|
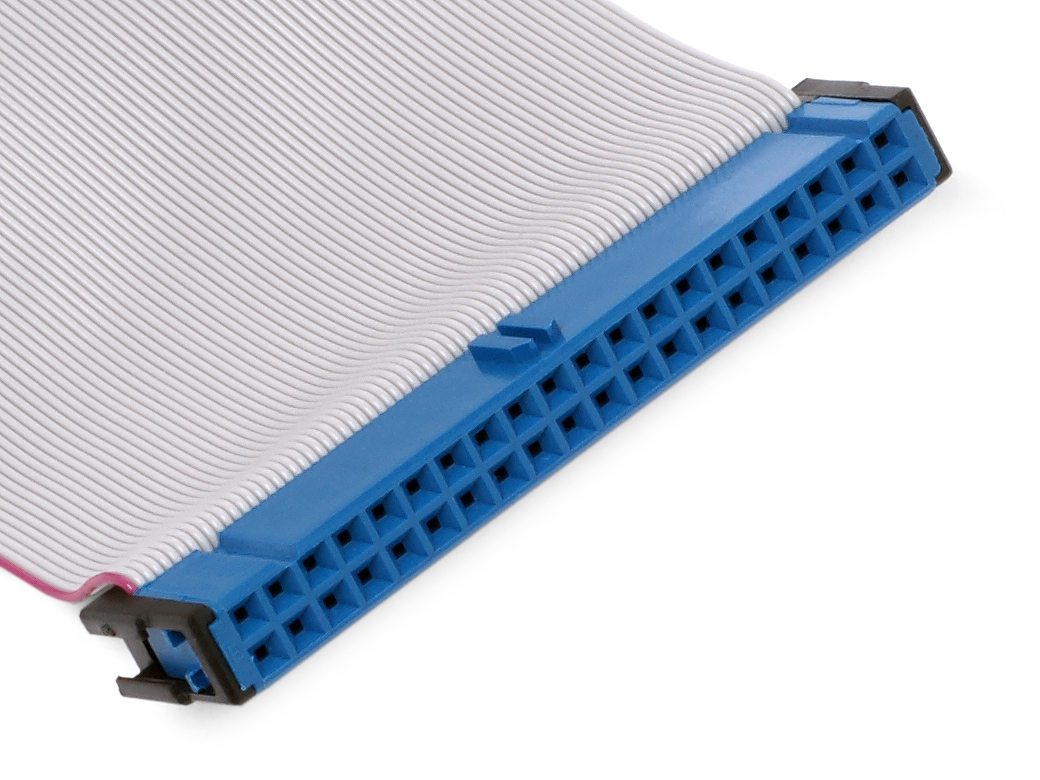
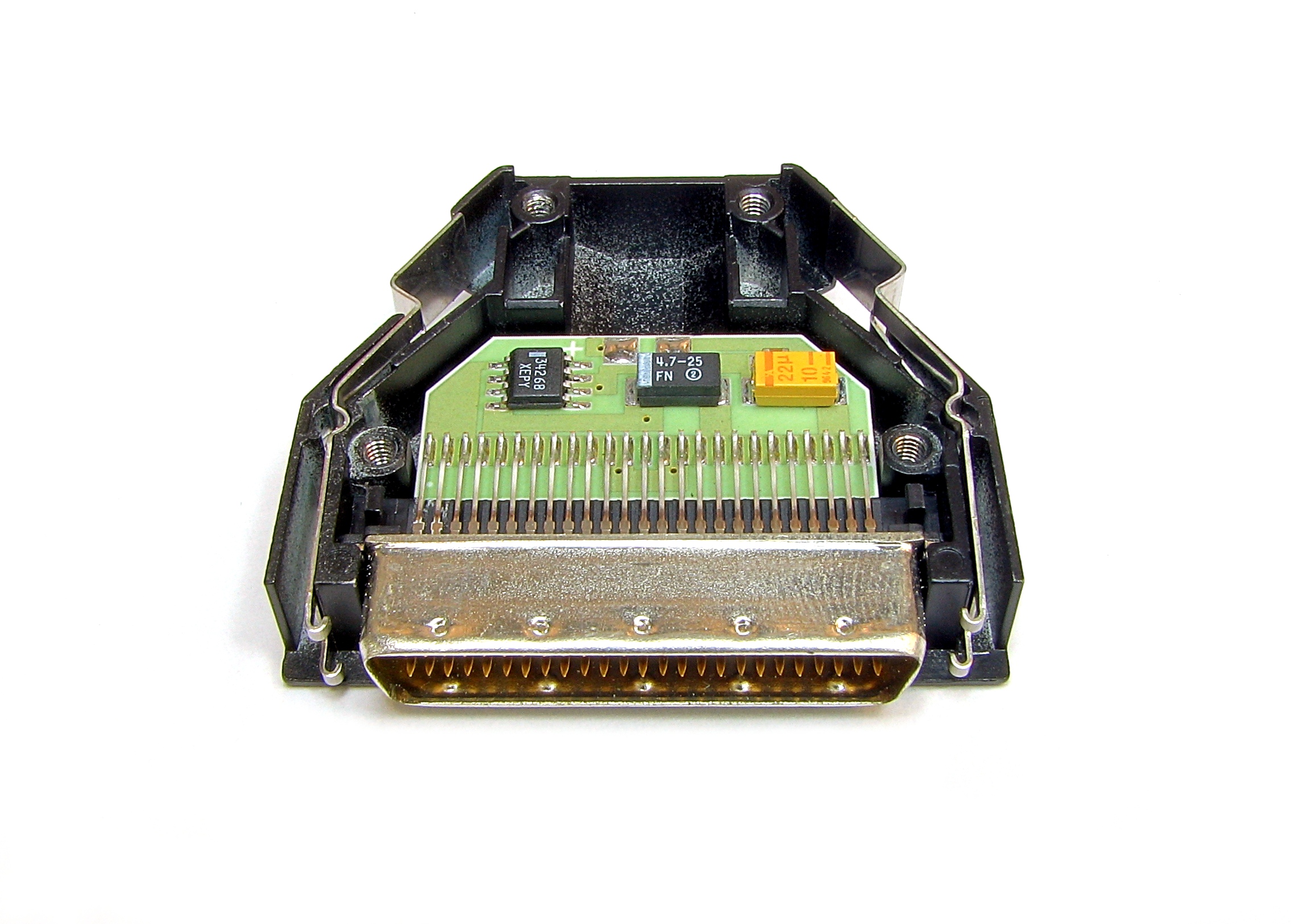
SCSI Request Sense Command
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scsi Logo
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers introduced by Commodore International, Commodore in 1985. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16- or 32-bit processors, 256 KB or more of RAM, mouse-based GUIs, and significantly improved graphics and audio compared to previous 8-bit systems. This includes the Atari ST—released earlier the same year—as well as the Macintosh and Acorn Archimedes. Based on the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, the Amiga differs from its contemporaries through the inclusion of custom hardware to accelerate graphics and sound, including sprite (computer graphics), sprites and a blitter, and a pre-emptive multitasking operating system called AmigaOS. The Amiga 1000 was released in July 1985, but production problems kept it from becoming widely available until early 1986. The best-selling model, the Amiga 500, was introduced in 1987 along with the more expandable Amiga 2000. The Amiga 3000 was introduced in 1990, followed by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAID
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to: Attack * Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground * Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business * Panty raid, a prankish raid by male college students on the living quarters of female students to steal panties as trophies * Police raid, a police action involving the entering of a house with the intent to capture personnel or evidence, often taking place early in the morning * Union raid, when an outsider trade union takes over the membership of an existing union Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Raid'' (1947 film), an East German film * ''Raid'' (2003 film), a 2003 Finnish film * ''Raid'' (2018 film), an Indian period crime thriller Gaming * Raid (gaming), a type of mission in a video game where a large number of people combine forces to defeat a powerful enemy * ''Raid'' (video game), a Nintendo Entertainment System title released by Sachen in 1989 * ''Raid over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atari Falcon
The Atari Falcon030 (usually shortened to Atari Falcon), released in 1992, was the final personal computer product from Atari Corporation. A high-end model of the Atari ST line, the machine is based on a Motorola 68030 CPU and a Motorola 56001 digital signal processor, a feature which distinguishes it from most other microcomputers of the era. It includes a new VIDEL programmable graphics system which greatly improves graphics capabilities. Shortly after release, Atari bundled the MultiTOS operating system in addition to TOS. TOS remained in ROM, and MultiTOS was supplied on floppy disk and could be installed to boot from hard disk. The Falcon was discontinued in late 1993–a year after its introduction–as Atari restructured itself to focus completely on the release and support of the Atari Jaguar video game console. The Falcon sold in relatively small numbers, mainly to hobbyists. Hardware The heart of the system is the 32-bit Motorola 68030 clocked at 16 MHz. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atari TT
The Atari TT030 is a member of the Atari ST family, released in 1990. It was originally intended to be a high-end Unix workstation, but Atari took two years to release a port of Unix SVR4 for the TT, which prevented the TT from ever being seriously considered in its intended market. In 1992, the TT was replaced by the Atari Falcon, a low-cost consumer-oriented machine with greatly improved graphics and sound capability, but with a slower and severely bottle-necked CPU. The Falcon possesses only a fraction of the TT's raw CPU performance. Though well priced for a workstation machine, the TT's high cost kept it mostly out of reach of the existing Atari ST market until after the TT was discontinued and sold at discount. The nascent open source movement eventually filled the void. Thanks to open hardware documentation, the Atari TT, along with the Amiga and Atari Falcon, were the first non-Intel machines to have Linux ported to them, though this work did not stabilize until after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atari MEGA STE
The Atari Mega STE is Atari Corporation's final personal computer in the Atari ST series. Released in 1991, the MEGA STE is a late-model Motorola 68000-based STE mounted in the case of an Atari TT computer. Description The MEGA STE is based on STE hardware. The 2 MB and 4 MB models shipped with a high resolution mono monitor, and an internal SCSI hard disk (the 1 MB model includes neither a monitor, hard disk, nor hard disk controller). While offering better ST compatibility than the TT, it also includes a number of TT features, from the ST-grey version of the TT case with separate keyboard and system unit, optional FPU, a VMEbus slot, two extra RS232 ports (all 9-pin rather than 25-pin as previous models had), a LocalTalk/RS-422 port (no AppleTalk software was ever produced) and a 1.44 MB HD floppy support. Support for a third/middle mouse button is also included. A unique feature of the MEGA STE in relation to previous Atari systems is the software-switchable CPU speed, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial ATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1394
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. Apple called the interface FireWire. It is also known by the brand names i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx ( Texas Instruments). The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber versions. The 1394 interface is comparable to USB. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices. History and development FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macintosh Quadra
The Macintosh Quadra is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from October 1991 to October 1995. The Quadra, named for the Motorola 68040 central processing unit, replaced the Macintosh II family as the high-end Macintosh model. The first models were the Quadra 700 and Quadra 900, both introduced in October 1991. The Quadra 800, 840AV and 605 were added through 1993. The Macintosh Centris line was merged with the Quadra in October 1993, adding the 610, 650 and 660AV to the range. After the introduction of the Power Macintosh line in early 1994, Apple continued to produce and sell new Quadra models; the 950 continued to be sold until October, 1995. The product manager for the Quadra family was Frank Casanova who was also the Product Manager for the Macintosh IIfx. Models The first computers bearing the Macintosh Quadra name were the Quadra 700 and Quadra 900, both introduced in 1991 with a central processing unit (CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel ATA
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as IDE, is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface (ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended IDE (EIDE) and Ultra ATA (UATA). After the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |