|
SMS Königsberg (1915)
SMS was the lead ship of the of light cruisers, built for the German (Imperial Navy) during World War I. She took the name of the earlier , which had been destroyed during the Battle of Rufiji Delta in 1915. The new ship was laid down in 1914 at the AG Weser shipyard, launched in December 1915, and commissioned into the High Seas Fleet in August 1916. Armed with eight 15 cm SK L/45 guns, the ship had a top speed of . saw action with the II Scouting Group; in September 1917 she participated in Operation Albion, a large amphibious operation against the Baltic islands in the Gulf of Riga. Two months later, she was attacked by British battlecruisers in the Second Battle of Heligoland Bight. She was hit by the battlecruiser , which caused a large fire and reduced her speed significantly. She escaped behind the cover of two German battleships, however. She was to have taken part in a sortie by the entire High Seas Fleet to attack the British Grand Fleet in the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a common naming theme, either being named after the same type of thing or person (places, constellations, heads of state) or with some kind of alliteration. Typically the ship class is named for the first ship of that class. Often, sisters become more differentiated during their service as their equipment (in the case of naval vessels, their armament) are separately altered. For instance, the U.S. warships , , , and are all sister ships, each being an . Perhaps the most famous sister ships were the White Star Line's s, consisting of , and . As with some other liners, the sisters worked as running mates. Other sister ships include the Royal Caribbean International's and . ''Half-sister'' refers to a ship of the same class but with some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belt Armor
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers. The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to the heart of a warship. When struck by an artillery shell or underwater torpedo, the belt armor either absorbs the impact and explosion with its sheer thickness and strength, or else uses sloping to redirect the projectile and its blast downwards. Typically, the main armor belt covers the warship from its main deck down to some distance below the waterline. If, instead of forming the outer hull, the armor belt is built inside the hull, it is installed at a sloped angle for improved protection, as described above. The torpedo bulkhead Frequently, the main belt's armor plates were supplemented with a torpedo bulkhead spaced several meters behind the main belt, designed to maintain the ship's watertight integrity even if the main belt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuttling Of The German Fleet In Scapa Flow
Shortly after the end of the First World War, the German Kaiserliche Marine was scuttled by its sailors while held off the harbor of the British Royal Navy base at Scapa Flow, in the Orkney Islands of Scotland. The High Seas Fleet was interned there under the terms of the Armistice while negotiations took place over the fate of the ships. Fearing that either the UK would seize the ships unilaterally or the German government at the time might reject the Treaty of Versailles and resume the war effort (in which case the ships could be used against Germany), Admiral Ludwig von Reuter decided to scuttle the fleet. The scuttling was carried out on 21 June 1919. Intervening British guard ships were able to beach some of the ships, but 52 of the 74 interned vessels sank. Many of the wrecks were salvaged over the next two decades and were towed away for scrapping. Those that remain are popular diving sites. The ships are a source of low-background steel. Background The signing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Meurer
Hugo Meurer (28 May 1869 – 4 January 1960) was a vice-admiral of the Kaiserliche Marine (German Imperial Navy). Meurer was the German naval officer who handled the negotiations of the internment of the German fleet in November 1918 at the end of the First World War. Life Meurer was born in Sallach in Carinthia. On 16 April 1886 he joined the Kaiserliche Marine. During the First World War he served as commander of at the Battle of Jutland, and from 1916 to 1917 as captain of the battleship . In 1917 he was promoted to the rank of rear-admiral (''Konteradmiral''), as the second Admiral of the 4th Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet, which he remained until the end of the war. From 21 February to 2 May 1918, as commander of the special unit (''Sonderverband'') of the Baltic Sea, he led the naval expedition for the German intervention in the ongoing civil war in Finland. In November 1918 Meurer negotiated as representative of Admiral Franz von Hipper with Admiral Dav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Fleet
The Grand Fleet was the main battlefleet of the Royal Navy during the First World War. It was established in August 1914 and disbanded in April 1919. Its main base was Scapa Flow in the Orkney Islands. History Formed in August 1914 from the First Fleet and part of the Second Fleet of the Home Fleets, the Grand Fleet included 25–35 modern capital ships. It was commanded initially by Admiral Sir John Jellicoe.Heathcote, p. 130 The 10th Cruiser Squadron carried out the Northern Patrol between the Shetlands and Norway and cruisers from Cromarty and Rosyth operated a second line (and screened the fleet) in enforcing the blockade of Germany. The administrative complications of the distant blockade across the northern exits of the North Sea overwhelmed the capacity of Vice Admiral Francis Miller, the Base Admiral in Chief from 7 August 1914, devolving on the commander in chief, Admiral John Jellicoe. To relieve the administrative burdens on Miller and Jellicoe, the post of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Heligoland Bight
The Second Battle of Heligoland Bight, also the Action in the Helgoland Bight and the , was an inconclusive naval engagement fought between British and German squadrons on 17 November 1917 during the First World War. Background British minelaying The British used sea mining defensively to protect sea lanes and trade routes and offensively to impede the transit of German submarines and surface ships in the North Sea, the danger of which was illustrated on 17 October 1917 by the sortie of the German ''Brummer''-class cruisers and (the action off Lerwick) against the Scandinavian Convoy. (During 1917, six U-boats were sunk by British mines and in two years, the German minesweeping counter-effort suffered the loss about 28 destroyers and 70 minesweepers and other ships.) The Germans had been forced into minesweeping up to into the Heligoland Bight and in the southern Baltic Sea, covered by light cruisers and destroyers, with occasional distant support by battleships. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battlecruisers
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attributes. Battlecruisers typically had thinner armour (to a varying degree) and a somewhat lighter main gun battery than contemporary battleships, installed on a longer hull with much higher engine power in order to attain greater speeds. The first battlecruisers were designed in the United Kingdom, as a development of the armoured cruiser, at the same time as the dreadnought succeeded the pre-dreadnought battleship. The goal of the design was to outrun any ship with similar armament, and chase down any ship with lesser armament; they were intended to hunt down slower, older armoured cruisers and destroy them with heavy gunfire while avoiding combat with the more powerful but slower battleships. However, as more and more battlecruisers were b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
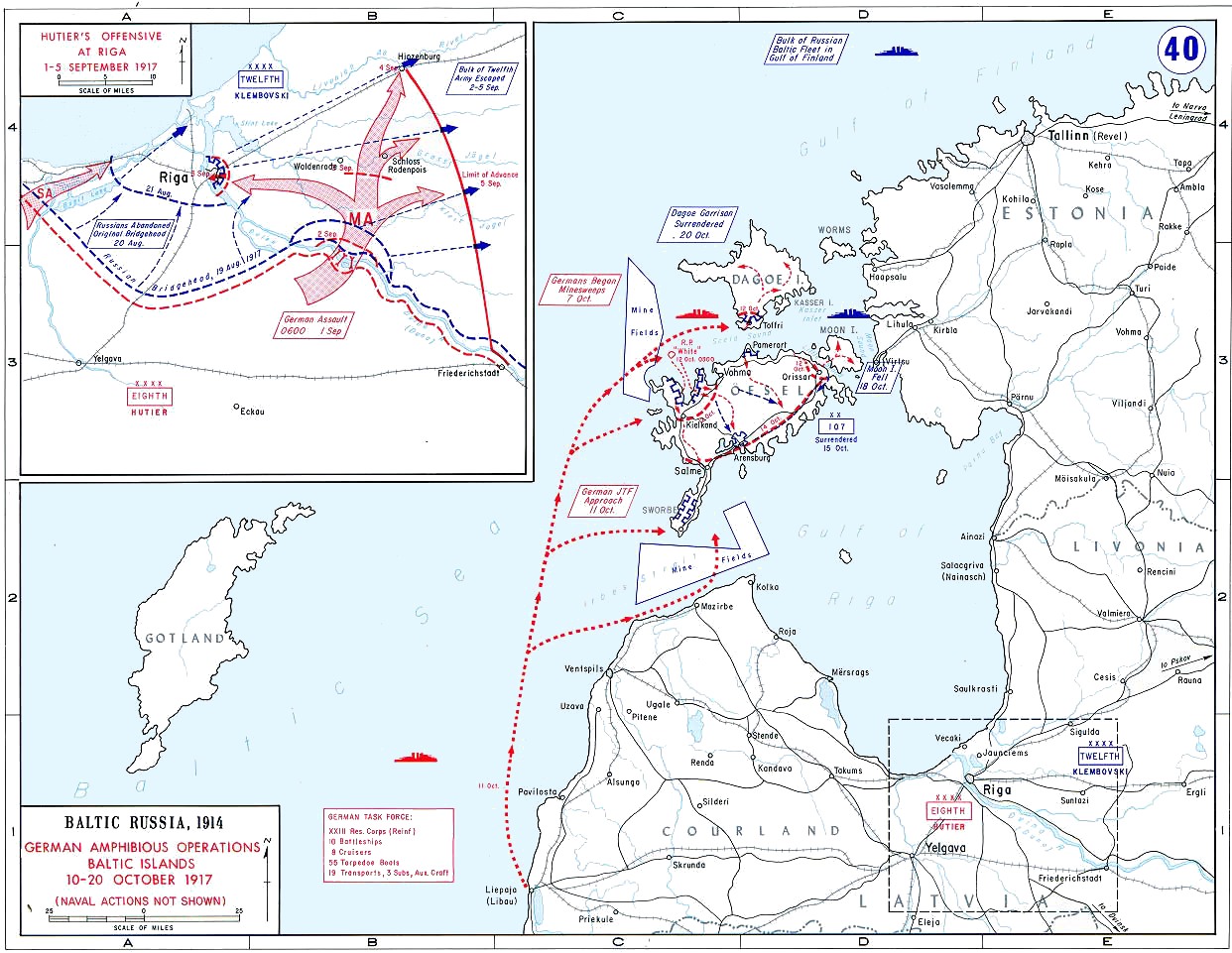
Operation Albion
Operation Albion was a World War I German air, land and naval operation against the Russian forces in October 1917 to occupy the West Estonian Archipelago. The land campaign opened with German landings at the Tagalaht bay on the island of Saaremaa, on 12 October 1917, after extensive naval operations to clear mines and subdue coastal artillery batteries. The Germans secured the island by 16 October and the Russian army evacuated Muhu on 20 October. After two failed attempts, the Germans landed on Hiiumaa on 12 October, capturing the island on the following day. The Russian Baltic Fleet had to withdraw from the Suur Strait after its losses at the Battle of Moon Sound. The Germans claimed 20,000 prisoners and 100 guns captured during Operation Albion from 12 to 20 October. Strategic significance At the beginning of World War I the islands were of little importance to the Russian Empire or Germany. After the revolutionary turmoil in Russia during the early part of 1917, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
II Scouting Group
II is the Roman numeral for 2. II may also refer to: Biology and medicine * Image intensifier, medical imaging equipment *Invariant chain, a polypeptide involved in the formation and transport of MHC class II protein *Optic nerve, the second cranial nerve Economics * Income inequality, or the wealth gap, in economics * Internationalization Index, used by the UN to rank nations and companies in evaluating their degree of integration with the world economy * ''Institutional Investor'' (magazine), an American finance magazine Music * Supertonic, in music * ''ii'', a 2018 song by CHVRCHES Albums * ''II'' (2 Unlimited album), 1998 * ''II'' (Aquilo album), 2018 * ''II'' (Bad Books album), 2012 * ''II'' (Boyz II Men album), 1994 * ''II'' (Capital Kings album), 2015 * ''II'' (Charade album), 2004 * ''II'' (The Common Linnets album), 2015 * ''II'' (Compact Disco album), 2011 * ''II'' (Cursed album), 2005 * ''II'' (Darna album), 2003 * ''II'' (Espers album), 2006 * ''II'' (Fuzz alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet (''Hochseeflotte'') was the battle fleet of the German Imperial Navy and saw action during the First World War. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet (''Heimatflotte'') was renamed as the High Seas Fleet. Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz was the architect of the fleet; he envisioned a force powerful enough to challenge the Royal Navy's predominance. Kaiser Wilhelm II, the German Emperor, championed the fleet as the instrument by which he would seize overseas possessions and make Germany a global power. By concentrating a powerful battle fleet in the North Sea while the Royal Navy was required to disperse its forces around the British Empire, Tirpitz believed Germany could achieve a balance of force that could seriously damage British naval hegemony. This was the heart of Tirpitz's "Risk Theory", which held that Britain would not challenge Germany if the latter's fleet posed such a significant threat to its own. The primary component of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rufiji Delta
The Battle of the Rufiji Delta was fought in German East Africa (modern Tanzania) from October 1914–July 1915 during the First World War, between the German Navy's light cruiser , and a powerful group of British warships. The battle was a series of attempts, ultimately successful, to sink the blockaded German light cruiser. Background In 1914 the most powerful German ship in the Indian Ocean was the light cruiser ''Königsberg''. After an engine failure following her sinking of the British protected cruiser HMS ''Pegasus'', ''Königsberg'' and her supply ship ''Somali'' hid in the delta of the Rufiji River while ''Königsbergs damaged machinery was transported overland to Dar es Salaam for repair. The British cruiser discovered ''Königsberg'' in the delta towards the end of October. On 5 November, two additional British cruisers, and , arrived at the scene, and blockaded the German ship in the delta. In early November, ''Chatham'' opened fire at long range and set fire to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.png)
_-_March_17%2C_1924.jpg)


