|
SHRDLU
SHRDLU was an early natural-language understanding computer program, developed by Terry Winograd at MIT in 1968–1970. In the program, the user carries on a conversation with the computer, moving objects, naming collections and querying the state of a simplified "blocks world", essentially a virtual box filled with different blocks. SHRDLU was written in the Micro Planner and Lisp programming language on the DEC PDP-6 computer and a DEC graphics terminal. Later additions were made at the computer graphics labs at the University of Utah, adding a full 3D rendering of SHRDLU's "world". The name SHRDLU was derived from ETAOIN SHRDLU, the arrangement of the letter keys on a Linotype machine, arranged in descending order of usage frequency in English. Functionality SHRDLU was primarily a language parser that allowed user interaction using English terms. The user instructed SHRDLU to move various objects around in the "blocks world" containing various basic objects: blocks, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terry Winograd
Terry Allen Winograd (born February 24, 1946) is an American professor of computer science at Stanford University, and co-director of the Stanford Human–Computer Interaction Group. He is known within the philosophy of mind and artificial intelligence fields for his work on natural language using the SHRDLU program. Education Winograd grew up in Colorado and graduated from Colorado College in 1966. He wrote SHRDLU as a PhD thesis at MIT in the years from 1968–70. In making the program Winograd was concerned with the problem of providing a computer with sufficient "understanding" to be able to use natural language. Winograd built a blocks world, restricting the program's intellectual world to a simulated "world of toy blocks". The program could accept commands such as, "Find a block which is taller than the one you are holding and put it into the box" and carry out the requested action using a simulated block-moving arm. The program could also respond verbally, for example, "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural-language Understanding
Natural-language understanding (NLU) or natural-language interpretation (NLI) is a subtopic of natural-language processing in artificial intelligence that deals with machine reading comprehension. Natural-language understanding is considered an AI-hard problem. There is considerable commercial interest in the field because of its application to automated reasoning, machine translation, question answering, news-gathering, text categorization, voice-activation, archiving, and large-scale content analysis. History The program STUDENT, written in 1964 by Daniel Bobrow for his PhD dissertation at MIT, is one of the earliest known attempts at natural-language understanding by a computer. Eight years after John McCarthy coined the term artificial intelligence, Bobrow's dissertation (titled ''Natural Language Input for a Computer Problem Solving System'') showed how a computer could understand simple natural language input to solve algebra word problems. A year later, in 1965, Joseph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planner Programming Language
Planner (often seen in publications as "PLANNER" although it is not an acronym) is a programming language designed by Carl Hewitt at MIT, and first published in 1969. First, subsets such as Micro-Planner and Pico-Planner were implemented, and then essentially the whole language was implemented as ''Popler'' by Julian Davies at the University of Edinburgh in the POP-2 programming language.Carl Hewitt Middle History of Logic Programming: Resolution, Planner, Prolog and the Japanese Fifth Generation Project ArXiv 2009. Derivations such as QA4, Conniver, QLISP and Ether (see scientific community metaphor) were important tools in artificial intelligence research in the 1970s, which influenced commercial developments such as Knowledge Engineering Environment (KEE) and Automated Reasoning Tool (ART). Procedural approach versus logical approach The two major paradigms for constructing semantic software systems were procedural and logical. The procedural paradigm was epitomized by Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planner (programming Language)
Planner (often seen in publications as "PLANNER" although it is not an acronym) is a programming language designed by Carl Hewitt at MIT, and first published in 1969. First, subsets such as Micro-Planner and Pico-Planner were implemented, and then essentially the whole language was implemented as ''Popler'' by Julian Davies at the University of Edinburgh in the POP-2 programming language.Carl Hewitt Middle History of Logic Programming: Resolution, Planner, Prolog and the Japanese Fifth Generation Project ArXiv 2009. Derivations such as QA4, Conniver, QLISP and Ether (see scientific community metaphor) were important tools in artificial intelligence research in the 1970s, which influenced commercial developments such as Knowledge Engineering Environment (KEE) and Automated Reasoning Tool (ART). Procedural approach versus logical approach The two major paradigms for constructing semantic software systems were procedural and logical. The procedural paradigm was epitomized by Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactive Fiction
'' Interactive fiction, often abbreviated IF, is software simulating environments in which players use text commands to control characters and influence the environment. Works in this form can be understood as literary narratives, either in the form of interactive narratives or interactive narrations. These works can also be understood as a form of video game, either in the form of an adventure game or role-playing game. In common usage, the term refers to text adventures, a type of adventure game where the entire interface can be " text-only", however, graphical text adventures still fall under the text adventure category if the main way to interact with the game is by typing text. Some users of the term distinguish between interactive fiction, known as "Puzzle-free", that focuses on narrative, and "text adventures" that focus on puzzles. Due to their text-only nature, they sidestepped the problem of writing for widely divergent graphics architectures. This feature meant that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Artificial Intelligence
The history of artificial intelligence (AI) began in antiquity, with myths, stories and rumors of artificial beings endowed with intelligence or consciousness by master craftsmen. The seeds of modern AI were planted by philosophers who attempted to describe the process of human thinking as the mechanical manipulation of symbols.This work culminated in the invention of the programmable digital computer in the 1940s, a machine based on the abstract essence of mathematical reasoning. This device and the ideas behind it inspired a handful of scientists to begin seriously discussing the possibility of building an electronic brain. The field of AI research was founded at a workshop held on the campus of Dartmouth College, USA during the summer of 1956. Those who attended would become the leaders of AI research for decades. Many of them predicted that a machine as intelligent as a human being would exist in no more than a generation, and they were given millions of dollars to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech recognition, computer vision, translation between (natural) languages, as well as other mappings of inputs. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' of Oxford University Press defines artificial intelligence as: the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. AI applications include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon and Netflix), understanding human speech (such as Siri and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Tesla), automated decision-making and competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and Go). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
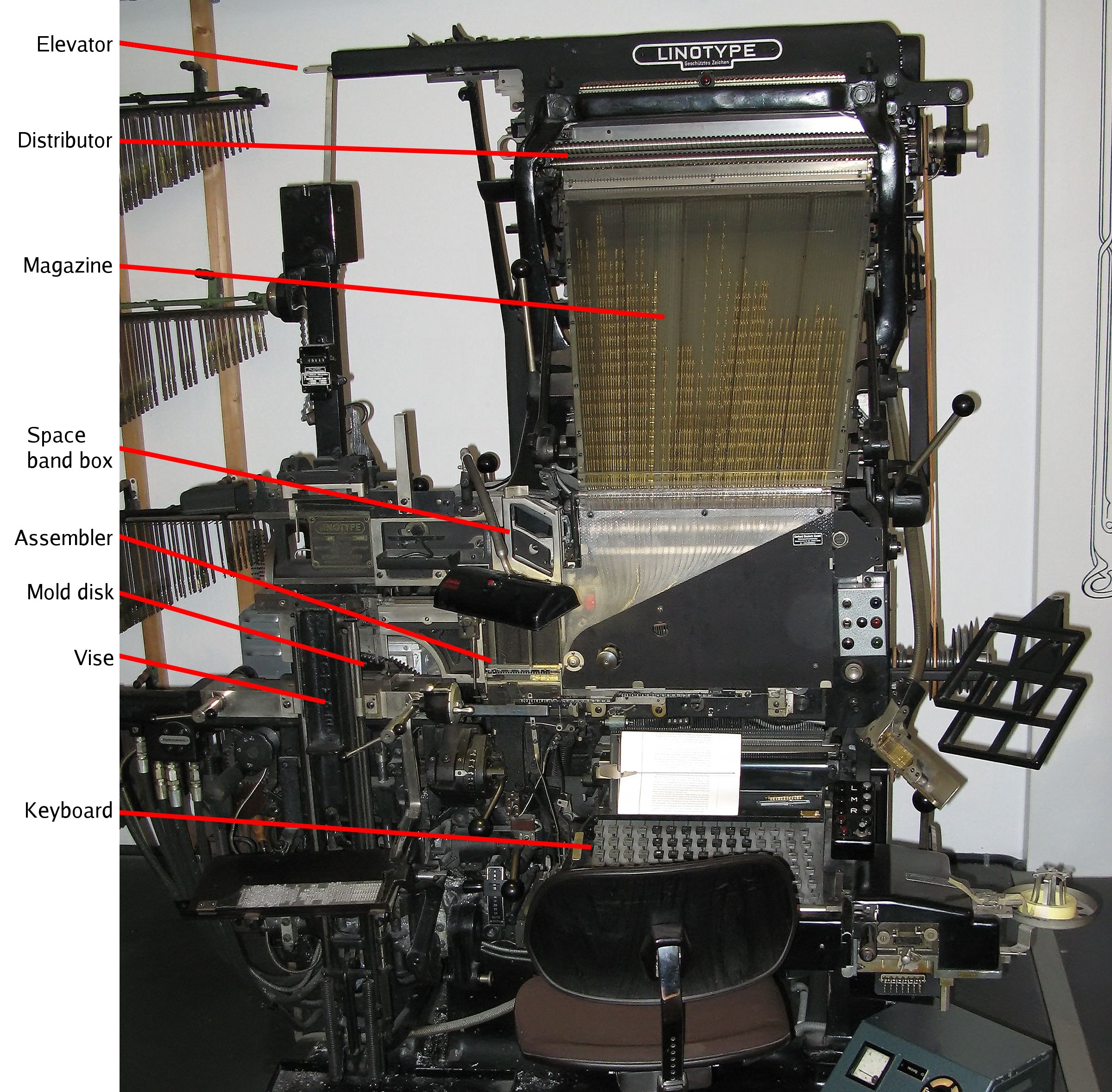
Linotype Machine
The Linotype machine ( ) is a "line casting" machine used in printing; manufactured and sold by the former Mergenthaler Linotype Company and related It was a hot metal typesetting system that cast lines of metal type for individual uses. Linotype became one of the mainstay methods to set type, especially small-size body text, for newspapers, magazines, and posters from the late 19th century to the 1970s and 1980s, when it was largely replaced by phototypesetting and digital typesetting. The name of the machine comes from the fact that it produces an entire line of metal type at once, hence a ''line-o'-type''. It was a significant improvement over the previous industry standard of manual, letter-by-letter typesetting using a composing stick and shallow subdivided trays, called "cases". The Linotype machine operator enters text on a 90-character keyboard. The machine assembles ''matrices'', which are molds for the letter forms, in a line. The assembled line is then cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blocks World
The blocks world is a Automated planning and scheduling, planning domain in artificial intelligence. The algorithm is similar to a set of wooden blocks of various shapes and colors sitting on a table. The goal is to build one or more vertical stacks of blocks. Only one block may be moved at a time: it may either be placed on the table or placed atop another block. Because of this, any blocks that are, at a given time, under another block cannot be moved. Moreover, some kinds of blocks cannot have other blocks stacked on top of them. The simplicity of this toy world lends itself readily to classical symbolic artificial intelligence approaches, in which the world is modeled as a set of abstract symbols which may be reasoned about. Motivation Artificial Intelligence can be researched in theory and with practical applications. The problem with most practical application is, that the engineers don't know how to program an AI system. Instead of rejecting the challenge at all the idea i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp Programming Language
Lisp (historically LISP) is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1960, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the read� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Negroponte
Nicholas Negroponte (born December 1, 1943) is a Greek American architect. He is the founder and chairman Emeritus of Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Media Lab, and also founded the One Laptop per Child Association (OLPC). Negroponte is the author of the 1995 bestseller ''Being Digital'' translated into more than forty languages. Early life Negroponte was born to Dimitrios Negropontis ( el, Νεγροπόντης), a Greek shipping magnate and alpine skier, and grew up in New York City's Upper East Side. He has three brothers. His elder one, John Negroponte, is the former United States Deputy Secretary of State. Michel Negroponte is an Emmy Award-winning filmmaker. George Negroponte is an artist and was President of the Drawing Center from 2002 to 2007. He attended Buckley School in New York, Fay School in Massachusetts, Le Rosey in Switzerland, and The Choate School (now Choate Rosemary Hall) in Wallingford, Connecticut, from which he graduated in 1961. Subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colossal Cave Adventure
''Colossal Cave Adventure'' (also known as ''Adventure'' or ''ADVENT'') is a text-based adventure game, released in 1976 by developer Will Crowther for the PDP-10 mainframe computer. It was expanded upon in 1977 by Don Woods. In the game, the player explores a cave system rumored to be filled with treasure and gold. The game is composed of dozens of locations, and the player moves between these locations and interacts with objects in them by typing one- or two-word commands which are interpreted by the game's natural language input system. The program acts as a narrator, describing the player's location and the results of the player's attempted actions. It is the first well-known example of interactive fiction, as well as the first well-known adventure game, for which it was also the namesake. The original game, written in 1975 and 1976, was based on Crowther's maps and experiences caving in Mammoth Cave in Kentucky, the longest cave system in the world; further, it was intended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |