|
SWEAP
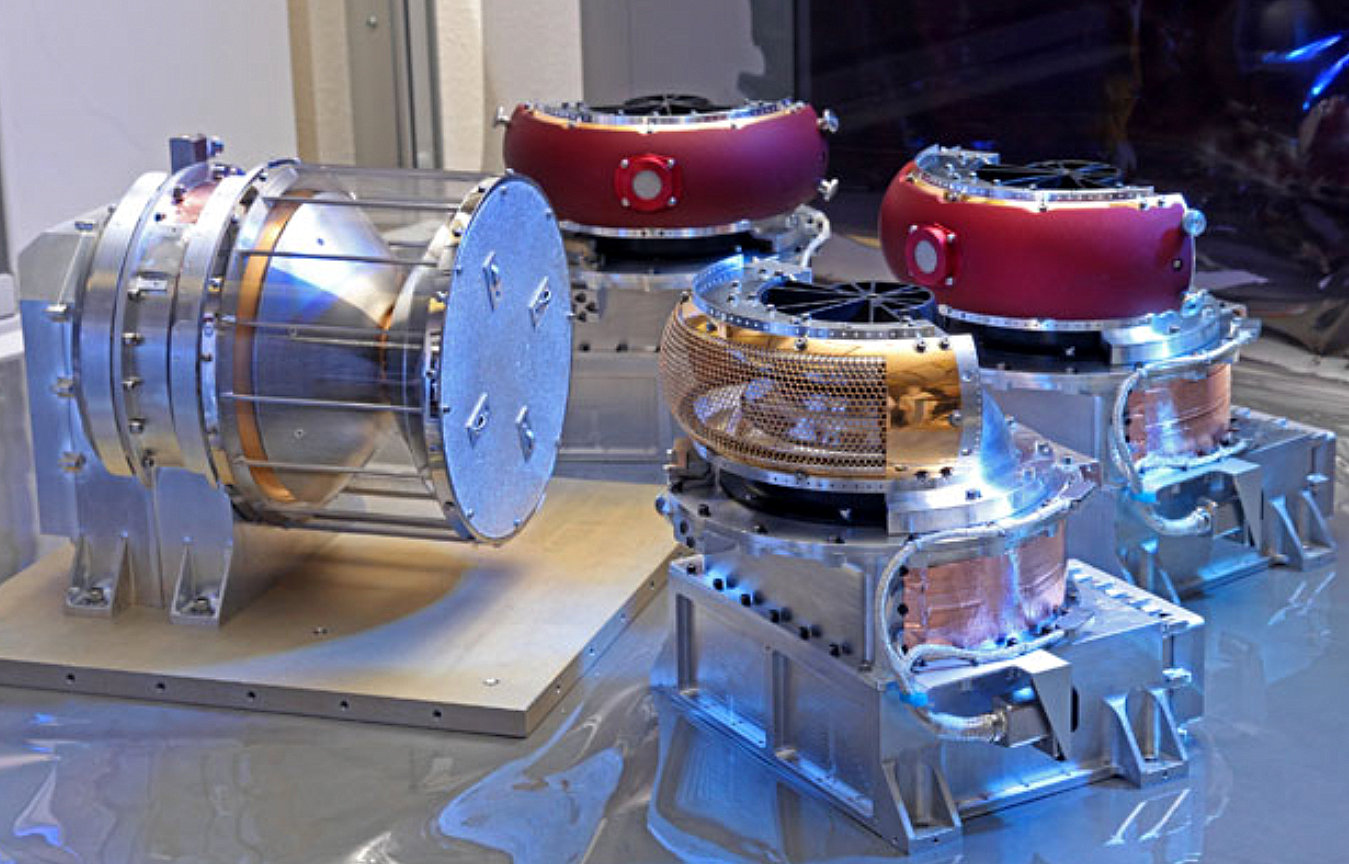
SWEAP (Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons) is an instrument on the unmanned space probe to the Sun, the Parker Solar Probe. The spacecraft with SWEAP on board was launched by a Delta IV Heavy on 12 August 2018 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. SWEAP includes two types of instruments, the Solar Probe Cup (SPC) and Solar Probe Analyzers (SPAN). SWEAP has four sensors overall, and is designed to take measurements of the Solar wind including electrons and ions of hydrogen (protons) and helium (these are the main components of the Solar wind and coronal plasma). Design SWEAP consists of the Solar Probe Cup (SPC), a faraday cup which faces the Sun and is designed to measure electrons and ions in the space environment near the Sun; the Solar Probe Analyzers (SPAN-A and SPAN-B); and the SWEAP electronics module (SWEM). The Solar Probe Cup is a Sun facing instrument directly exposed to the Sun, and had to be designed to handle the high temperature conditions at 9-10 Solar radii from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker Solar Probe
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 with the mission of making observations of the outer corona of the Sun. It will approach to within 9.86 solar radii (6.9 million km or 4.3 million miles) from the center of the Sun, and by 2025 will travel, at closest approach, as fast as , or 0.064% the speed of light. It is the fastest object ever built. The project was announced in the fiscal 2009 budget year. The cost of the project is US$1.5 billion. Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory designed and built the spacecraft, which was launched on 12 August 2018. It became the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person, honoring nonagenarian physicist Eugene Newman Parker, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago. A memory card containing the names of over 1.1 million people was mounted on a plaque and installed below the spacecraft's high-gain antenna on 18 May 2018. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
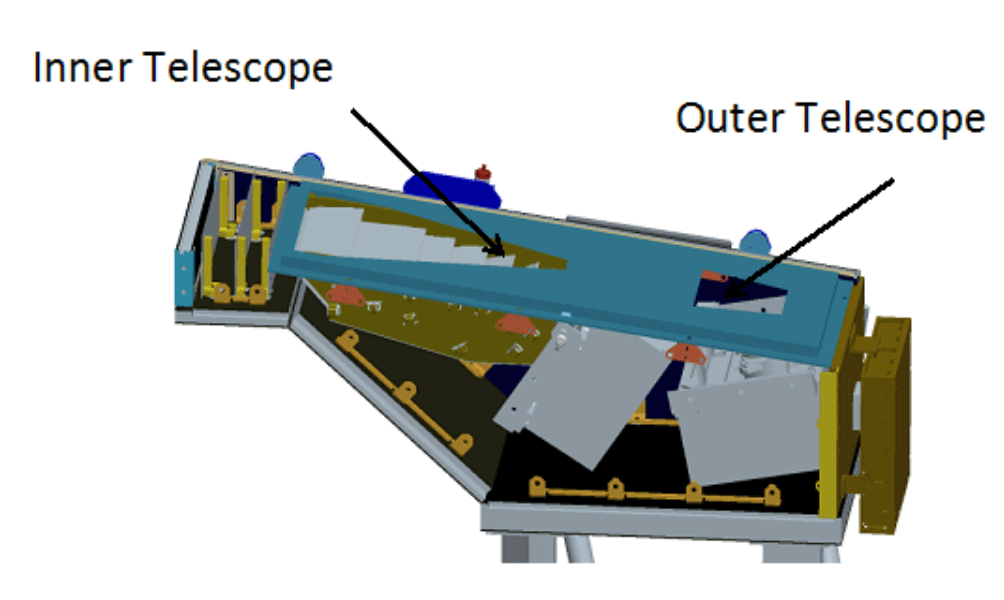
WISPR
The Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR) is an imaging instrument of the ''Parker Solar Probe'' mission to the Sun, launched in August 2018. Imaging targets include visible light images of the corona, solar wind, shocks, solar ejecta, etc. Development of WISPR was led by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. The ''Parker Solar Probe'' with WISPR on board was launched by a Delta IV Heavy on 12 August 2018 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. WISPR is intended take advantage of the spacecraft's proximity to the Sun by taking coronagraph-style images of the solar corona and features like coronal streamers, plumes, and mass ejections. One of the goals is to better understand the structure of the solar corona near the Sun. WISPR is designed to study the electron density and velocity structure of the corona. The instrument field of view is planned to extend from 13 to 108 degrees away from the Sun, and does not directly image the Sun; the area of interest is a very wide field extending awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SWAP (New Horizons)
SWAP (Solar Wind Around Pluto) is an science instrument aboard the unmanned ''New Horizons'' space probe, which was designed to flyby dwarf planet Pluto. SWAP was designed to record Solar Wind en route, at, and beyond Pluto. At Pluto, SWAP's purpose was to record the relationship between the solarwind and ions and/or material entering space from the atmosphere of Pluto. Background The atmosphere of Pluto was discovered in 1988, but it remained enigmatic and it was hard to understand an atmosphere existing in such low temperatures (45 Kelvin (–380° Fahrenheit)). One of the ideas about Pluto is atmospheric loss, with Pluto being compared to losses from comets. The idea of atmospheric loss was suggested in 1980, even before the atmosphere was discovered. One idea is the photoionization of escaping neutral particles might alter the flow solar wind around the dwarf planet. The atmosphere was known to be very tenuous compared to Earth, and one of the questions was how the gases we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment
Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE) is an instrument that detects and measures ions and electrons around the spacecraft. It is a suite of detectors on the ''Juno'' Jupiter orbiter (launched 2011, orbiting Jupiter since 2016). JADE includes JADE-E, JADE-I, and the EBox. JADE-E and JADE-I are sensors that are spread out on the spacecraft, and the EBox is located inside the Juno Radiation Vault. EBox stands for ''Electronics Box''. JADE-E is for detecting electrons from 0.1 to 100 keV, and there are three JADE-E sensors on ''Juno''. JADE-I is for detecting ions from 5 eV to 50 keV. It is designed to return data ''in situ'' on Jupiter's auroral region and magnetospheric plasmas, by observing electrons and ions in this region. It is primarily focused on Jupiter, but it was turned on in January 2016 while still en route to study inter-planetary space (It was several million miles from Jupiter at that time). JADE was built by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), located in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Cup
A Faraday cup is a metal (conductive) cup designed to catch charged particles in vacuum. The resulting current can be measured and used to determine the number of ions or electrons hitting the cup. The Faraday cup was named after Michael Faraday who first theorized ions around 1830. Examples of devices which use Faraday cups include space probes (Voyager 1, & 2, Parker Solar Probe, etc.) and mass spectrometers. Principle of operation When a beam or packet of ions hits the metallic body of the cup, the apparatus gains a small net charge while the ions are neutralized as the charge is transferred to the metal walls. The metal part can then be discharged to measure a small current proportional to the number of impinging ions. The Faraday cup is essentially part of a circuit where ions are the charge carriers in vacuum and it is the interface to the solid metal where electrons act as the charge carriers (as in most circuits). By measuring the electric current (the number of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, chromium, vanadium, or magnesium. The name sapphire is derived via the Latin "sapphirus" from the Greek "sappheiros", which referred to Lapis lazuli, lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs scale (the third hardest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IS☉IS
Integrated Science Investigation of the Sun or IS☉IS, is an instrument aboard the '' Parker Solar Probe'', a space probe designed to study the Sun. IS☉IS is focused on measuring energetic particles from the Sun, including electrons, protons, and ions. The parent spacecraft was launched in early August 2018, and with multiple flybys of Venus will study the heliosphere of the Sun from less than 4 million kilometers or less than 9 solar radii. IS☉IS consists of two detectors, EPI-Lo and EPI-Hi, corresponding to detection of relatively lower and higher energy particles. EPI-Lo is designed to detect from about 20 k eV per nucleon up to 15 MeV (mega electronvolts) total energy, and for electrons from about 25 keV up to 1000 keV. EPI-Hi is designed to measure charged particles from about 1– to 200 MeV per nucleon and electrons from about 0.5 to 6 MeV, according to a paper about the device. The shortname includes a symbol for the Sun, a circle with a dot in it: ☉. NASA suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIELDS
Fields may refer to: Music *Fields (band), an indie rock band formed in 2006 *Fields (progressive rock band), a progressive rock band formed in 1971 * ''Fields'' (album), an LP by Swedish-based indie rock band Junip (2010) * "Fields", a song by Sponge from ''Rotting Piñata'' (1994) Businesses * Field's, a shopping centre in Denmark * Fields (department store), a chain of discount department stores in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada Places in the United States * Fields, Oregon, an unincorporated community * Fields (Frisco, Texas), an announced planned community Other uses * Fields (surname), a list of people with that name * Fields Avenue (other), various roads * Fields Institute, a research centre in mathematical sciences at the University of Toronto * Fields Medal, for outstanding achievement in mathematics * Caulfield Grammarians Football Club, also known as The Fields * FIELDS, a spacecraft instrument on the Parker Solar Probe See also * Mrs. Fields, an A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with a team led by Alan Stern, the spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a Planetary flyby, flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System, fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. On January 19, 2006, ''New Horizons'' was launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station by an Atlas V rocket directly into an Earth-and-solar Escape velocity, escape trajectory with a speed of about . It was the fastest (average speed with respect to Earth) man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JEDI
Jedi (), Jedi Knights, or collectively the Jedi Order are the main heroic protagonists of many works of the '' Star Wars'' franchise. Working symbiotically alongside the Old Galactic Republic, and later supporting the Rebel Alliance, the Jedi Order is depicted as a monastic, academic, military, and meritocratic peacekeeping organization whose origin dates back thousands of years before the events of the first film released in the franchise. The fictional organization has inspired a real-world new religious movement and parody religion: Jediism. Within the fictional ''Star Wars'' galaxy, the Jedi are powerful guardians of order and justice, who, through intuition, rigorous training, and intensive self-discipline, are able to wield a supernatural power known as the Force, thus achieving for example the ability to move objects with the mind, perform incredible feats of strength, and connect to certain people's thoughts. As ''Star Wars'' creator George Lucas explains, the Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of View
The field of view (FoV) is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation. Humans and animals In the context of human and primate vision, the term "field of view" is typically only used in the sense of a restriction to what is visible by external apparatus, like when wearing spectacles or virtual reality goggles. Note that eye movements are allowed in the definition but do not change the field of view when understood this way. If the analogy of the eye's retina working as a sensor is drawn upon, the corresponding concept in human (and much of animal vision) is the visual field. It is defined as "the number of degrees of visual angle during stable fixation of the eyes".Strasburger, Hans; Pöppel, Ernst (2002). Visual Field. In G. Adelman & B.H. Smith (Eds): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''; 3rd edition, on CD-ROM. El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)