|
SWE Order Of Vasa - Knight 2nd Class BAR , the language's ISO 639-2 and ISO 639-3 language code
{{disambiguation ...
SWE may refer to: * Sensor Web Enablement, an Open Geospatial Consortium framework for defining a Sensor Web * Shallow water equations, a set of equations that describe flow below a pressure surface * Snow water equivalent * Society of Women Engineers, a non-profit engineering organization * Society of Wood Engravers, a British printmakers' group * Software engineer * Staebler–Wronski effect, light-induced changes in the properties of silicon * Sweden, the country's ISO 3166-1 alpha-3-code * Swedish language Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic language spoken predominantly in Sweden and in parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, the fourth most spoken Germanic language and the first among any other of its type in the Nordic countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensor Web Enablement
Sensor Web Enablement (SWE) is a suite of standards developed and maintained by Open Geospatial Consortium. SWE standards enable developers to make all types of sensors, transducers and sensor data repositories discoverable, accessible and usable via the Web. SWE Standards include: * Sensor Observation Service * Sensor Planning Service * Observations and Measurements * Sensor Model Language * SensorThings API SensorThings API is an Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standard providing an open and unified framework to interconnect IoT sensing devices, data, and applications over the Web. It is an open standard addressing the syntactic interoperabilit ... References {{Open Geospatial Consortium standards Open Geospatial Consortium Internet Standards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shallow Water Equations
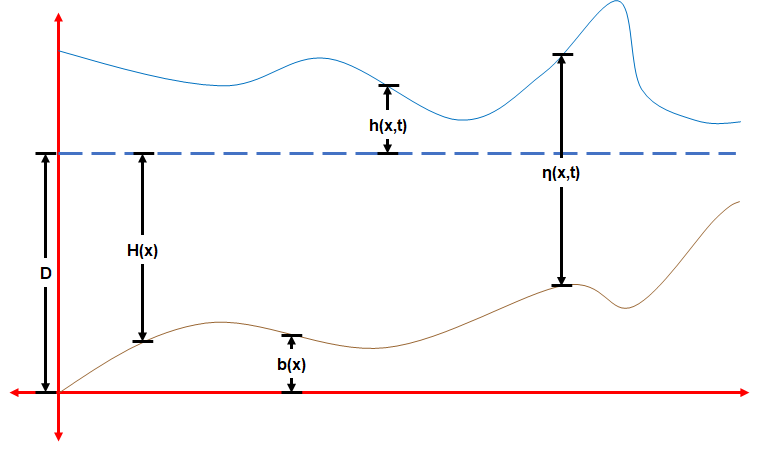
The shallow-water equations (SWE) are a set of hyperbolic partial differential equations (or parabolic if viscous shear is considered) that describe the flow below a pressure surface in a fluid (sometimes, but not necessarily, a free surface). The shallow-water equations in unidirectional form are also called Saint-Venant equations, after Adhémar Jean Claude Barré de Saint-Venant (see the related section below). The equations are derived from depth-integrating the Navier–Stokes equations, in the case where the horizontal length scale is much greater than the vertical length scale. Under this condition, conservation of mass implies that the vertical velocity scale of the fluid is small compared to the horizontal velocity scale. It can be shown from the momentum equation that vertical pressure gradients are nearly hydrostatic, and that horizontal pressure gradients are due to the displacement of the pressure surface, implying that the horizontal velocity field is consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Water Equivalent
Snow science addresses how snow forms, its distribution, and processes affecting how snowpacks change over time. Scientists improve storm forecasting, study global snow cover and its effect on climate, glaciers, and water supplies around the world. The study includes physical properties of the material as it changes, bulk properties of in-place snow packs, and the aggregate properties of regions with snow cover. In doing so, they employ on-the-ground physical measurement techniques to establish ground truth and remote sensing techniques to develop understanding of snow-related processes over large areas. History Snow was described in China, as early as 135 BCE in Han Ying's book ''Disconnection'', which contrasted the pentagonal symmetry of flowers with the hexagonal symmetry of snow. Albertus Magnus proved what may be the earliest detailed European description of snow in 1250. Johannes Kepler attempted to explain why snow crystals are hexagonal in his 1611 book, ''Strena seu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Women Engineers
The Society of Women Engineers (SWE) is an international not-for-profit educational and service organization. Founded in 1950 and headquartered in the United States, the Society of Women Engineers is a major advocate for women in engineering and technology. SWE has over 40,000 members in nearly 100 professional sections, 300 collegiate sections, and 60 global affiliate groups throughout the world. Antecedents The SWE archives contain a series of letters from the Elsie Eaves Papers (bequeathed to the Society), which document the origins of the Society in the early 20th century. In 1919, a group of women at the University of Colorado helped establish a small community of women with an engineering or science background, called the American Society of Women Engineers and Architects. While this organization was only recognized within the campus community, it set the foundation for the development of the international Society of Women Engineers. This group included Lou Alta Melton, Hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Wood Engravers
The Society of Wood Engravers (SWE) is a UK-based artists’ exhibiting society, formed in 1920, one of its founder-members being Eric Gill. It was originally restricted to artist-engravers printing with oil-based inks in a press, distinct from the separate discipline of woodcuts. Today, its support extends to other forms of relief printmaking, and awards honorary membership to collectors and enthusiasts. History The Society of Wood Engravers was founded on 27 March 1920 by a group of 10 artists who all wanted to promote wood engraving as a medium for modern artists. Unlike other societies of the time devoted to various aspects of relief printmaking, the SWE survived, successfully engaging up-coming generations, and celebrates its centenary in 2020. The liberation of wood engraving as a medium for artists was begun in the 1890s. Charles Ricketts and Charles Haslewood Shannon were the first in modern times to cut the blocks of their own designs or, more to the point, create their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineer
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development. A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term ''programmer'' is sometimes used as a synonym, but may also lack connotations of engineering education or skills. Engineering techniques are used to inform the software development process which involves the definition, implementation, assessment, measurement, management, change, and improvement of the software life cycle process itself. It heavily uses software configuration management which is about systematically controlling changes to the configuration, and maintaining the integrity and traceability of the configuration and code throughout the system life cycle. Modern processes use software versioning. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was seen as its own type of engineering. Additionally, the development of softwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staebler–Wronski Effect
The Staebler–Wronski Effect (SWE) refers to light-induced metastability, metastable changes in the properties of hydrogenated amorphous silicon. The defect density of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) increases with light exposure, causing an increase in the carrier generation and recombination, recombination current and reducing the efficiency of the conversion of sunlight into electricity. It was discovered by David L. Staebler and Christopher R. Wronski in 1977. They showed that the dark current (physics), dark current and photoconductivity of hydrogenated amorphous silicon can be reduced significantly by prolonged illumination with intense light. However, on heating the samples to above 150 °C, they could reverse the effect. Explanation Some experimental results * Photoconductivity and dark conductivity decrease rapidly at first before stabilizing at a lower value. * Interruptions in the illumination has no effect on the subsequent rate of change. Once the samp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridgetunnel across the Öresund. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country, the third-largest country in the European Union, and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of , with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden has a nature dominated by forests and a large amount of lakes, including some of the largest in Europe. Many long rivers run from the Scandes range through the landscape, primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)