|
SK Radar
SK was an American-made air-search radar used during World War II by the United States Navy. Models include SK-1, SK-2 and SK-3. Overview Long wave search set for large ships. Furnishes range and bearing of surface vessels and aircraft, and can be used for control of interception. Set has both "A" and PPI scopes, provisions for operating with remote PPI's and for IFF connections, and built-in BL and BI antennas. Reliable maximum range, with antenna at , is on medium bombers at altitude. Range accuracy is ± . Azimuth accuracy, ± 3°. There is no elevation control, but elevation can be estimated roughly from positions of maximum, and minimum signal strength. Shipment includes spares, with tubes for 400 hours, and separate generator if ship's power is DC. Not air transportable. SK has 10 components weighing approximately . Heaviest unit, at , is the antenna assembly. Antenna measures x . Antenna should be or more above water. Minimum operators required are one per shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Long Island (CVE-1)
USS ''Long Island'' (CVE-1) (originally AVG-1 and then ACV-1) was lead ship of Long Island-class escort carrier, her class and the first escort carrier of the United States Navy. She was also the second ship to be named after Long Island, New York. Construction and commissioning ''Long Island'' was laid down on 7 July 1939, as the C-3 cargo liner ''Mormacmail'', under Maritime Commission contract, by the Sun Shipbuilding and Drydock Company, Chester, Pennsylvania as Yard No 185, launched on 11 January 1940, sponsored by Ms. Dian B. Holt, acquired by the Navy on 6 March 1941, and commissioned on 2 June 1941 as ''Long Island'' (AVG-1), Commander (United States), Commander Donald B. Duncan in command. Service history World War II In the tense months before the attack on Pearl Harbor, ''Long Island'' operated out of Norfolk, Virginia, conducting experiments to prove the feasibility of aircraft operations from converted cargo ships. The data gathered by her crew greatly improved the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify '' current'' or '' voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
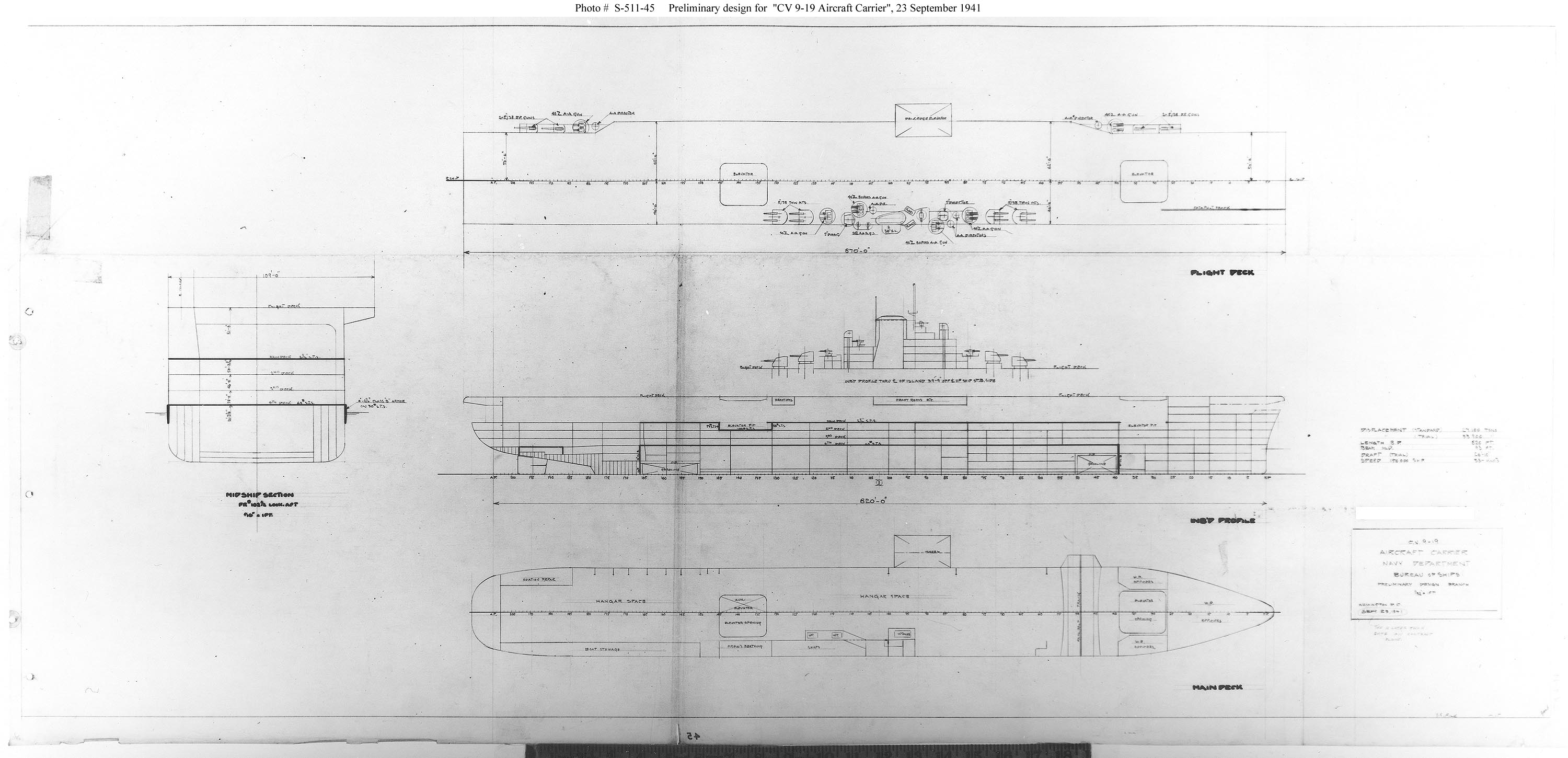
Iowa-class Battleship
The ''Iowa'' class was a class of six fast battleships ordered by the United States Navy in 1939 and 1940. They were initially intended to intercept fast capital ships such as the Japanese while also being capable of serving in a traditional battle line alongside slower battleships and act as its "fast wing". The ''Iowa'' class was designed to meet the Second London Naval Treaty's "escalator clause" limit of standard displacement. Four vessels, , , , and , were completed; two more, and , were laid down but canceled in 1945 and 1958, respectively, before completion, and both hulls were scrapped in 1958–1959. The four ''Iowa''-class ships were the last battleships commissioned in the US Navy. All older US battleships were decommissioned by 1947 and stricken from the ''Naval Vessel Register'' (NVR) by 1963. Between the mid-1940s and the early 1990s, the ''Iowa''-class battleships fought in four major US wars. In the Pacific Theater of World War II, they served primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Honolulu (CL-48) At Anchor In 1944
Several US Navy ships have been named USS ''Honolulu'': * USS ''Honolulu'' (ID-1843), a cargo ship in commission from 1917 to 1919 *, a light cruiser in commission from 1938 from 1947 *, a submarine in commission from 1985 to 2007 {{DEFAULTSORT:Honolulu United States Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogue-class Escort Carrier
The ''Bogue'' class were a class of 45 escort carriers built in the United States for service with the US Navy and the Royal Navy, through the Lend-Lease program, during World War II. Following the war, ten ''Bogue''-class ships were kept in service by the US Navy and were reclassified for helicopter and aircraft transport operations. The first 22 ships of the class were converted from finished, or near finished, Maritime Commission C3-S-A1 and C3-S-A2 ships, with 11 retained by the US Navy, and the other 11 transferring to the Royal Navy, where they were renamed and grouped as the . was the last of the USN ships built and comprised all of the lessons learned in the earlier ships, sometimes it is referred to as its own subclass of the ''Bogue'' class. The remaining 23 ships were built from the keel up on C3-class designs and classified as , or the ''Ameer''-class. Following the war, those ships that served with the Royal Navy were returned to the United States and were either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casablanca-class Escort Carrier
The ''Casablanca''-class escort carrier were a series of escort carriers constructed for the United States Navy during World War II. They are the most numerous class of aircraft carriers ever built. Fifty were laid down, launched and commissioned within the space of less than two years – 3 November 1942 through to 8 July 1944. These were nearly one third of the 143 aircraft carriers built in the United States during the war. Despite their numbers, and the preservation of more famous and larger carriers as museums, none of these modest ships survive today. Five were lost to enemy action during World War II and the remainder were scrapped. ''Casablanca'' was the first class to be designed from keel up as an escort carrier. It had a larger and more useful hangar deck than previous conversions. It also had a larger flight deck than the . Unlike larger carriers which had extensive armor, protection was limited to splinter plating. Their small size made them useful for transpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Saratoga (CV-3)
USS ''Saratoga'' (CV-3) was a built for the United States Navy during the 1920s. Originally designed as a battlecruiser, she was converted into one of the Navy's first aircraft carriers during construction to comply with the Washington Naval Treaty of 1922. The ship entered service in 1928 and was assigned to the Pacific Fleet for her entire career. ''Saratoga'' and her sister ship, , were used to develop and refine carrier tactics in a series of annual exercises before World War II. On more than one occasion these exercises included successful surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. She was one of three prewar US fleet aircraft carriers, along with and , to serve throughout World War II. Shortly after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, ''Saratoga'' was the centerpiece of the unsuccessful American effort to relieve Wake Island and was torpedoed by a Japanese submarine a few weeks later. After lengthy repairs, the ship supported forces participating in the Guadalcanal Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Enterprise (CV-6)
USS ''Enterprise'' (CV-6) was a carrier built for the United States Navy during the 1930s. She was the seventh U.S. Navy vessel of that name. Colloquially called "The Big E", she was the sixth aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. Launched in 1936, she was one of only three American carriers commissioned before World War II to survive the war (the others being and ). She participated in more major actions of the war against Japan than any other United States ship. These actions included the attack on Pearl Harbor — 18 Douglas SBD Dauntless dive bombers of her air group arrived over the harbor during the attack; seven were shot down with eight airmen killed and two wounded, making her the only American aircraft carrier with men at Pearl Harbor during the attack and the first to sustain casualties during the Pacific War — the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Eastern Solomons, the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, various other air-sea engagements during the Guad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Independence''-class aircraft carriers were a class of light carriers built for the United States Navy that served during World War II. Development Adapted from the design for the light cruisers, this class of ship resulted from the interest of President Franklin D. Roosevelt in naval air power. With war looming, Roosevelt, a former Assistant Secretary of the Navy, noted no new fleet aircraft carriers were expected to be completed before 1944. He proposed to convert some of the many cruisers then under construction to carriers. Studies of cruiser-size aircraft carriers had shown the type had serious limitations, and on 13 October 1941, the General Board of the United States Navy replied that such a conversion showed too many compromises to be effective. Undeterred, President Roosevelt ordered another study. On 25 October 1941, the Navy's Bureau of Ships reported that aircraft carriers converted from cruiser hulls would be of lesser capability, but available much soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Essex'' class was a class of aircraft carriers of the United States Navy. The 20th century's most numerous class of capital ship, the class consisted of 24 vessels, which came in "short-hull" and "long-hull" versions. Thirty-two ships were ordered, but as World War II wound down, six were canceled before construction, and two were canceled after construction had begun. Fourteen saw combat during World War II. None were lost to enemy action, though several sustained crippling damage. ''Essex''-class carriers were the backbone of the U.S. Navy from mid-1943 and, with the three carriers added just after the war, continued to be the heart of U.S. naval strength until supercarriers joined the fleet in the 1960s and 1970s. Several of the carriers were rebuilt to handle heavier and faster aircraft of the early jet age, and some served until well after the Vietnam War. Overview The preceding s and the designers' list of trade-offs and limitations forced by arms control treaty o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_in_Measure_12_camouflage_-_19-N-27986.jpg)



_-_19-N-11981.jpg)
_in_Puget_Sound%2C_September_1945.jpg)