|
SECISBP2
SECIS-binding protein 2 (commonly referred to as SBP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SECISBP2'' gene. Function The incorporation of selenocysteine into a protein requires the concerted action of an mRNA element called a sec insertion sequence (SECIS), a selenocysteine-specific translation elongation factor and a SECIS binding protein. With these elements in place, a UGA codon can be decoded as selenocysteine. SBP2 is a nuclear protein that functions as a SECIS binding protein, but experimental evidence indicates that SBP2 is cytoplasmic. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been associated with a reduction in activity of a specific thyroxine deiodinase, a selenocysteine-containing enzyme, and abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. See also * Thyroid hormone resistance Thyroid hormone resistance (also resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH), and sometimes Refetoff syndrome) describes a rare syndrome in which the thyroid hormone levels are elevated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormone Resistance
Thyroid hormone resistance (also resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH), and sometimes Refetoff syndrome) describes a rare syndrome in which the thyroid hormone levels are elevated but the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level is not suppressed, or not completely suppressed as would be expected. The first report of the condition appeared in 1967. Essentially this is decreased end organ responsiveness to thyroid hormones. A new term "impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormone" has been suggested in March 2014 by Refetoff et al. Presentation The syndrome can present with variable symptoms, even between members of the same family harboring the same mutation. Typically most or all tissues are resistant to thyroid hormone, so despite raised measures of serum thyroid hormone the individual may appear euthyroid (have no symptoms of over- or underactivity of the thyroid gland). The most common symptoms are goiter and tachycardia. It has also been linked to some cases of attention deficit hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur. Selenocysteine is present in several enzymes (for example glutathione peroxidases, tetraiodothyronine 5′ deiodinases, thioredoxin reductases, formate dehydrogenases, glycine reductases, selenophosphate synthetase 2, methionine-''R''-sulfoxide reductase B1 ( SEPX1), and some hydrogenases). It occurs in all three domains of life, including important enzymes (listed above) present in humans. Selenocysteine was discovered by biochemist Thressa Stadtman at the National Institutes of Health. Chemistry Selenocysteine is the Se-analogue of cysteine. It is rarely encountered outside of living tissue (and is not available commercially) because it is very susceptible to air-oxidation. More common is the oxidized derivative sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SECIS Element
In biology, the SECIS element (SECIS: ''selenocysteine insertion sequence'') is an RNA element around 60 nucleotides in length that adopts a stem-loop structure. This structural motif (pattern of nucleotides) directs the cell to translate UGA codons as selenocysteines (UGA is normally a stop codon). SECIS elements are thus a fundamental aspect of messenger RNAs encoding selenoproteins, proteins that include one or more selenocysteine residues. In bacteria the SECIS element appears soon after the UGA codon it affects. In archaea and eukaryotes, it occurs in the 3' UTR of an mRNA, and can cause multiple UGA codons within the mRNA to code for selenocysteine. One archaeal SECIS element, in ''Methanococcus,'' is located in the 5' UTR. The SECIS element appears defined by sequence characteristics, i.e. particular nucleotides tend to be at particular positions in it, and a characteristic secondary structure. The secondary structure is the result of base-pairing of complementary RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deiodinase
Deiodinase (or "Monodeiodinase") is a peroxidase enzyme that is involved in the activation or deactivation of thyroid hormones. Types Types of deiodinases include: Iodothyronine deiodinases catalyze release of iodine directly from the thyronine hormones. They are selenocysteine-dependent membrane proteins with a catalytic domain resembling Peroxiredoxins (Prx). Three related isoforms, deiodinase type I, II, and III, contribute to activation and inactivation of the initially released hormone precursor T4 (thyroxine) into T3 (triiodothyronine) or rT3 ( reverse triiodothyronine) in target cells. The enzymes catalyze a reductive elimination of iodine (the different isoforms attack different thyronine positions), thereby oxidizing themselves similar to Prx, followed by a reductive recycling of the enzyme. Iodotyrosine deiodinase contributes to breakdown of thyroid hormones. It releases iodine, for renewed use, from iodinated tyrosines resulting from catabolism of iodothyronines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
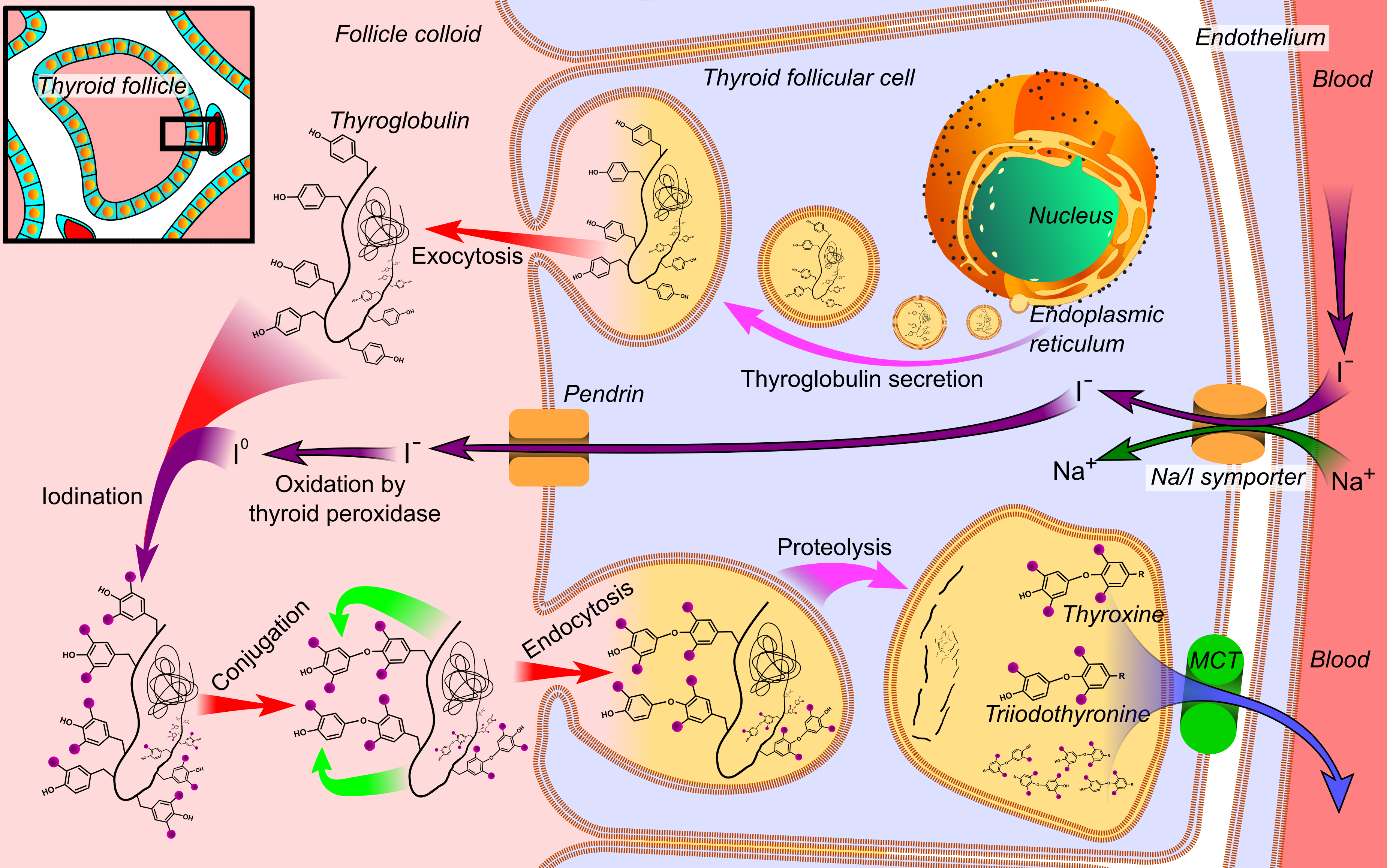
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are any hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one week ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |