|
SYM Sport Rider 125i
The SYM Sport Rider 125i (also known as the SYM StarX 125i in Vietnam) is the first fuel injection, fuel-injected underbone motorcycle model by Taiwanese motorcycle company SYM Motors. The SYM Sport Rider 125i is powered by a fuel-injected 125 cc 4-stroke gasoline engine. It was debuted in Malaysia on 27 August 2016 before being sold in other markets like Vietnam and the Philippines. Model history The SYM Sport Rider 125i made its global debut in Malaysia on 27 August 2016. It was developed through a collaboration between SYM Motors Taiwan and its Malaysian distributor, MForce Bike Holdings Sdn. Bhd. Later in October 2016, the Sport Rider 125i was launched as the SYM StarX 125i in Vietnam. The SYM Sport Rider 125i is powered by an all-new 125 cc SOHC 2-valve 4-stroke ECOTECH engine with fuel injection that is capable to produce of power at 8,000 rpm and of torque at 5,500 rpm. The usage of fuel injection technology enables the Sport Rider to become European emission standards, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Peso
The Philippine peso, also referred to by its Tagalog name ''piso'' (Philippine English: , , plural pesos; tl, piso ; sign: ₱; code: PHP), is the official currency of the Philippines. It is subdivided into 100 ''sentimo'', also called centavos. The Philippine peso sign is denoted by the symbol "₱", introduced under American rule in place of the original peso sign "$" used throughout Spanish America. Alternative symbols used are "PHP", "PhP", "Php", or just "P". The monetary policy of the Philippines is conducted by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP), established on July 3, 1993, as its central bank. It produces the country's banknotes and coins at its Security Plant Complex, which is set to move to New Clark City in Capas, Tarlac."Overview of the BSP" Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) Official Website. Retrieved on October 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Dong
Vietnamese may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia ** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam. * Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam ** Overseas Vietnamese, Vietnamese people living outside Vietnam within a diaspora * Vietnamese language * Vietnamese alphabet * Vietnamese cuisine * Vietnamese culture See also * List of Vietnamese people A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goods And Services Tax (Malaysia)
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an abolished value-added tax in Malaysia. GST is levied on most transactions in the production process, but is refunded with exception of Blocked Input Tax, to all parties in the chain of production other than the final consumer. The existing standard rate for GST effective from 1 April 2015 is 6%. Many domestically consumed items such as fresh foods, water and electricity are zero-rated, while some supplies such as education and health services are GST exempted. After Pakatan Harapan won the 2018 Malaysian general election, GST was reduced to 0% on 1 June 2018. The then Government of Malaysia tabled the first reading of the Bill to repeal GST in Parliament on 31 July 2018 (Dewan Rakyat). GST was replaced with the Sales Tax and Service Tax starting 1 September 2018. Background GST was scheduled to be implemented by the government during the third quarter of 2011, but the implementation was delayed until 1 April 2015. Its purpose was to repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysian Ringgit
The Malaysian ringgit (; plural: ringgit; symbol: RM; currency code: MYR; Malay name: ''Ringgit Malaysia''; formerly the Malaysian dollar) is the currency of Malaysia. It is divided into 100 ''sen'' (formerly ''cents''). The ringgit is issued by the Central Bank of Malaysia. Etymology The word ''ringgit'' is an obsolete term for "jagged" in the Malay language. The word was originally used to refer to the serrated edges. The first European coins to circulate widely in the region were Spanish "pieces of eight" or "cob", their crude appearance resembling stones, hence the word jagged. The availability and circulation of this Spanish currency were due to the Spanish controlling nearby Philippines. An early printed source, the ''Dictionary of the Malayan Language'' from 1812 had already referred to the ringgit as a unit of money. In modern usage, ''ringgit'' is used almost solely for the currency. Due to the common heritage of the three modern currencies, the Singapore dollar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Gauge
In automotive and aerospace engineering, a fuel gauge is an instrument used to indicate the amount of fuel in a fuel tank. In electrical engineering, the term is used for ICs determining the current State of Charge of accumulators. Motor vehicles As used in vehicles, the gauge consists of two parts: * The sending unit - in the tank * The indicator - on the dashboard The sending unit usually uses a float connected to a potentiometer, typically printed ink design in a modern automobile. As the tank empties, the float drops and slides a moving contact along the resistor, increasing its resistance. In addition, when the resistance is at a certain point, it will also turn on a "low fuel" light on some vehicles. Meanwhile, the indicator unit (usually mounted on the dashboard) is measuring and displaying the amount of electric current flowing through the sending unit. When the tank level is high and maximum current is flowing, the needle points to "F" indicating a full tank. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speedometer
A speedometer or speed meter is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the early 20th century, and as standard equipment from about 1910 onwards. Other vehicles may use devices analogous to the speedometer with different means of sensing speed, eg. boats use a pit log, while aircraft use an airspeed indicator. Charles Babbage is credited with creating an early type of a speedometer, which was usually fitted to locomotives. The electric speedometer was invented by the Croatian Josip Belušić in 1888 and was originally called a velocimeter. Operation The speedometer was originally patented by Josip Belušić (Giuseppe Bellussich) in 1888. He presented his invention at the 1889 Exposition Universelle in Paris. His invention had a pointer and a magnet, using electricity to work. German inventor Otto Schultze patented his version (which, like Belušić's, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachometer
A tachometer (revolution-counter, tach, rev-counter, RPM gauge) is an instrument measuring the rotation speed of a shaft or disk, as in a motor or other machine. The device usually displays the revolutions per minute (RPM) on a calibrated analogue dial, but digital displays are increasingly common. The word comes from Greek ''τάχος'' (''táchos'' "speed") and ''μέτρον'' (''métron'' "measure"). Essentially the words tachometer and speedometer have identical meaning: a device that measures speed. It is by arbitrary convention that in the automotive world one is used for engine revolutions and the other for vehicle speed. In formal engineering nomenclature, more precise terms are used to distinguish the two. History The first tachometer was described by an Donkin in a paper to the Royal Society of Arts in 1810 for which he was awarded the Gold medal of the society. This consisted of a bowl of mercury constructed in such a way that centrifugal force caused the level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylight Running Lamp
A daytime running lamp (DRL, also daytime running light) is an automotive lighting and bicycle lighting device on the front of a roadgoing motor vehicle or bicycle, automatically switched on when the vehicle's handbrake has been pulled down, when the vehicle is in gear, or when the engine is started, emitting white, yellow, or amber light. Their intended use is not to help the driver see the road or their surroundings, but to help other road users identify an active vehicle. Implementations Depending on prevailing regulations and equipment, vehicles may implement the daytime-running light function by functionally turning on specific lamps, by operating low-beam headlamps or fog lamps at full or reduced intensity, by operating high-beam headlamps at reduced intensity, or by steady-burning operation of the front turn signals. Compared to any mode of headlamp operation to produce the daytime running light, functionally dedicated DRLs maximize the potential benefits in safety pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogen Lamp
A halogen lamp (also called tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen, and quartz iodine lamp) is an incandescent lamp consisting of a tungsten filament sealed in a compact transparent envelope that is filled with a mixture of an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen, such as iodine or bromine. The combination of the halogen gas and the tungsten filament produces a halogen-cycle chemical reaction, which redeposits evaporated tungsten on the filament, increasing its life and maintaining the clarity of the envelope. This allows the filament to operate at a higher temperature than a standard incandescent lamp of similar power and operating life; this also produces light with higher luminous efficacy and color temperature. The small size of halogen lamps permits their use in compact optical systems for projectors and illumination. The small glass envelope may be enclosed in a much larger outer glass bulb, which has a lower temperature, protects the inner bulb from contamination, and mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
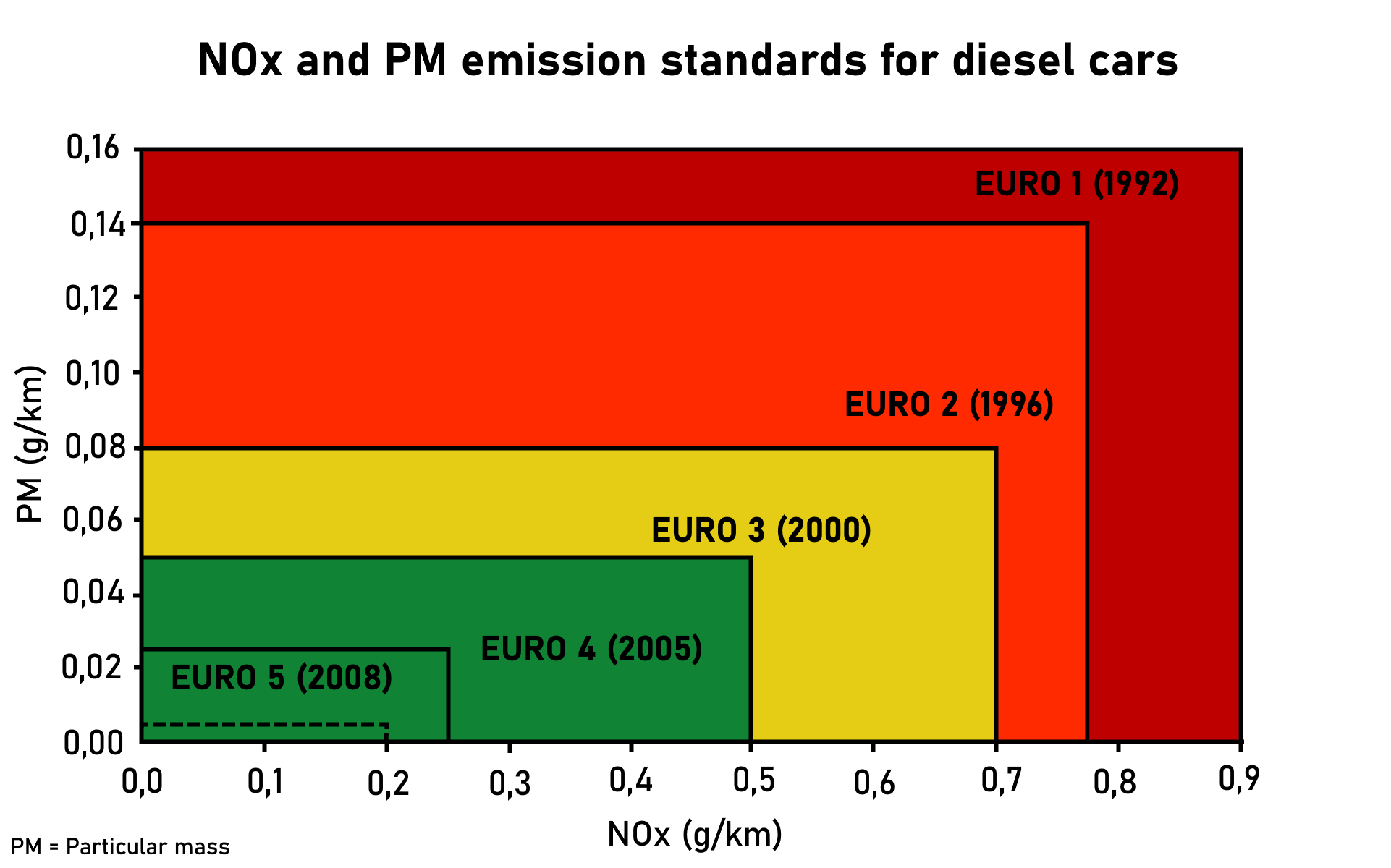
European Emission Standards
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |