|
SS Ohioan (1914)
SS ''Ohioan'' was a cargo ship built in 1914 for the American-Hawaiian Steamship Company. During World War I, she was taken over by the United States Navy and commissioned as USS ''Ohioan'' (ID-3280). ''Ohioan'' was built by the Maryland Steel Company as one of eight sister ships ordered by the American-Hawaiian Steamship Company for inter-coastal service cargo via the Panama Canal. When the canal was temporarily closed by landslides in late 1915, ''Ohioan'' sailed via the Straits of Magellan until the canal reopened in mid 1916. During World War I, USS ''Ohioan'' carried cargo, animals, and a limited number of passengers to France, and returned over 8,000 American troops after the Armistice, including the highly decorated American soldier Alvin York. After ''Ohioan''s naval service ended in 1919, she was returned to her original owners. ''Ohioan''s post-war career was relatively uneventful until 8 October 1936, when she ran aground near Seal Rock at the Golden Gate, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Ohioan
SS ''Ohioan'' may refer to one of two ships owned by the American-Hawaiian Steamship Company The American-Hawaiian Steamship Company was founded in 1899 to carry cargos of sugar from Hawaii to the United States and manufactured goods back to Hawaii. Brothers-in-law George Dearborn and Lewis Henry Lapham were the key players in the foun ... * , built for American-Hawaiian in 1914, served as USS ''Ohioan'' in World War I, ran aground near San Francisco in 1936 * , the former ''Pawlet'', purchased by American-Hawaiian in 1937, sunk by German submarine ''U-564'' in World War II {{DEFAULTSORT:Ohioan, Ss Ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait. Colombia, France, and later the United States controlled the territory surrounding the canal during construction. France began work on the canal in 1881, but stopped because of lack of investors' confidence due to engineering problems and a high worker mortality rate. The United States took over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Of The United States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S. states of California, Oregon, and Washington, but sometimes includes Alaska and Hawaii, especially by the United States Census Bureau as a U.S. geographic division. Definition There are conflicting definitions of which states comprise the West Coast of the United States, but the West Coast always includes California, Oregon, and Washington as part of that definition. Under most circumstances, however, the term encompasses the three contiguous states and Alaska, as they are all located in North America. For census purposes, Hawaii is part of the West Coast, along with the other four states. ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' refers to the North American region as part of the Pacific Coast, including Alaska and British Columbia. Although the enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Naming And Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadweight Tonnage
Deadweight tonnage (also known as deadweight; abbreviated to DWT, D.W.T., d.w.t., or dwt) or tons deadweight (DWT) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry. It is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water, ballast water, provisions, passengers, and crew. DWT is often used to specify a ship's maximum permissible deadweight (i.e. when it is fully loaded so that its Plimsoll line is at water level), although it may also denote the actual DWT of a ship not loaded to capacity. Definition Deadweight tonnage is a measure of a vessel's weight carrying capacity, not including the empty weight of the ship. It is distinct from the displacement (weight of water displaced), which includes the ship's own weight, or the volumetric measures of gross tonnage or net tonnage (and the legacy measures gross register tonnage and net register tonnage). Deadweight tonnage was historically expressed in long tonsOne long ton (LT) is but is now usually given internationally in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cargo Ships
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usually specially designed for the task, often being equipped with cranes and other mechanisms to load and unload, and come in all sizes. Today, they are almost always built of welded steel, and with some exceptions generally have a life expectancy of 25 to 30 years before being scrapped. Definitions The words ''cargo'' and ''freight'' have become interchangeable in casual usage. Technically, "cargo" refers to the goods carried aboard the ship for hire, while "freight" refers to the act of carrying of such cargo, but the terms have been used interchangeably for centuries. Generally, the modern ocean shipping business is divided into two classes: # Liner business: typically (but not exclusively) container vessels (wherein "general carg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelo Joseph Rossi
Angelo Joseph Rossi (January 22, 1878 – April 5, 1948) was a United States of America, U.S. political figure who served as the 31st mayor of San Francisco, California, San Francisco. Life and career Rossi was born in Volcano, California, Volcano, Amador County, California, Amador County, California, and came to San Francisco in 1890 with his widowed mother and six siblings after the family home and general store burned to the ground in minutes. (His father, also named Angelo, left Italy in 1849 at the age of 16 aboard a ship loaded with marble that departed from Genoa. When he arrived in Amador County, he mined for gold and opened his general store.) When Angelo arrived in San Francisco with his family in 1890, he attended school but left after 6th grade to work in jobs that ranged from cash boy to a clerk in a couple of different florist shops, including Carbone and Sons and Pelicano and Sons, which became Pelicano and Rossi when he became a partner in the early 1900s. Even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland. San Francisco Bay drains water from approximately 40 percent of California. Water from the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers, and from the Sierra Nevada mountains, flow into Suisun Bay, which then travels through the Carquinez Strait to meet with the Napa River at the entrance to San Pablo Bay, which connects at its south end to San Francisco Bay. It then connects to the Pacific Ocean via the Golden Gate strait. However, this entire group of interconnected bays is often called the ''San Francisco Bay''. The bay was designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance on February 2, 2017. Size The bay covers somewhere between , depending on which sub-bays (such as San Pablo Bay), estuaries, wetlands, and so on are included in the measurement. The main part of the bay meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by the Golden Gate Bridge. The entire shoreline and adjacent waters throughout the strait are managed by the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Geology During the last ice age, when sea level was several hundred feet lower, the waters of the glacier-fed Sacramento River and the San Joaquin River scoured a deep channel through the bedrock on their way to the ocean. (A similar process created the undersea Hudson Canyon off the coast of New York and New Jersey.) The strait is well known today for its depth and powerful tidal currents from the Pacific Ocean. Many small whirlpools and eddies can form in its waters. With its strong currents, rocky reefs and fog, the Golden Gate is the site of over 100 shipwrecks. Climate The Golden Gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Rock (San Francisco County, California)
Seal Rock (or ''Seal Rocks'') is a group of small rock formation islands in the Lands End area of the Outer Richmond District in western San Francisco, California. They are located just offshore in the Pacific Ocean, at the north end of the Ocean Beach, near the Cliff House and Sutro Baths ruins. The name is derived from the population of Steller's sea lions (''Eumetopias jubatus'') and California sea lions (''Zalophus californianus''), who haul out on the rock. Both species are often colloquially called "seals". The formations and wildlife are protected within the Golden Gate National Recreation Area. Geology Near the end of the last ice age, this part of the coastline was thought to be between eight and twenty five miles westward of its current position - around five thousand years ago, with the melting of the ice, the sea level rose to its current level. The coastal features found here today were formed by the actions of waves, wind, and the movement of sand. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
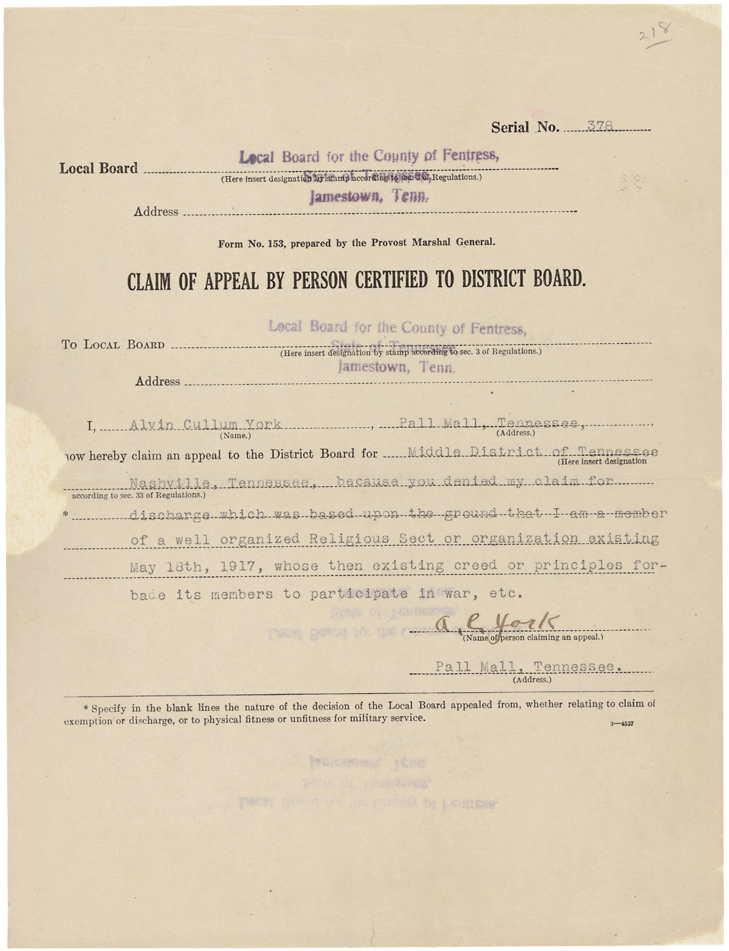
Alvin York
Alvin Cullum York (December 13, 1887 – September 2, 1964), also known as Sergeant York, was one of the most decorated United States Army soldiers of World War I. He received the Medal of Honor for leading an attack on a German machine gun nest, gathering 35 machine guns, killing at least 25 enemy soldiers and capturing 132 prisoners. York's Medal of Honor action occurred during the United States-led portion of the Meuse-Argonne Offensive in France, which was intended to breach the Hindenburg line and force the Germans to surrender. He earned decorations from several allied countries during WWI, including France, Italy and Montenegro. York was born in rural Tennessee, in what is now the community of Pall Mall in Fentress County. His parents farmed, and his father worked as a blacksmith. The eleven York children had minimal schooling because they helped provide for the family, including hunting, fishing, and working as laborers. After the death of his father, York ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)