|
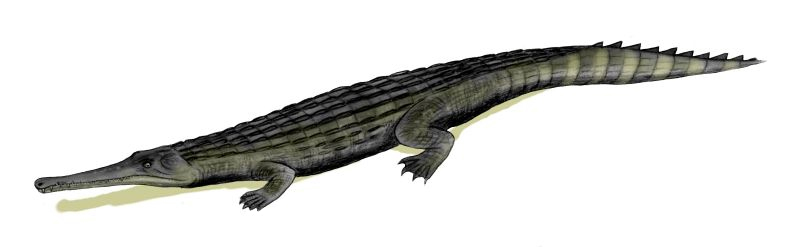
Sabinosuchus
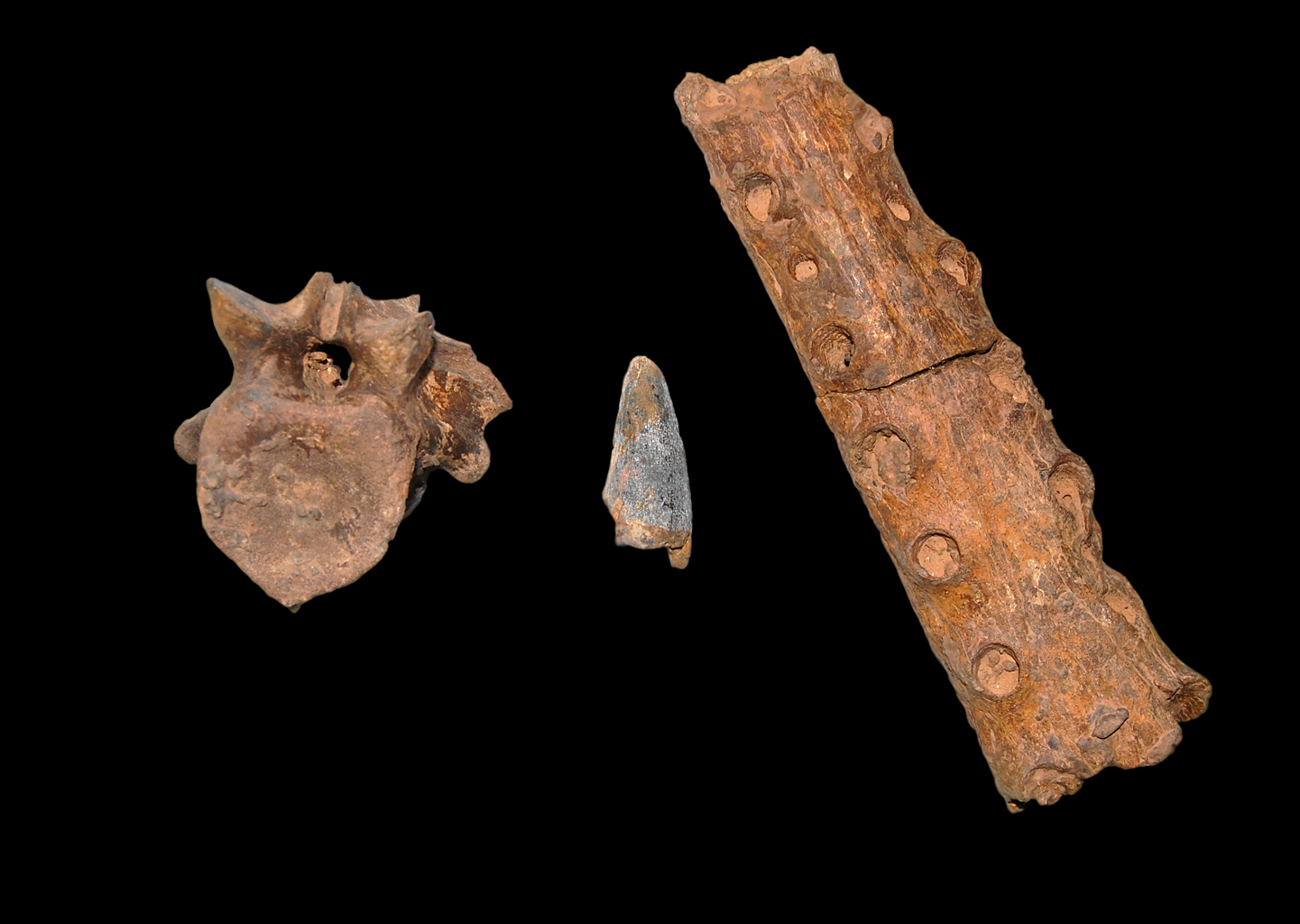
''Sabinosuchus'' (meaning "Sabinas crocodile") is a genus of Mesoeucrocodylian, from the Maastrichtian Escondido Formation of Coahuila, Mexico, with ''Sabinosuchus coahuilensis'' as the type species. First described as a putative dyrosauridae, dyrosaurid by Shiller II ''et al.'' (2016), it was later recovered as a pholidosauridae, pholidosaurid by Jouve & Jalil (2020). History and naming ''Sabinosuchus'' was discovered by amateur paleontologist of the Palaeontologos Aficionados de Sabinas A.C. (PASAC) in 2002 in Mexico. All fossils of Sabinosuchus found by the team stem from the Maastrichtian Escondido Formation, although earlier reports wrongfully believed them to stem from the underlying Olmos Formation. The material collected constitutes two individuals known from fragmentary remains that were later reassembled. Due to this the material was catalogued under several specimen numbers. The holotype material was initially catalogued as specimens PAS 945 to PAS 949 and PAS 952 once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidosauridae
Pholidosauridae is an extinct family of aquatic neosuchian mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs. Fossils have been found in Europe (Denmark, England, France, Germany, Spain and Sweden), Africa (Algeria, Niger, Mali, Morocco and Tunisia), North America (Canada and the United States) and South America (Brazil and Uruguay). The pholidosaurids first appeared in the fossil record during the Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic. Jouve & Jalil (2020) described postcranial material of a pholidosaurid from the Paleocene (Danian) of Ouled Abdoun Basin (Morocco), representing the most recent record of the family. The authors also reinterpreted putative Maastrichtian dyrosaurid ''Sabinosuchus'' as a pholidosaurid, and argued that at least two independent pholidosaurid lineages reached the Maastrichtian, among which one survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Before the publication of this study it was thought that the family became extinct during the Late Turonian stage of the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosauridae
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantosuchus Coupatezi
''Atlantosuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from Morocco. One defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other long-snouted dyrosaurids was its proportionally elongate snout, the longest in proportion to body size of any dyrosaurid. ''Rhabdognathus'', a hyposaurine dyrosaurid, is believed to have been the closest relative of the genus.Jouve, S., B. Bouya, and M. Amaghzaz (2008). A long-snouted dyrosaurid (Crocodyliformes, Mesoeucrocodylia) from the Paleocene of Morocco: phylogenetic and palaoebiogeographic implications. Palaeontology 51(2):281-294. References External links ''Atlantosuchus''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Paleocene crocodylomorphs Fossils of Morocco Dyrosaurids Prehistoric pse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosaurus Phosphaticus
''Dyrosaurus'' is a genus of extinct crocodylomorph that lived during the early Eocene. The name ''Dyrosaurus'' comes from () the Greek for lizard or reptile, and Dyr for Djebel Dyr (mountain) close to where the type species was discovered. It was a large reptile with an estimated body length of . Species Although the family Dyrosauridae is quite diverse and contains a variety of species, the genus ''Dyrosaurus'' has only two described species: ''D. phosphaticus'' and ''D. maghribensis''. ''D. phosphaticus'' was first discovered in Algeria and Tunisia whereas ''D. maghribensis'' has only been found in Morocco. ''D. maghribensis'' differs from ''D. phosphaticus'' by several synapomorphies, most notably: a smooth dorsal margin of the parietal and widely opened choanae, interfenestral bar wide and strongly T-shaped instead of moderately T-shaped. In ''D. maghribensis'' the lateral and medial dorsal osteoderms are not sutured and have no serrated margin. The anterolateral margin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosaurus Maghribensis
''Dyrosaurus'' is a genus of extinct crocodylomorph that lived during the early Eocene. The name ''Dyrosaurus'' comes from () the Greek for lizard or reptile, and Dyr for Djebel Dyr (mountain) close to where the type species was discovered. It was a large reptile with an estimated body length of . Species Although the family Dyrosauridae is quite diverse and contains a variety of species, the genus ''Dyrosaurus'' has only two described species: ''D. phosphaticus'' and ''D. maghribensis''. ''D. phosphaticus'' was first discovered in Algeria and Tunisia whereas ''D. maghribensis'' has only been found in Morocco. ''D. maghribensis'' differs from ''D. phosphaticus'' by several synapomorphies, most notably: a smooth dorsal margin of the parietal and widely opened choanae, interfenestral bar wide and strongly T-shaped instead of moderately T-shaped. In ''D. maghribensis'' the lateral and medial dorsal osteoderms are not sutured and have no serrated margin. The anterolateral margin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arambourgisuchus Khouribgaensis
''Arambourgisuchus'' ("Prof. Camille Arambourg's crocodile") is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from the late Palaeocene of Morocco, found in the region of Sidi Chenane in 2000, following collaboration by French and Moroccan institutions, and described in 2005 by a team led by palaeontologist Stéphane Jouve. ''Arambourgisuchus'' was a large animal with an elongated skull 1 meter in length. History and naming The fossils of ''Arambourgisuchus'' were unearthed in the Spring of 2000 thanks to the collaboration of French (French National Centre for Scientific Research, National Museum of Natural History, France) and Moroccon (Office Chérifien des Phosphates, Ministére de l’Energie et des Mines, Morocco) researchers in the phosphatic deposits of the Ouled Abdoun Basin, Morocco. The deposits of the basin range from the latest Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the middle Eocene (Lutetian), with the deposits yielding ''Arambourgisuchus'' dating to the Thanetian age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokotosuchus
''Sokotosuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodyliform which existed during the Maastrichtian in western Africa. Fossils of the genus were found in the Dukamaje Formation of Nigeria, and some cranial material has possibly been found in Mali Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali .... References Bibliography * Further reading * L. B. Halstead. 1975. ''Sokotosuchus ianwilsoni'' n. g., g. sp., a new teleosaur crocodile from the Upper Cretaceous of Nigeria. Journal of Mining and Geology 11(1-2):101-103 Dyrosaurids Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Prehistoric marine crocodylomorphs Maastrichtian genera Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs of Africa Cretaceous Nigeria Fossils of Nigeria Fossil taxa described in 1975 {{paleo-archosaur-stub Fossils of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatosaurus Gavialoides
''Phosphatosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph. It existed during the early Eocene, with fossils having been found from North Africa in Tunisia and Mali. Named in 1955, ''Phosphatosaurus'' is a monotypic genus; the type species is ''P. gavialoides''. A specimen has been discovered from Niger, but it cannot be classified at the species level. ''Phosphatosaurus'' is closely related to the Cretaceous genus ''Sokotosuchus'', which is known from Niger and Mali. Because ''Phosphatosaurus'' is only known from Paleogene localities, the close relationship with ''Sokotosuchus'' implies that there is a long ghost lineage extending back into the Maastrichtian that is not known in the fossil record. Description ''Phosphatosaurus'' is a large dyrosaurid estimated at in length, with blunt teeth. The tip of the snout is spoon-shaped from a lateral expansion of the rostral portion of the mandible. The dentition is nonhomodont. Alveolar "couplets" are present in the lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyposaurus Rogersii
''Hyposaurus'' is a genus of extinct marine dyrosaurid crocodyliform. Fossils have been found in Paleocene aged rocks of the Iullemmeden Basin in West Africa, Campanian–Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) Shendi Formation of Sudan and Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) through Danian (Early Paleocene) strata in New Jersey, Alabama and South Carolina. Isolated teeth comparable to ''Hyposaurus'' have also been found in Thanetian (Late Paleocene) strata of Virginia.Denton Jr., R. K., Dobie, J. L. and D. C. Parris, 1997. The Marine Crocodilian ''Hyposaurus'' in North America. from Ancient Marine Reptiles, editors J. M. Callaway and E. L. Nicholls, Academic Press. It was related to ''Dyrosaurus''. The priority of the species ''H. rogersii'' has been debated,Norell, M. A. and G. W. Storrs. 1989. Catalogue and review of the type fossil crocodilians in the Yale Peabody Museum. Postilla 203:1-28 however there is no sound basis for the recognition of more than one species from North America. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerrejonisuchus Improcerus
''Cerrejonisuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph. It is known from a complete skull and mandible from the Cerrejón Formation in northeastern Colombia, which is Paleocene in age. Specimens belonging to ''Cerrejonisuchus'' and to several other dyrosaurids have been found from the Cerrejón open-pit coal mine in La Guajira. The length of the rostrum is only 54-59% of the total length of the skull, making the snout of ''Cerrejonisuchus'' the shortest of all dyrosaurids. Description At an estimated length of to , ''Cerrejonisuchus'' was small for a dyrosaur. This size estimate is based on the dorsal skull lengths of specimens UF/IGM 29 and UF/IGM 31. ''Cerrejonisuchus'' has the shortest body length of any known dyrosaur, much smaller than that of the longest dyrosaur, '' Phosphatosaurus gavialoides'', which was to in length. Currently the only known specimens of ''Cerrejonisuchus'' are UF/IGM 29 (the type specimen), UF/IGM 30, UF/IGM 31, and UF/IGM 32. Of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |