|
Sabacola
Sabacola (or Sowalki) was a Native American town and chiefdom in what is now the Southeastern United States of America during the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries. Usually regarded as belonging to the Apalachicola people, Sabacola had poorly understood connections to the Apalachee people. Although usually described as speaking the Hitchiti language, at least one source stated that the Sabacola spoke another, unidentified language. The town moved to several locations along the Chattahoochee River, sometimes with more than one town including Sabacola in its name at the same time. The town of Sabacola moved to the Ocmulgee River area of central Georgia for about 25 years, before returning to the Chattahoochee River. Sabacola was the only Apalachicola town to have a mission established by the Spanish. The Apalachicola towns, including Sabacola, evolved into the Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy (called the Lower Creeks by the English). Between Apalachee and Apalachicola On fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachicola People
Apalachicola (sometimes Palachacola) was the name of a Native American town and chiefdom, and of the people living in it, and of a group of towns associated with it, located along the lower part of the Chattahoochee River in present-day Alabama and Georgia. The Spanish called the association of towns the Apalachicola Province. It is believed that before the 17th century, the residents of all the Apalachicola towns spoke the Hitchiti language, although other towns whose people spoke Muscogee relocated among the Apalachicolas along the Chattahoochee River in the middle- to later- 17th century. All of the Apalachicola towns moved to central Georgia at the end of the 17th century, where the English called them "Ochese Creek Indians". They moved back to the Chattahoochee River after 1715, with the English then calling them "Lower Creeks" ("Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy"), while the Spanish called them "Ochese". Origins In the first half of the 17th century, a number of town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chisca
The Chisca were a tribe of Native Americans living in present-day eastern Tennessee and southwestern Virginia in the 16th century, and in present day Alabama, Georgia, and Florida in the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries, by which time they were known as Yuchi. The Hernando de Soto expedition heard of, and may have had brief contact with, the Chisca in 1540. The Juan Pardo expeditions of 1566 and 1568 encountered the Chisca, and engaged in battles with them. By early in the 17th century, Chisca people were present in several parts of Spanish Florida, engaged at various times and places in alternately friendly or hostile relations with the Spanish and the peoples of the Spanish mission system. After the capture of a fortified Chisca town by the Spanish and Apalachee in 1677, some Chisca took refuge in northern Tennessee, where they were absorbed into the Shawnee, and in Muscogee towns in Alabama. Around the turn of the 18th century some Chisca, by then generally called Yuchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitchiti
The Hitchiti ( ) were a historic indigenous tribe in the Southeast United States. They formerly resided chiefly in a town of the same name on the east bank of the Chattahoochee River, four miles below Chiaha, in western present-day Georgia. The natives possessed a narrow strip of good land bordering on the river. The Hitchiti had a reputation of being honest and industrious. Their autonym was possibly ''Atcik-hata'', while the Coushatta knew them as the ''At-pasha-shliha'', "mean people". Under pressure from European Americans, the Hitchiti moved into Florida. While some survived there, others signed a treaty for their land in exchange for lands in Indian Territory, and were forced west. English "Hitchiti" was Spanish "Achito". Location The Hitchiti are often associated with an area in present-day Chattahoochee County. But at an earlier period, they occupied land on the lower course of the Ocmulgee River. Early English maps show their town on the site where present-day Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russell County, Alabama
Russell County is a county in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 59,183. Its county seat is Phenix City. Its name is in honor of Colonel Gilbert C. Russell, who fought in the wars against the Creek Indians. Russell County is part of the Columbus, GA-AL Metropolitan Statistical Area. Of all counties in the United States, Russell County has the most amount of people working in a state other than their own, at over 54% of the population, most of whom work in Columbus, Georgia. History Russell County was established by an act of the state general assembly on December 18, 1832, from lands ceded to the state by the Creek Native Americans. The county seat has changed several times: Girard (1833–1839), Crawford originally Crockettsville (1839–1868), Seale (1868–1935) and Phenix City (1935–present). It was named for War of 1812, Col. Gilbert Christian Russell Sr., 1782–1861, 3rd U.S. Infantry. In the 1940s an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro De Olivera Y Fullana
Pedro de Olivera y Fullana, was the governor and captain general of Spanish Florida from July 13 to October 30, 1716. He died at the provincial capital, St. Augustine, just over three months into his term of office. Biography In 1716, Chislacaliche, a ''mico'', or chief, of the Lower Creek peoples, asked Olivera to send a Spanish envoy to the Creek territory to restore friendly relations and distribute gifts, as was customary among the Indians. Olivera, wanting to persuade the other Creeks to follow Chilacaliche and return to Apalachee Province in Florida, sent the retired lieutenant Diego Peña and four soldiers to their rebuilt towns on the Chattahoochee River. Peña departed St. Augustine on August 4 of that year, and on September 28 arrived at Apalachicola, where he summoned the chiefs of the province to distribute their expected gifts and beseech them to relocate to the "old fields" of Apalachee. He distributed firearms and ammunition to the chieftains, who in their turn gai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
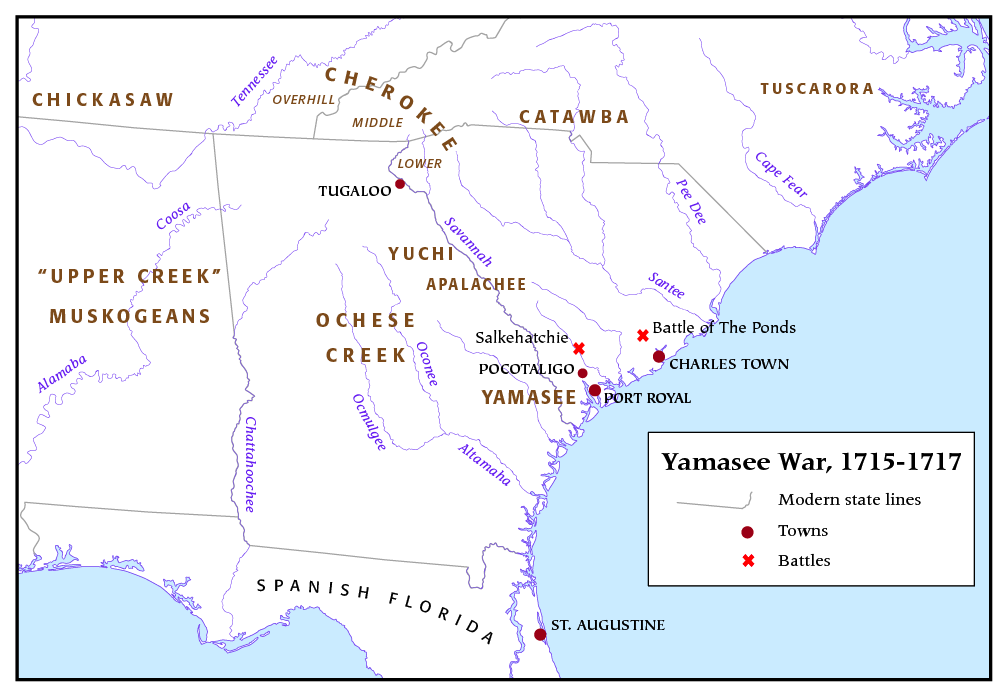
Yamassee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee and a number of other allied Native American peoples, including the Muscogee, Cherokee, Catawba, Apalachee, Apalachicola, Yuchi, Savannah River Shawnee, Congaree, Waxhaw, Pee Dee, Cape Fear, Cheraw, and others. Some of the Native American groups played a minor role, while others launched attacks throughout South Carolina in an attempt to destroy the colony. Native Americans killed hundreds of colonists and destroyed many settlements, and they killed traders throughout the southeastern region. Colonists abandoned the frontiers and fled to Charles Town, where starvation set in as supplies ran low. The survival of the South Carolina colony was in question during 1715. The tide turned in early 1716 when the Cherokee sided with the colonists against the Creek, their traditional enemy. The last Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towaliga River
The Towaliga River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 21, 2011 tributary of the Ocmulgee River in central Georgia. The Towaliga begins in Henry County and passes through High Falls State Park in northwestern Monroe County, then traverses the county and joins the Ocmulgee near the town of Juliette. The river begins north of Cole Reservoir in Henry County where it is joined by multiple creeks, including Thompson Creek, Troublesome Creek in Spalding County, Long Branch, and Lee Creek to gain size. The river is fairly muddy above High Falls Lake, but it clears once below the falls where most of the river is rock bottomed. This region is about south of Atlanta and about north of Macon. The river was featured in a scene from the made-for-television movie ''Murder in Coweta County'' in which the ashes of the murdered victim are found floating in the nook of tree hollow along the bank of the river. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive strong point against any enemy that does not possess siege equipment or, in modern times, artillery, air force and cruise missiles. A fortification intended to resist these weapons is more likely to qualify as a fortress or a redoubt, or in modern times, be an underground bunker. However, a blockhouse may also refer to a room within a larger fortification, usually a battery or redoubt. Etymology The term ''blockhouse'' is of uncertain origin, perhaps related to Middle Dutch ''blokhus'' and 18th-century French '' blocus'' (blockade). In ancient Greece Blockhouses existed in ancient Greece, for example the one near Mycenae. Early blockhouses in England Early blockhouses were designed solely to protect a particular area by the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson County, Florida
Jackson County is a county located in the U.S. state of Florida, on its northwestern border with Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 47,319. Its county seat is Marianna. History Jackson County was created by the Florida Territorial Council in 1822 out of Escambia County, at the same time that Duval County was organized from land of St. Johns County, making them the third and fourth counties in the Territory. The county was named for Andrew Jackson, a General of the War of 1812, who had served as Florida's first military governor for six months in 1821. Jackson County originally extended from the Choctawhatchee River on the west to the Suwannee River on the east. By 1840 the county had been reduced close to its present boundaries through the creation of new counties from its original territory, following an increase of population in these areas. Minor adjustments to the county boundaries continued through most of the 19th century, however. There were no to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatot
The Chatot (also Chacato or Chactoo) were a Native American tribe who lived in the upper Apalachicola River and Chipola River basins in what is now Florida. They spoke a Muskogean language, which may have been the same as that of the Pensacola people. The Spanish established three or four missions to the Chatot by 1675; Asunción/Asumpción del Puerto, la Encarnación (also called Santa Cruz de Sábacola el menor), San Nicolás de Tolentino (listed only in Geiger, 1940) and San Carlos de los Chacatos. These missions were located near the upper Apalachicola River. The historian John Hann places the missions of Asunción, la Encarnatión and San Carlos in the Apalachee The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River, ... province of the Spanish mission system in Florida. The hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The Mobile River and Tensaw River empty into the northern end of the bay, making it an estuary. Several smaller rivers also empty into the bay: Dog River, Deer River, and Fowl River on the western side of the bay, and Fish River on the eastern side. Mobile Bay is the fourth largest estuary in the United States with a discharge of of water per second. Annually, and often several times during the summer months, the fish and crustaceans will swarm the shallow coastline and shore of the bay. This event, appropriately named a jubilee, draws a large crowd because of the abundance of fresh, easily caught seafood. Mobile Bay is in area. It is long by a maximum width of . The deepest areas of the bay are located within the shipping channel, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Márquez Cabrera
Juan Márquez Cabrera was a Spanish soldier who served as governor of Honduras (1668 – 1672) and then of Spanish Florida (1680 – 1687), until he was dismissed for abuses in office against the native peoples and Spanish citizens of Florida. He, as did the three previous governors, spent much time supervising construction of the Castillo de San Marcos and other fortifications in the presidio of St. Augustine as well as defending Florida against incursions from the British to the north. Career Juan Márquez Cabrera joined the Spanish Army in his youth. He excelled in his military career, attaining the rank of Sergeant Major. In 1668, he was appointed governor of Honduras, an office he occupied until 1672. On September 28, 1680, Cabrera was appointed governor of Florida to replace Pablo de Hita y Salazar.Cahoon, BenU.S. States F-K Florida government Early years in the Florida government He arrived at St. Augustine, capital of the province, on November 30 of that year. On his ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |