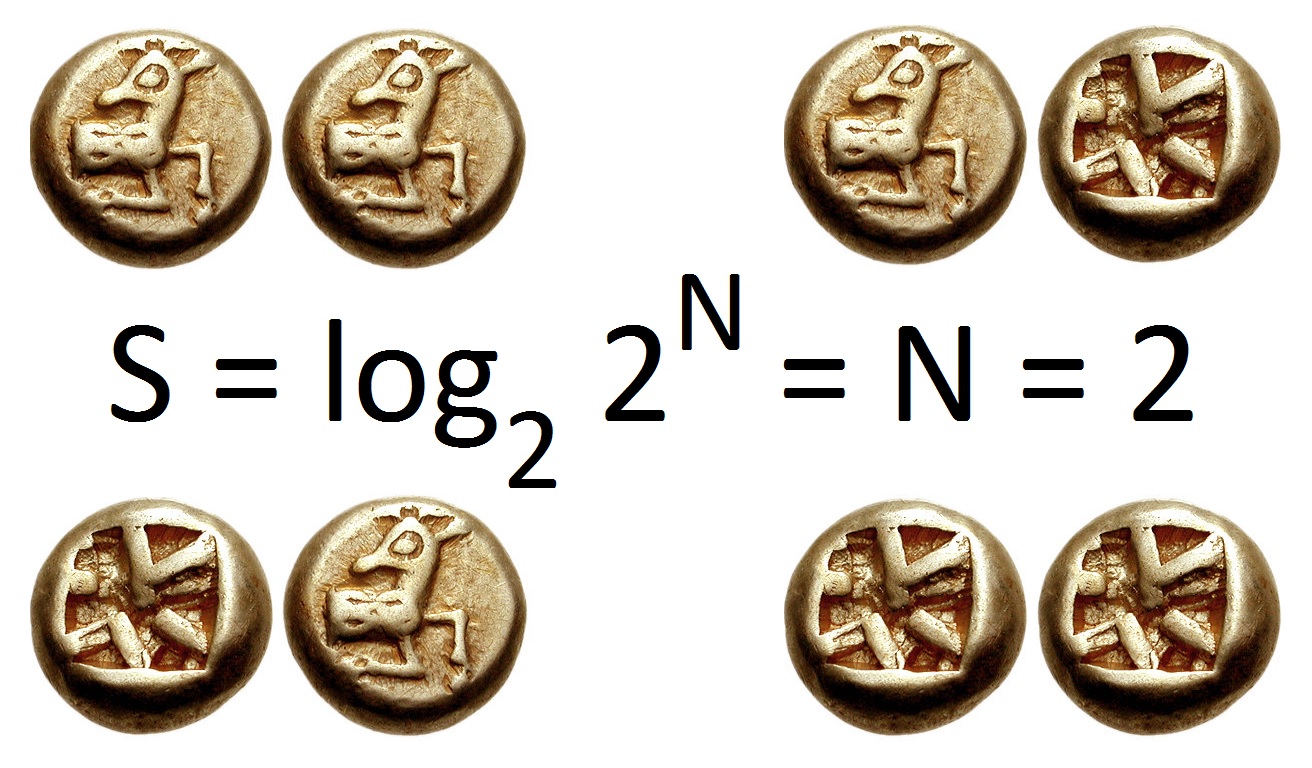|
Sackur–Tetrode Equation
The Sackur–Tetrode equation is an expression for the entropy of a monatomic ideal gas. It is named for Hugo Martin Tetrode (1895–1931) and Otto Sackur (1880–1914), who developed it independently as a solution of Boltzmann's gas statistics and entropy equations, at about the same time in 1912. Formula The Sackur–Tetrode equation expresses the entropy S of a monatomic ideal gas in terms of its thermodynamic state—specifically, its volume V, internal energy U, and the number of particles N: : \frac = \ln \left \frac VN \left(\frac\frac UN\right)^\right , where k_\mathrm is the Boltzmann constant, m is the mass of a gas particle and h is the Planck constant. The equation can also be expressed in terms of the thermal wavelength \Lambda: : \frac = \ln\left(\frac\right)+\frac , For a derivation of the Sackur–Tetrode equation, see the Gibbs paradox. For the constraints placed upon the entropy of an ideal gas by thermodynamics alone, see the ideal gas article. The above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Mass Constant
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u) is a non-SI unit of mass widely used in physics and chemistry. It is defined as of the mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and at rest. The atomic mass constant, denoted ''m''u, is defined identically, giving . This unit is commonly used in physics and chemistry to express the mass of atomic-scale objects, such as atoms, molecules, and elementary particles, both for discrete instances and multiple types of ensemble averages. For example, an atom of helium-4 has a mass of . This is an intrinsic property of the isotope and all helium-4 atoms have the same mass. Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), , has an average mass of approximately . However, there are no acetylsalicylic acid molecules with this mass. The two most common masses of individual acetylsalicylic acid molecules are , having the most common isotopes, and , in which one carbon is carbon-13. The molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equations Of State
In physics, chemistry, and thermodynamics, an equation of state is a thermodynamic equation relating state variables, which describe the state of matter under a given set of physical conditions, such as pressure, volume, temperature, or internal energy. Most modern equations of state are formulated in the Helmholtz free energy. Equations of state are useful in describing the properties of pure substances and mixtures in liquids, gases, and solid states as well as the state of matter in the interior of stars. Overview At present, there is no single equation of state that accurately predicts the properties of all substances under all conditions. An example of an equation of state correlates densities of gases and liquids to temperatures and pressures, known as the ideal gas law, which is roughly accurate for weakly polar gases at low pressures and moderate temperatures. This equation becomes increasingly inaccurate at higher pressures and lower temperatures, and fails to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Journal Of Physics
The ''European Journal of Physics'' is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal dedicated to maintaining and improving the standard of physics education in higher education. The journal, published since 1980, is now published by IOP Publishing on behalf of the European Physical Society. The current editor-in-chief is Mojca Čepič of the Ljubljana University, Slovenia. It does not include original research in physics, but rather: *Surveys of research at a level accessible to students *Original insights into the derivation of results *Descriptions of new laboratory exercises *Scholarly or reflective articles at appropriate levels *Descriptions of successful original student projects *Discussions of the history and philosophy of physics. *Reports of new developments in methods for teaching physics and in the physics curriculum. The journal had an Impact factor of 0.781 for 2020, according to the Journal Citation Reports. It is indexed In Chemical Abstracts, Engineering Index/Ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Studies In History And Philosophy Of Science Part B
Study or studies may refer to: General * Education **Higher education * Clinical trial * Experiment * Observational study * Research * Study skills, abilities and approaches applied to learning Other * Study (art), a drawing or series of drawings done in preparation for a finished piece * ''Study'' (film), a 2012 film by Paolo Benetazzo * ''Study'' (Flandrin), an 1835/36 painting by Hippolyte Flandrin * Study (room), a room in a home used as an office or library * ''Study'' (soundtrack), a soundtrack album from the 2012 film * The Study, a private all-girls school in Westmount, Quebec, Canada * ''Studies'' (journal), published by the Jesuits in Ireland * Eduard Study (1862–1930), German mathematician * Facebook Study, a market research app See also * Étude, a short musical composition * * * * Studie Studie is a Japanese tuning company of BMW and a Super GT team which participates in GT300 class. Since 2018 the team also participates in the GT World Challenge Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stirling Approximation
In mathematics, Stirling's approximation (or Stirling's formula) is an approximation for factorials. It is a good approximation, leading to accurate results even for small values of n. It is named after James Stirling, though a related but less precise result was first stated by Abraham de Moivre. One way of stating the approximation involves the logarithm of the factorial: \ln(n!) = n\ln n - n +O(\ln n), where the big O notation means that, for all sufficiently large values of n, the difference between \ln(n!) and n\ln n-n will be at most proportional to the logarithm. In computer science applications such as the worst-case lower bound for comparison sorting, it is convenient to use instead the binary logarithm, giving the equivalent form \log_2 (n!) = n\log_2 n - n\log_2 e +O(\log_2 n). The error term in either base can be expressed more precisely as \tfrac12\log(2\pi n)+O(\tfrac1n), corresponding to an approximate formula for the factorial itself, n! \sim \sqrt\left(\frac\ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is an academic publisher of scientific, technical, and medical books and journals headquartered in Singapore. The company was founded in 1981. It publishes about 600 books annually, along with 135 journals in various fields. In 1995, World Scientific co-founded the London-based Imperial College Press together with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine. Company structure The company head office is in Singapore. The Chairman and Editor-in-Chief is Dr Phua Kok Khoo, while the Managing Director is Doreen Liu. The company was co-founded by them in 1981. Imperial College Press In 1995 the company co-founded Imperial College Press, specializing in engineering, medicine and information technology Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identical Particles
In quantum mechanics, identical particles (also called indistinguishable or indiscernible particles) are particles that cannot be distinguished from one another, even in principle. Species of identical particles include, but are not limited to, elementary particles (such as electrons), composite subatomic particles (such as atomic nuclei), as well as atoms and molecules. Quasiparticles also behave in this way. Although all known indistinguishable particles only exist at the quantum scale, there is no exhaustive list of all possible sorts of particles nor a clear-cut limit of applicability, as explored in quantum statistics. There are two main categories of identical particles: bosons, which can share quantum states, and fermions, which cannot (as described by the Pauli exclusion principle). Examples of bosons are photons, gluons, phonons, helium-4 nuclei and all mesons. Examples of fermions are electrons, neutrinos, quarks, protons, neutrons, and helium-3 nuclei. The fact t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Principle
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle (also known as Heisenberg's uncertainty principle) is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physical quantities of a particle, such as position, ''x'', and momentum, ''p'', can be predicted from initial conditions. Such variable pairs are known as complementary variables or canonically conjugate variables; and, depending on interpretation, the uncertainty principle limits to what extent such conjugate properties maintain their approximate meaning, as the mathematical framework of quantum physics does not support the notion of simultaneously well-defined conjugate properties expressed by a single value. The uncertainty principle implies that it is in general not possible to predict the value of a quantity with arbitrary certainty, even if all initial conditions are specified. Introduced first in 1927 by the German physicist Wern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable is the average level of "information", "surprise", or "uncertainty" inherent to the variable's possible outcomes. Given a discrete random variable X, which takes values in the alphabet \mathcal and is distributed according to p: \mathcal\to , 1/math>: \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x) = \mathbb \log p(X), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or " shannons"), while base ''e'' gives "natural units" nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or " hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a variable. The concept of information entropy was introduced by Claude Shannon in his 1948 paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication",PDF archived froherePDF archived frohere and is also referred to as Shannon entropy. Shannon's theory def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification, storage, and communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley, in the 1920s, and Claude Shannon in the 1940s. The field is at the intersection of probability theory, statistics, computer science, statistical mechanics, information engineering, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (with two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a die (with six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measures in information theory are mutual information, channel capacity, error exponents, and relative entropy. Important sub-fields of information theory include s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |