|
SN 2005df
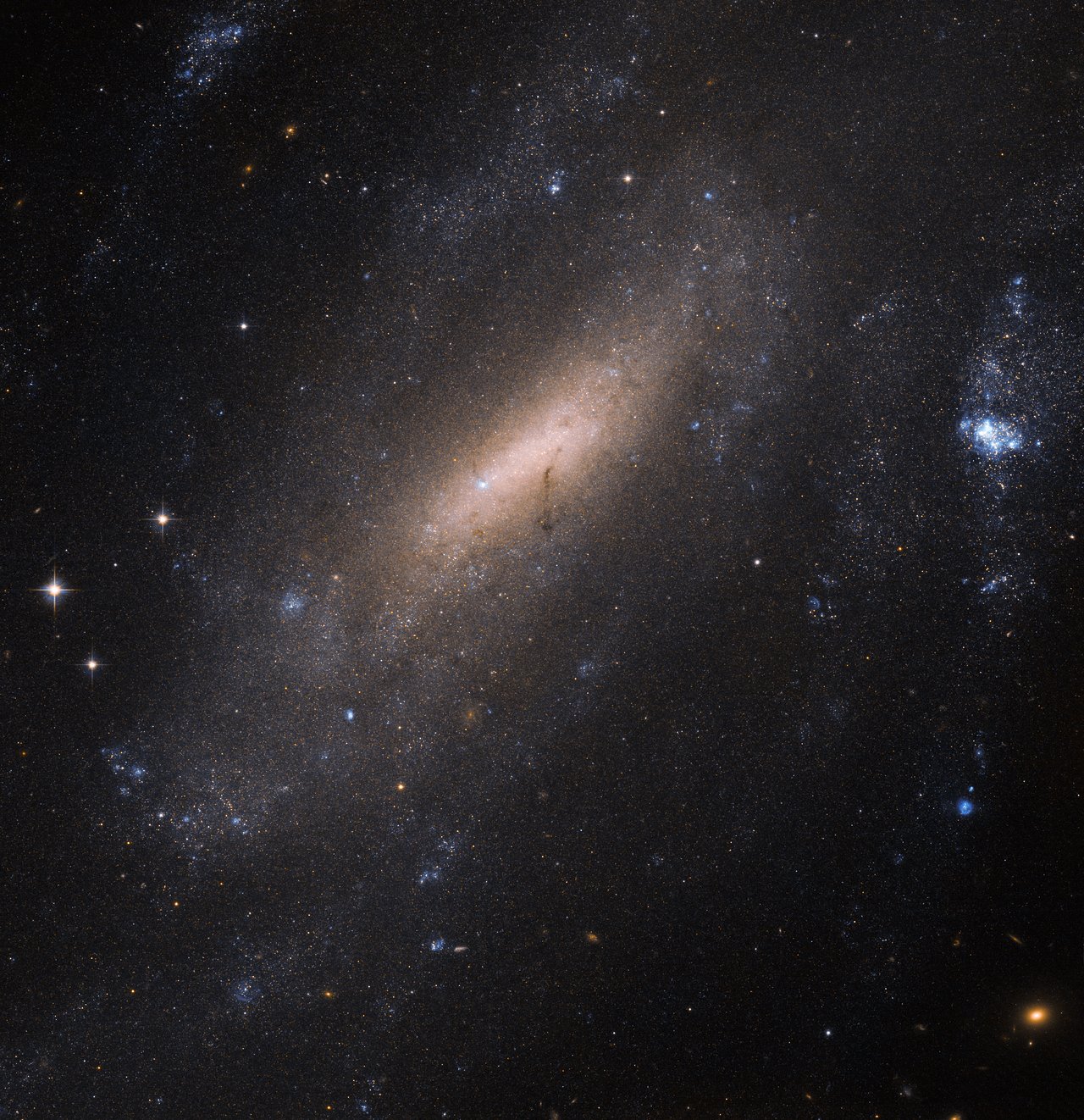
SN 2005df was a Type Ia supernova in the barred spiral galaxy NGC 1559, which is located in the southern constellation of Reticulum. The event was discovered in Australia by Robert Evans on the early morning of August 5, 2005 with a 13.8 magnitude, and was confirmed by A. Gilmore on August 6. The supernova was classified as Type Ia by M. Salvo and associates. It was positioned at an offset of east and north of the galaxy's nucleus, reaching a maximum brightness of 12.3 on August 18. The supernova luminosity appeared unreddened by dust from its host galaxy. The progenitor was a carbon-oxygen white dwarf close to the Chandrasekhar limit, making a merger scenario unlikely. Modelling of the explosion shows a low central density for a hydrogen accretion scenario, suggesting the donating companion was a helium star A helium star is a class O or B star (blue), which has extraordinarily strong helium lines and weaker than normal hydrogen lines, indicating strong stellar winds and a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed between October and December, and save for one main star visible in ideal conditions, cannot be seen from north of the 30th parallel north. History A constellation in this area was introduced by Isaac Habrecht II in his celestial globe in 1621, who named it ''Rhombus''. It was replaced with a somewhat different constellation by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the eighteenth century; during his stay at the Cape of Good Hope, he named the constellation le Réticule Rhomboide to commemorate the reticle in his telescope eyepiece. The name was later Latinized to Reticulum in his star catalogue ''Coelum Australe Stelliferum''. In 1810, the stars of Reticulum were used by William Croswell to produce the constellation '' Marmor Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 1559
NGC 1559 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Reticulum. It is also a Seyfert galaxy. Although it was originally thought to be a member of the Dorado Group, subsequent observations have shown that it is in fact not a member of any galaxy group or cluster and does not have any nearby companions. NGC 1559 has massive spiral arms and strong star formation. It contains a small bar which is oriented nearly east-west and spans 40. Its bar and disc are the source of very strong radio emissions. Four supernovae have been observed in NGC 1559. Australian amateur astronomer Robert Evans discovered the first three: SN 1984J ( type II, mag. 13.5), SN 1986L (type II, mag. 13.5), and SN 2005df ( Type Ia, mag 12.3). SN 2009ib (type IIP, mag. 14.7) Retrieved 25 March 2023. was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes from the emission of residual thermal energy; no fusion takes place in a white dwarf. The nearest known white dwarf is at 8.6 light years, the smaller component of the Sirius binary star. There are currently thought to be eight white dwarfs among the hundred star systems nearest the Sun. The unusual faintness of white dwarfs was first recognized in 1910. The name ''white dwarf'' was coined by Willem Luyten in 1922. White dwarfs are thought to be the final evolutionary state of stars whose mass is not high enough to become a neutron star or black hole. This includes over 97% of the other stars in the Milky Way. After the hydrogen- fusing period of a main-sequence star of low or medium mass ends, such a star will expand to a red giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernovae
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Ia Supernova
A Type Ia supernova (read: "type one-A") is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller white dwarf. Physically, carbon–oxygen white dwarfs with a low rate of rotation are limited to below 1.44 solar masses (). Beyond this "critical mass", they reignite and in some cases trigger a supernova explosion; this critical mass is often referred to as the Chandrasekhar mass, but is marginally different from the absolute Chandrasekhar limit, where electron degeneracy pressure is unable to prevent catastrophic collapse. If a white dwarf gradually accretes mass from a binary companion, or merges with a second white dwarf, the general hypothesis is that a white dwarf's core will reach the ignition temperature for carbon fusion as it approaches the Chandrasekhar mass. Within a few seconds of initiation of nuclear fusion, a substantial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barred Spiral Galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Evans (astronomer)
Robert Owen Evans, Order of Australia, OAM (20 February 1937 - 8 November 2022) was a minister (Christianity), minister of the Uniting Church in Hazelbrook, New South Wales and an amateur astronomer who holds the record for visual discoveries of supernovae (42). Ministry Evans was born on 20 February 1937 in Sydney, Australia. He graduated from the University of Sydney, majoring in philosophy and modern history. Coming from a religious family, Evans trained to become a Methodism, Methodist minister and was ordained by the New South Wales Conference in 1967. He served as a circuit preacher, circuit minister until his retirement in 1998. He is the author of a number of books on the history of evangelism. Supernova search Evans took up supernova hunting around 1955, but his first adequate instrument, a 10-inch (25 cm) Newtonian telescope was assembled only about 1968. He made his first official supernova discovery in 1981 and found nine more before using larger telescopes. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan C
Alan may refer to: People * Alan (surname), an English and Turkish surname * Alan (given name), an English given name **List of people with given name Alan ''Following are people commonly referred to solely by "Alan" or by a homonymous name.'' *Alan (Chinese singer) (born 1987), female Chinese singer of Tibetan ethnicity, active in both China and Japan *Alan (Mexican singer) (born 1973), Mexican singer and actor * Alan (wrestler) (born 1975), a.k.a. Gato Eveready, who wrestles in Asistencia Asesoría y Administración *Alan (footballer, born 1979) (Alan Osório da Costa Silva), Brazilian footballer *Alan (footballer, born 1998) (Alan Cardoso de Andrade), Brazilian footballer *Alan I, King of Brittany (died 907), "the Great" *Alan II, Duke of Brittany (c. 900–952) * Alan III, Duke of Brittany(997–1040) *Alan IV, Duke of Brittany (c. 1063–1119), a.k.a. Alan Fergant ("the Younger" in Breton language) *Alan of Tewkesbury, 12th century abbott *Alan of Lynn (c. 1348–1423), 15th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction (astronomy)
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of galactic dust. For stars that lie near the plane of the Milky Way and are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies (photometric system) is roughly 1.8 magnitudes per kiloparsec. For Earth-bound observers, extinction arises both from the interstellar medium (ISM) and the Earth's atmosphere; it may also arise from circumstellar dust around an observed object. Strong extinction in earth's atmosphere of some wavelength regions (such as X-ray, ultraviolet, and infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrasekhar Limit
The Chandrasekhar limit () is the maximum mass of a stable white dwarf star. The currently accepted value of the Chandrasekhar limit is about (). White dwarfs resist gravitational collapse primarily through electron degeneracy pressure, compared to main sequence stars, which resist collapse through thermal pressure. The Chandrasekhar limit is the mass above which electron degeneracy pressure in the star's core is insufficient to balance the star's own gravitational self-attraction. Consequently, a white dwarf with a mass greater than the limit is subject to further gravitational collapse, evolving into a different type of stellar remnant, such as a neutron star or black hole. Those with masses up to the limit remain stable as white dwarfs.Sean Carroll, Ph.D., Caltech, 2007, The Teaching Company, ''Dark Matter, Dark Energy: The Dark Side of the Universe'', Guidebook Part 2 page 44, Accessed Oct. 7, 2013, "...Chandrasekhar limit: The maximum mass of a white dwarf star, about 1.4 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |