|
SEPTA Route 29
SEPTA Route 29 is a former streetcar and trackless trolley line and current bus route, operated by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) in South Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The line runs between the Gray's Ferry neighborhood and the vicinity of Pier 70 along the Delaware River. Route 29 was a streetcar line from its inception in 1913 until 1947, and a trolley bus line until 2003. Route description Unlike the nearby SEPTA Route 79, Route 29 runs primarily along one-way streets. Eastbound buses run primarily along Morris Street, while westbound buses run primarily along Tasker Street. The west end of the Tasker Street segment turns north at 33rd Street, then east at Dickinson Street, then south at 32nd Street before heading east to Morris Street. Recent redevelopment of the Gray's Ferry area has disrupted this pattern. At 25th Street, a viaduct above the two streets is for a former Pennsylvania Railroad rail spur designed to serve neighb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
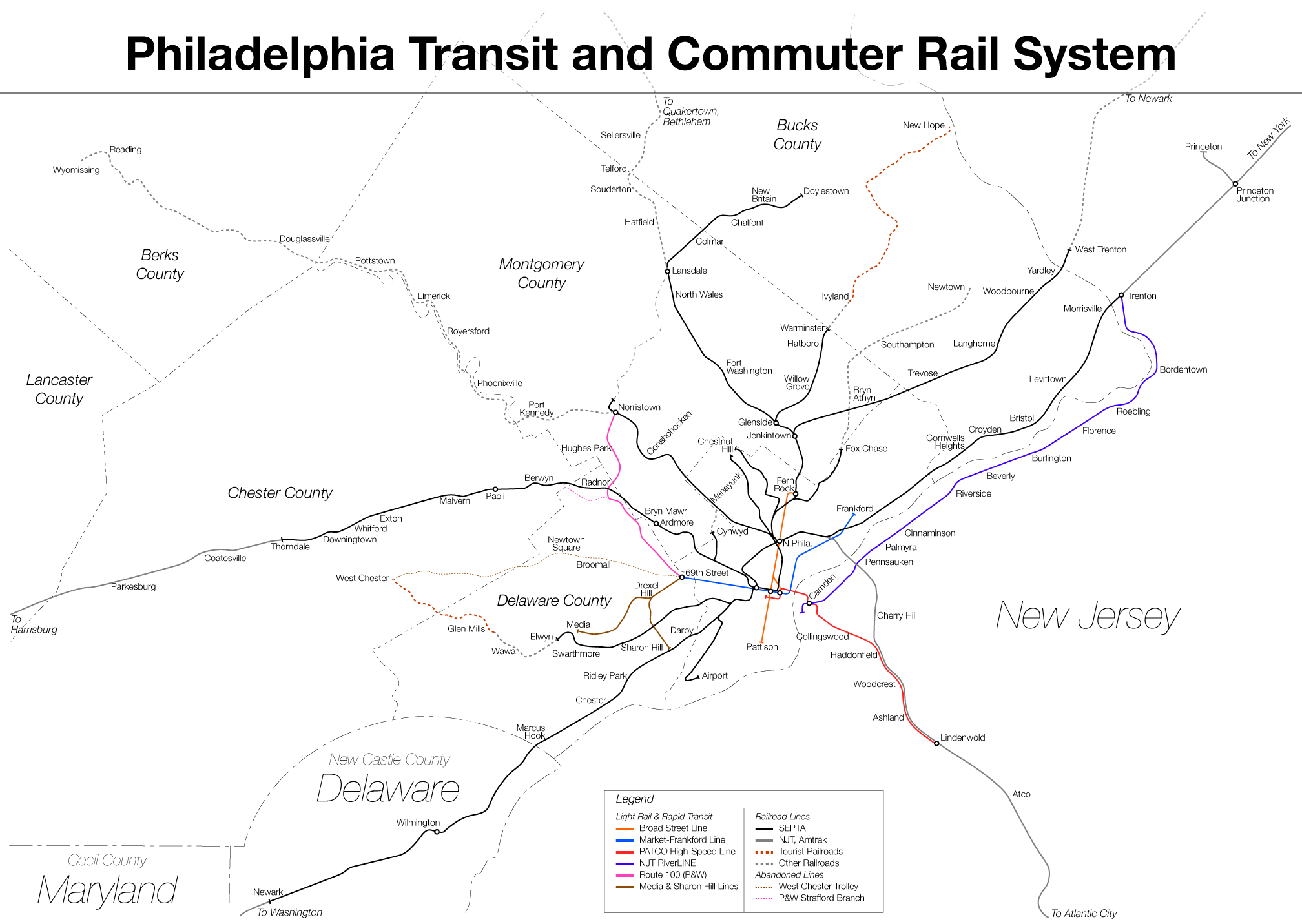
SEPTA
The Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) is a regional public transportation authority that operates bus, rapid transit, commuter rail, light rail, and electric trolleybus services for nearly 4 million people in five counties in and around Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It also manages projects that maintain, replace and expand its infrastructure, facilities and vehicles. SEPTA is the major transit provider for Philadelphia and the counties of Delaware, Montgomery, Bucks, and Chester. It is a state-created authority, with the majority of its board appointed by the five Pennsylvania counties it serves. While several SEPTA commuter rail lines terminate in the nearby states of Delaware and New Jersey, additional service to Philadelphia from those states is provided by other agencies: the PATCO Speedline from Camden County, New Jersey is run by the Delaware River Port Authority, a bi-state agency; NJ Transit operates many bus lines and a commuter rail line to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
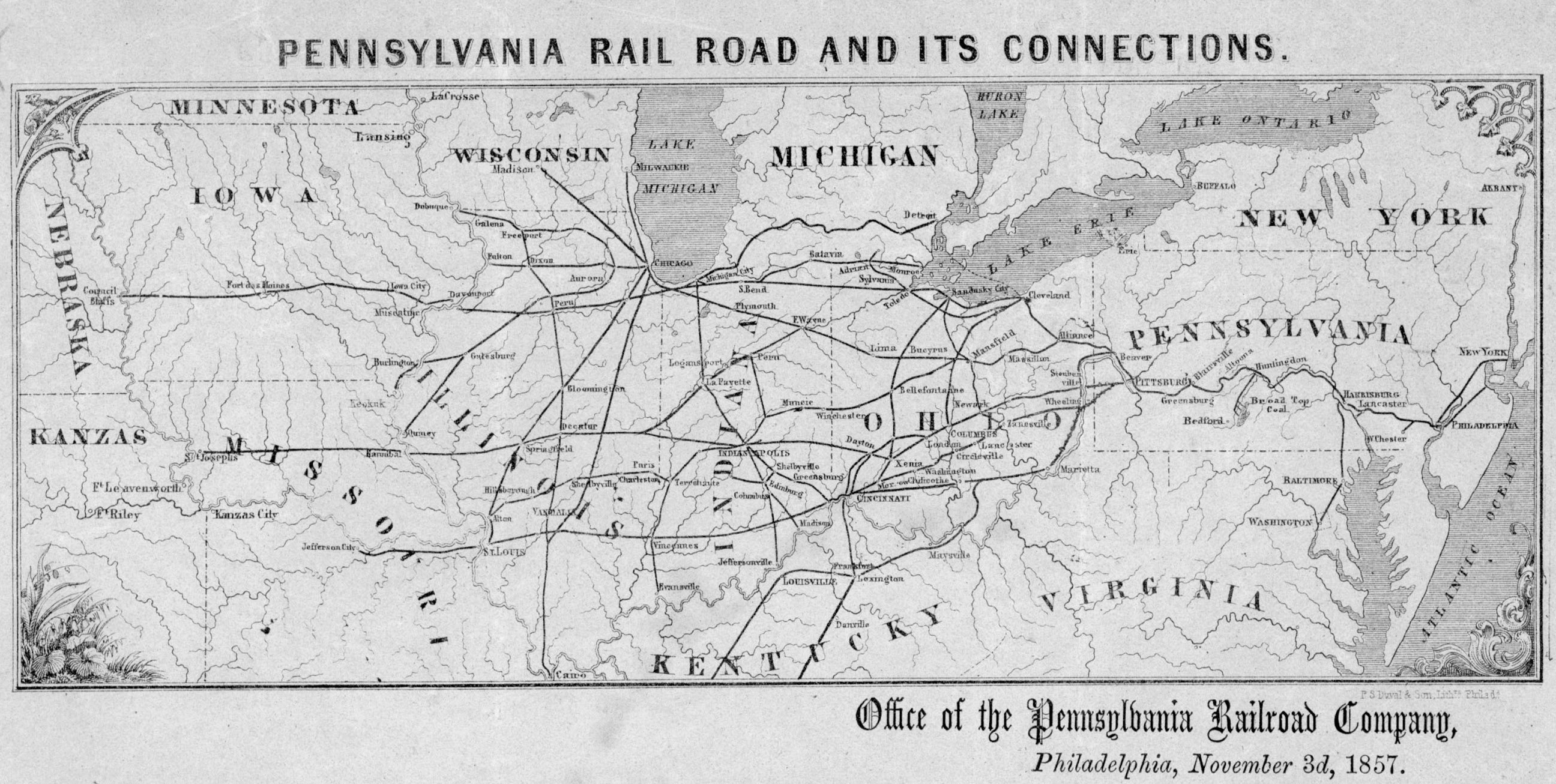
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trolleybuses In Philadelphia
The Philadelphia trolleybus system forms part of the public transportation network serving Philadelphia, in the state of Pennsylvania, United States. It opened on October 14, 1923, and is now the second-longest-lived trolleybus system in the world. One of only five such systems currently operating in the U.S., it presently comprises three lines, and is operated by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA), with a fleet of 38 trolleybuses, or trackless trolleys as SEPTA calls them. The three surviving routes serve North and Northeast Philadelphia and connect with SEPTA's Market–Frankford rapid transit line. History The first ''trackless trolley'' (trolley bus) service in Philadelphia was operated by the Philadelphia Rapid Transit Company, which had been established in 1902 by the merger of several then-independent transit companies operating within the city and its environs. Through a reorganization, the company became the Philadelphia Transportation Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Transit Administration
The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) is an agency within the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) that provides financial and technical assistance to local public transportation systems. The FTA is one of ten modal administrations within the DOT. Headed by an Administrator who is appointed by the President of the United States, the FTA functions through Washington, D.C headquarters office and ten regional offices which assist transit agencies in all states, the District of Columbia, and the territories. Until 1991, it was known as the Urban Mass Transportation Administration (UMTA). Public transportation includes buses, subways, light rail, commuter rail, monorail, passenger ferry boats, trolleys, inclined railways, and people movers. The federal government, through the FTA, provides financial assistance to develop new transit systems and improve, maintain, and operate existing systems. The FTA oversees grants to state and local transit providers, primarily t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Electric Bus
A battery electric bus is an electric bus that is driven by an electric motor and obtains energy from on-board batteries. Many trolleybuses use batteries as an auxiliary or emergency power source. In 2018, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that total operating costs per mile of an electric bus fleet and a diesel bus fleet in the United States are about equal. History The London Electrobus Company started running the first ever service of battery-electric buses between London's Victoria station and Liverpool Street on 15 July 1907. However, the weight and inefficiency of batteries meant that other propulsion technology - such as electric trolleybuses or diesel buses - became commonplace. The first battery buses were mostly small, mini- or midi- buses. The improvement of battery technology from around 2010 led to the emergence of the battery bus, including heavier units such as standard buses and articulated buses. China was the first country to int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEPTA Route 75
Route 75 is a trackless trolley route operated by SEPTA in North and Northeast Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. It connects to the Market–Frankford Line at Arrott Transportation Center Station, and runs primarily along Wyoming Avenue. Route 75 connects to the Wyoming (BSL station) local line and goes to Wayne Junction in Nicetown. The route is operated by trolleybuses, locally called trackless trolleys, which replaced streetcars (trolley cars) on the route on April 19, 1948, following one day of temporary bus operation.Wiegand, W. F. (c1976). ''SEPTA routing changes - Numbered routes and High Speed'', Route 75, p. 2. Philadelphia, PA (US): Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority. No ISBN. As far back as 1922, the President of Philadelphia Rapid Transit recommended converting the route into a feeder route for the Market-Frankford Line.Electric Railway Journal">Frankford Elevated News (1915-1927) at Electric Railway Journal (WorldNYCSubway.org)/ref> The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEPTA Route 66
SEPTA Route 66 is a trackless trolley route in Northeast Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. It connects the Market–Frankford Line at the Frankford Transportation Center to Wissinoming, Mayfair, Holmesburg, and Torresdale along Frankford Avenue, which is US 13 and includes the historic, colonial Frankford Avenue Bridge. The route's eastern terminus is at City Line Loop, located at Frankford Avenue and Knights Road in Morrell Park. However, some weekday trips are truncated to Gregg Loop, located at Gregg Street and Frankford Avenue. Some weekday rush hour service begin/end at Frankford and Cottman Ave in the city's Mayfair neighborhood. The route is operated by trolleybuses, locally called trackless trolleys, replaced streetcars (trolley cars) on September 11, 1955.Springirth, Kenneth C. (2008). ''Southeastern Pennsylvania Trolleys'', pp. 10 and 115–116. Charleston, SC (US): Arcadia Publishing. . The last day of streetcar operation was actually July 30, 1955, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEPTA Route 59
Route 59 is a trackless trolley line operated by SEPTA that runs from the Market–Frankford Line at Arrott Transportation Center Station to Bells Corner in Rhawnhurst, primarily along Oxford and Castor Avenues. Major stops along the route include Oxford Circle and the Alma Loop in Castor, which is near a shopping center and a junior high and senior high school. The trackless trolleys (or trolleybuses) replaced trolley cars (streetcars) on the route on in June 25, 1950.Springirth, Kenneth C. (2008). ''Southeastern Pennsylvania Trolleys'', pp. 10 and 115–116. Charleston, SC (US): Arcadia Publishing. . Diesel buses temporarily replaced trackless trolleys on route 59 in June 2002, because of reconstruction of Frankford Depot (garage) and the adjacent Market-Frankford "El" viaduct and station, which required the temporary removal of the overhead trolley wires used by trackless trolleys both at the garage and along the deadhead route (under the El viaduct) connecting rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americans With Disabilities Act Of 1990
The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 or ADA () is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination based on disability. It affords similar protections against discrimination to Americans with disabilities as the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which made discrimination based on race, religion, sex, national origin, and other characteristics illegal, and later sexual orientation and gender identity. In addition, unlike the Civil Rights Act, the ADA also requires covered employers to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, and imposes accessibility requirements on public accommodations. In 1986, the National Council on Disability had recommended the enactment of an Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and drafted the first version of the bill which was introduced in the House and Senate in 1988. A broad bipartisan coalition of legislators supported the ADA, while the bill was opposed by business interests (who argued the bill imposed costs on busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Many recently built tramways use the contemporary term light rail. The vehicles are called streetcars or trolleys (not to be confused with trolleybus) in North America and trams or tramcars elsewhere. The first two terms are often used interchangeably in the United States, with ''trolley'' being the preferred term in the eastern US and ''streetcar'' in the western US. ''Streetcar'' or ''tramway'' are preferred in Canada. In parts of the United States, internally powered buses made to resemble a streetcar are often referred to as "trolleys". To avoid further confusion with trolley buses, the American Public Transportation Association (APTA) refers to them as "trolley-replica buses". In the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SEPTA Route 23
SEPTA Trolley Route 23 is a former streetcar line now operated with buses. It is operated by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The line runs between the Chestnut Hill and Center City neighborhoods via Germantown Avenue, 11th, and 12th Streets. Route 23 was once Philadelphia's longest streetcar route, extending south to Broad Street and Oregon Avenue in South Philadelphia, and was one of three suspended by SEPTA in 1992. A restoration of trolley service has been proposed in recent years, with a feasibility study planned between 2021 and 2027. The route is consistently one of SEPTA's most heavily-traveled bus lines, coming in as the fourth-busiest for daily ridership in 2018, as well as an average weekday ridership of 14,322. Route description Route 23 begins in Center City Philadelphia. The southern terminal is the intersection of 11th and Market streets, adjacent to the Market–Frankford Line's 11th S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |