|
SNPs On Chromosome 13
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (biology)
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Ford E.B. 1965. ''Genetic polymorphism''. Faber & Faber, London. Put simply, polymorphism is when there are two or more possibilities of a trait on a gene. For example, there is more than one possible trait in terms of a jaguar's skin colouring; they can be light morph or dark morph. Due to having more than one possible variation for this gene, it is termed 'polymorphism'. However, if the jaguar has only one possible trait for that gene, it would be termed "monomorphic". For example, if there was only one possible skin colour that a jaguar could have, it would be termed monomorphic. The term polyphenism can be used to clarify that the different forms arise from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
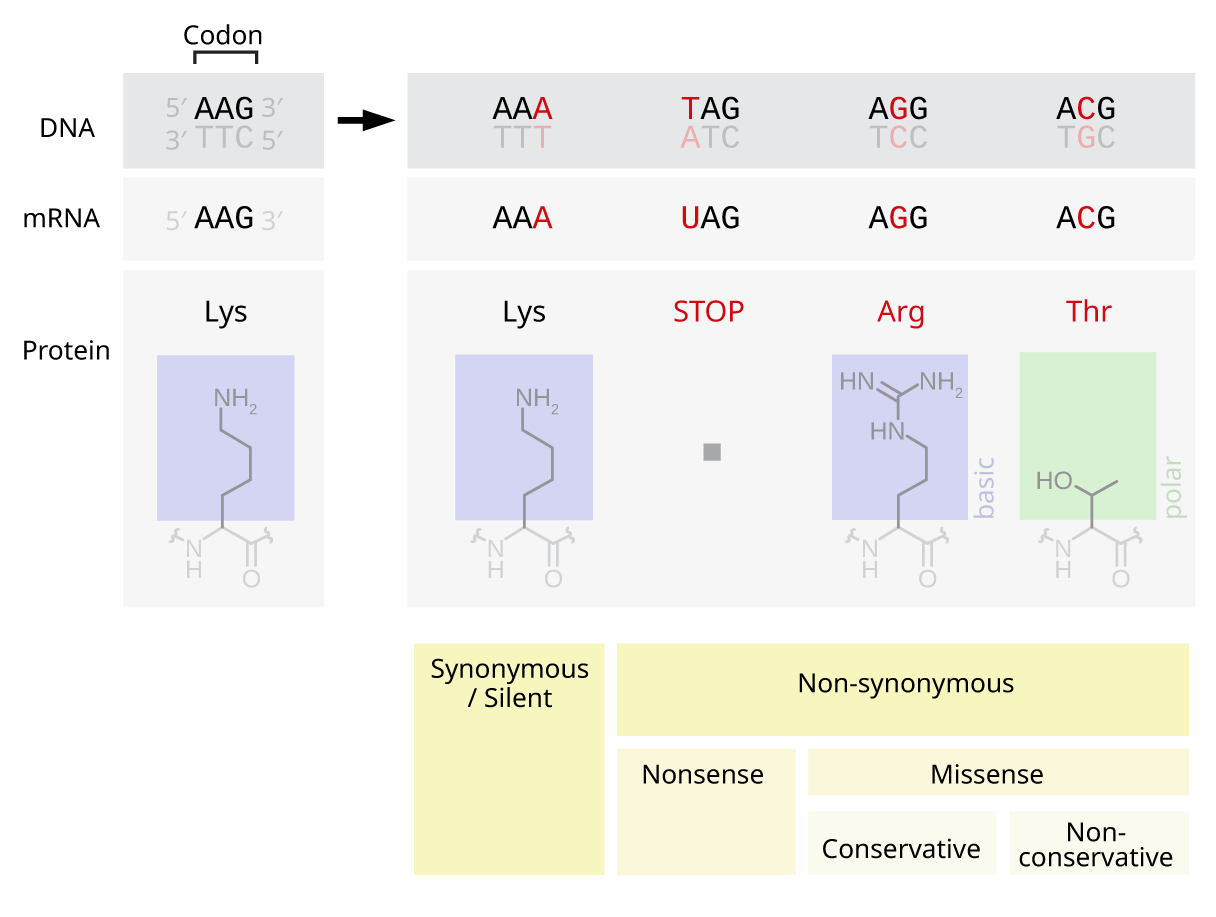
Nonsynonymous Substitution
A nonsynonymous substitution is a nucleotide mutation that alters the amino acid sequence of a protein. Nonsynonymous substitutions differ from synonymous substitutions, which do not alter amino acid sequences and are (sometimes) silent mutations. As nonsynonymous substitutions result in a biological change in the organism, they are subject to natural selection. Nonsynonymous substitutions at a certain locus can be compared to the synonymous substitutions at the same locus to obtain the Ka/Ks ratio. This ratio is used to measure the evolutionary rate of gene sequences. If a gene has lower levels of nonsynonymous than synonymous nucleotide substitution, then it can be inferred to be functional because a Ka/Ks ratio < 1 is a hallmark of sequences that are being constrained to code for proteins. Nonsynonymous substitutions are also referred to as replacement mutations. Types There are several common types of nonsynonymous substitutions. ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein 1 (permeability glycoprotein, abbreviated as P-gp or Pgp) also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein of the cell membrane that pumps many foreign substances out of cells. More formally, it is an ATP-dependent efflux pump with broad substrate specificity. It exists in animals, fungi, and bacteria, and it likely evolved as a defense mechanism against harmful substances. P-gp is extensively distributed and expressed in the intestinal epithelium where it pumps xenobiotics (such as toxins or drugs) back into the intestinal lumen, in liver cells where it pumps them into bile ducts, in the cells of the proximal tubule of the kidney where it pumps them into urinary filtrate (in the proximal tubule), and in the capillary endothelial cells composing the blood–brain barrier and blood–testis barrier, where it pumps them back into the capillar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonymous Substitution
A synonymous substitution (often called a ''silent'' substitution though they are not always silent) is the evolutionary substitution of one base for another in an exon of a gene coding for a protein, such that the produced amino acid sequence is not modified. This is possible because the genetic code is "degenerate", meaning that some amino acids are coded for by more than one three-base-pair codon; since some of the codons for a given amino acid differ by just one base pair from others coding for the same amino acid, a mutation that replaces the "normal" base by one of the alternatives will result in incorporation of the same amino acid into the growing polypeptide chain when the gene is translated. Synonymous substitutions and mutations affecting noncoding DNA are often considered silent mutations; however, it is not always the case that the mutation is silent. A synonymous mutation can affect transcription, splicing, mRNA transport, and translation, any of which could alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coding Region
The coding region of a gene, also known as the coding sequence (CDS), is the portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for protein. Studying the length, composition, regulation, splicing, structures, and functions of coding regions compared to non-coding regions over different species and time periods can provide a significant amount of important information regarding gene organization and evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This can further assist in mapping the human genome and developing gene therapy. Definition Although this term is also sometimes used interchangeably with exon, it is not the exact same thing: the exon is composed of the coding region as well as the 3' and 5' untranslated regions of the RNA, and so therefore, an exon would be partially made up of coding regions. The 3' and 5' untranslated regions of the RNA, which do not code for protein, are termed non-coding regions and are not discussed on this page. There is often confusion between coding region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EQTL
Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) are genomic loci that explain variation in expression levels of mRNAs. Distant and local, trans- and cis-eQTLs, respectively An expression quantitative trait is an amount of an mRNA transcript or a protein. These are usually the product of a single gene with a specific chromosomal location. This distinguishes expression quantitative traits from most complex traits, which are not the product of the expression of a single gene. Chromosomal loci that explain variance in expression traits are called eQTLs. eQTLs located near the gene-of-origin (gene which produces the transcript or protein) are referred to as local eQTLs or cis-eQTLs. By contrast, those located distant from their gene of origin, often on different chromosomes, are referred to as distant eQTLs or trans-eQTLs. The first genome-wide study of gene expression was carried out in yeast and published in 2002. The initial wave of eQTL studies employed microarrays to measure genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding Region
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules (e.g. transfer RNA, microRNA, piRNA, ribosomal RNA, and regulatory RNAs). Other functional regions of the non-coding DNA fraction include regulatory sequences that control gene expression; scaffold attachment regions; origins of DNA replication; centromeres; and telomeres. Some non-coding regions appear to be mostly nonfunctional such as introns, pseudogenes, intergenic DNA, and fragments of transposons and viruses. Fraction of non-coding genomic DNA In bacteria, the coding regions typically take up 88 % of the genome. The remaining 12 % consists largely of non-coding genes and regulatory sequences, which means that almost all of the bacterial genome has a function. The amount of coding DNA in eukaryrotes is usually a much smaller fraction of the genome because eukaryotic genomes contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Code
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the RNA codon table). That scheme is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though variant codes (such as in mitochondria) exist. History Effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |