|
SKOS
Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS) is a W3C recommendation designed for representation of thesauri, classification schemes, taxonomies, subject-heading systems, or any other type of structured controlled vocabulary. SKOS is part of the Semantic Web family of standards built upon RDF and RDFS, and its main objective is to enable easy publication and use of such vocabularies as linked data. History DESIRE II project (1997–2000) The most direct ancestor to SKOS was the RDF Thesaurus work undertaken in the second phase of the EU DESIRE project . Motivated by the need to improve the user interface and usability of multi-service browsing and searching, a basic RDF vocabulary for Thesauri was produced. As noted later in the SWAD-Europe workplan, the DESIRE work was adopted and further developed in the SOSIG and LIMBER projects. A version of the DESIRE/SOSIG implementation was described in W3C's QL'98 workshop, motivating early work on RDF rule and query languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 25964
ISO 25964 is the international standard for thesauri, published in two parts as follows: ''ISO 25964'' '' Information and documentation - Thesauri and interoperability with other vocabularies'' ''Part 1: Thesauri for information retrieval'' ublished August 2011 ''Part 2: Interoperability with other vocabularies'' ublished March 2013 It was issued by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, and its official website is maintained by its secretariat in NISO, the USA National Information Standards Organization. Each part of the standard can be purchased separately from ISO or from any of its national member bodies (such as ANSI, BSI, AFNOR, DIN, etc.). Some parts of it are available free of charge from the official website. History The first international standard for thesauri was ISO 2788, ''Guidelines for the establishment and development of monolingual thesauri'', originally published in 1974 and updated in 1986. In 1985 it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDF Schema
RDF Schema (Resource Description Framework Schema, variously abbreviated as RDFS, , RDF-S, or RDF/S) is a set of classes with certain properties using the RDF extensible knowledge representation data model, providing basic elements for the description of ontologies. It uses various forms of RDF vocabularies, intended to structure RDF resources. RDF and RDFS can be saved in a triplestore, then one can extract some knowledge from them using a query language, like SPARQL. The first version was published by the World-Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in April 1998, and the final W3C recommendation was released in February 2014. Many RDFS components are included in the more expressive Web Ontology Language (OWL). Terminology RDFS constructs are the RDFS classes, associated properties and utility properties built on the vocabulary of RDF. Classes ; : Represents the class of everything. All things described by RDF are resources. ; : An ''rdfs:Class'' declares a resource as a class for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge Organization System
Knowledge organization system (KOS), concept system, or concept scheme is the generic term used in knowledge organization (KO) for the selection of concepts with an indication of selected semantic relations.Hjørland, Birger. 2016. Knowledge organization. ''Knowledge Organization'' 43, no. 6: 475-84. Also available in Hjørland, Birger, ed. ''ISKO Encyclopedia of Knowledge Organization'', https://www.isko.org/cyclo/knowledge_organization. Despite their differences in type, coverage, and application, all KOS aim to support the organization of knowledge and information to facilitate their management and retrieval. KOS vary in complexity from simple sorted lists to complex relational networks. They represent both structural and functional features, and serve to eliminate ambiguity, control synonyms, establish relationships, and present properties. From their origins in library and information science (LIS), KOS have been applied to other domains and disciplines within science and indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a method to describe and exchange graph data. It was originally designed as a data model for metadata by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It provides a variety of syntax notations and formats, of which the most widely used is Turtle ( Terse RDF Triple Language). RDF is a directed graph composed of triple statements. An RDF graph statement is represented by: (1) a node for the subject, (2) an arc from subject to object, representing a predicate, and (3) a node for the object. Each of these parts can be identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). An object can also be a literal value. This simple, flexible data model has a lot of expressive power to represent complex situations, relationships, and other things of interest, while also being appropriately abstract. RDF was adopted as a W3C recommendation in 1999. The RDF 1.0 specification was published in 2004, and the RDF 1.1 specification in 2014. SPARQL is a standard query ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Ontology Language
The Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a family of Knowledge representation and reasoning, knowledge representation languages for authoring Ontology (information science), ontologies. Ontologies are a formal way to describe Taxonomy, taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects. Ontologies resemble class hierarchies in object-oriented programming but there are several critical differences. Class hierarchies are meant to represent structures used in source code that evolve fairly slowly (perhaps with monthly revisions) whereas ontologies are meant to represent information on the Internet and are expected to be evolving almost constantly. Similarly, ontologies are typically far more flexible as they are meant to represent information on the Internet coming from all sorts of heterogeneous data sources. Class hierarchies on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies such as Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL) are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For example, Ontology (information science), ontology can describe concepts, relationships between Entity–relationship model, entities, and categories of things. These embedded semantics offer significant advantages such as reasoning engine, reasoning over data and operating with heterogeneous data sources. These standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, fundamentally the RDF. According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Term
In information retrieval, an index term (also known as subject term, subject heading, descriptor, or keyword) is a term that captures the essence of the topic of a document. Index terms make up a controlled vocabulary for use in bibliographic records. They are an integral part of bibliographic control, which is the function by which libraries collect, organize and disseminate documents. They are used as keywords to retrieve documents in an information system, for instance, a catalog or a search engine. A popular form of keywords on the web are tag (metadata), tags, which are directly visible and can be assigned by non-experts. Index terms can consist of a word, phrase, or alphanumerical term. They are created by analyzing the document either manually with subject indexing or automatically with Index (search engine), automatic indexing or more sophisticated methods of keyword extraction. Index terms can either come from a controlled vocabulary or be freely assigned. Keywords are sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
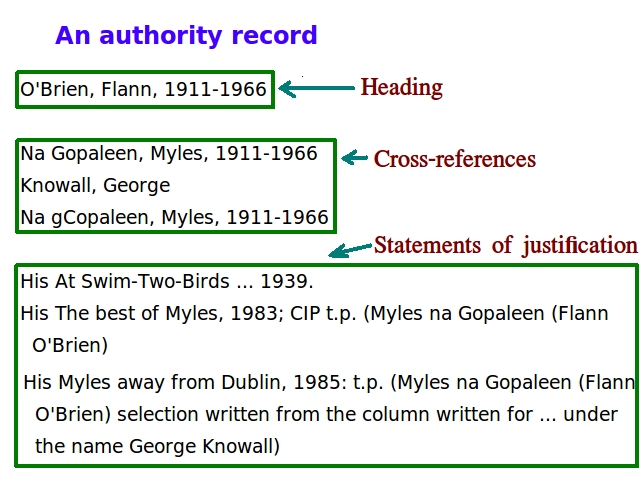
Authority Control
In information science, authority control is a process that organizes information, for example in library catalogs, by using a single, distinct spelling of a name (heading) or an identifier (generally persistent and alphanumeric) for each topic or concept. The word ''authority'' in ''authority control'' derives from the idea that the names of people, places, things, and concepts are ''authorized,'' i.e., they are established in one particular form. Note: root words for both ''author'' and ''authority'' are words such as ''auctor'' or ''autor'' and ''autorite'' from the 13th century. These one-of-a-kind headings or identifiers are applied consistently throughout catalogs which make use of the respective authority file, and are applied for other methods of organizing data such as linkages and cross references. Each controlled entry is described in an authority ''record'' in terms of its scope and usage, and this organization helps the library staff maintain the catalog and make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Data Archive
The UK Data Archive is a national centre of expertise in data archiving in the United Kingdom. It houses the largest collection of social sciences and population digital data in the UK. It is certified under CoreTrustSeal as a trusted digital repository. It is also certified under the international ISO 27001 standard for information security. Located in Colchester, the UK Data Archive is a specialist department of the University of Essex, co-located with the Institute for Social and Economic Research (ISER). It is primarily funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) and the University of Essex. Many of the data services formerly hosted by the UK Data Archive joined the ESRC-funded UK Data Service, established 1 October 2012. The UK Data Archive is listed in the Registry of Research Data Repositories re3data.org. Scope and purpose The UK Data Archive supports social science research and teaching by acquiring, developing and managing data and related digital r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol University
The University of Bristol is a public research university in Bristol, England. It received its royal charter in 1909, although it can trace its roots to a Merchant Venturers' school founded in 1595 and University College, Bristol, which had been in existence since 1876. Bristol Medical School, founded in 1833, was merged with the University College in 1893, and later became the university's school of medicine. The university is organised into six academic faculties composed of multiple schools and departments running over 200 undergraduate courses, largely in the Tyndalls Park area of the city. It had a total income of £1.06 billion in 2023–24, of which £294.1 million was from research grants and contracts, with an expenditure of £768.7 million. It is the largest independent employer in Bristol. Current academics include 23 fellows of the Academy of Medical Sciences, 13 fellows of the British Academy, 43 fellows of the Academy of Social Sciences, 13 fellows of the Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |