|
SB George Smeed
George Smeed is a Thames barge built in 1882 by Smeed Dean & Co. Ltd. in Murston. Name The barge is named after the Sittingbourne entrepreneur, George Smeed (1812–1881) who began business in 1846 in Murston. The building of Victorian London created a vast demand for bricks. The yellow Kent Stock Brick which was cheaper to make than the more traditional red brick; Sittingbourne had the brickearth needed to make them, and easy access to the Swale and the London River. By 1860 he owned expanding brickfields, shipyards along the creek and barges. The business traded as Smeed-Dean Co Ltd until 1926 when it was sold. Owners *1882 Built for Smeed Dean & Co. Ltd. *Passing to A.P.C.M. *1922 Rebuilt at 64 ton, *Francis & Gilders *Browns for lighterage. *1970s housebarge at Heybridge *1980 onwards Ken and Carol Greenhalgh for renovation *2017 Rebuilt and rerigged Based at Maldon owned by Carol Greenhalgh. Description She was built in 1881 egistered in 1882in Murston Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maldon, Essex
Maldon (, locally ) is a town and civil parish on the Blackwater estuary in Essex, England. It is the seat of the Maldon District and starting point of the Chelmer and Blackwater Navigation. It is known for Maldon Sea Salt which is produced in the area. History Early and medieval history The place-name ''Maldon'' is first attested in 913 in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', where it appears as ''Maeldun''. Maldon's name comes from ''mǣl'' meaning 'monument or cross' and ''dūn'' meaning 'hill', so translates as 'monument hill'. East Saxons settled the area in the 5th century and the area to the south is still known as the Dengie Peninsula after the Dæningas. It became a significant Saxon port with a hythe or quayside and artisan quarters. Evidence of imported pottery from this period has been found in archaeological digs. From 958 there was a royal mint issuing coins for the late Anglo-Saxon and early Norman kings. It was one of the only two towns in Essex (Colchester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the Bank (geography), south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is the administrative centre of the Gravesham, Borough of Gravesham. Its geographical situation has given Gravesend strategic importance throughout the maritime history, maritime and History of communication, communications history of South East England. A Thames Gateway commuter town, it retains strong links with the River Thames, not least through the Port of London Authority Pilot Station and has witnessed rejuvenation since the advent of High Speed 1 rail services via Gravesend railway station. The station was recently refurbished and now has a new bridge. Toponymy Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and Roman Catholic Diocese of Bayeux, Bishop of Bayeux, the half-broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nautical Terminology
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin ''nauticus'', from Greek ''nautikos'', from ''nautēs'': "sailor", from ''naus'': "ship". Further information on nautical terminology may also be found at Nautical metaphors in English, and additional military terms are listed in the Multiservice tactical brevity code article. Terms used in other fields associated with bodies of water can be found at Glossary of fishery terms, Glossary of underwater diving terminology, Glossary of rowing terms, and Glossary of meteorology. This glossary is split into two articles: * terms starting with the letters A to L are at Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) * terms starting with the letters M to Z are at Glossary of nautical terms (M-Z) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
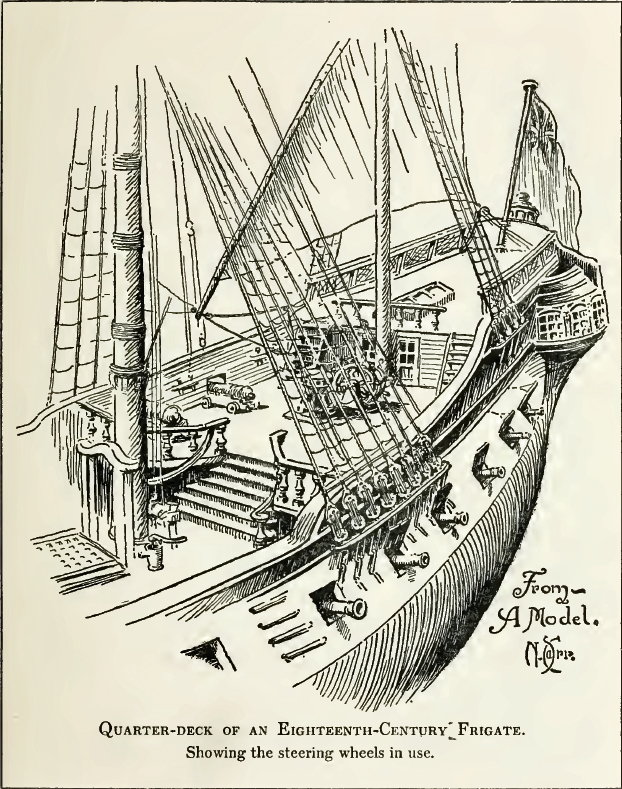
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swin (Thames)
The Swin is a passage in the Thames estuary between Maplin Sands, Foulness Sand and Gunfleet Sand northwest and the Barrow and Sunk sand ridges (shoals), southeast. The Swin was used by barges and leisure craft from the Essex rivers, and coasters and colliers from Hull, Great Grimsby, North East England, Edinburgh and other similar sets of trading ports. In 1874 R.M. Ballantyne wrote: The channel is formed of a series of deep water passages through sandbanks. Approaching from the northeast craft enter the East Swin between NE Gunfleet and Sunk Head Tower buoys. This part is also known as the King's Channel centred on . From here is a choice of the Middle Deep or continuing with the East Swin centred on . Craft may also pass down the parallel Wallet channel and cross into the East Swin at the Spitway. Halfway along this part, at the Maplin Approach buoy, deeper draught vessels need to pass through to the Middle Deep centred on . Shallower draught craft, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitaker Channel
Whitaker (also Whittaker) is a surname of English and Scottish origin, meaning the white acre, also spelled " Whittaker" and " Whitacre." Notable people with the surname include: People with the name * The Whitaker iron family - a family important in the iron and steel industry in 19th and 20th century America * A. J. Whitaker (''Ayana Jean Whitaker''; born 1992), American volleyball player * Alexander Whitaker (1585–1616), American religious leader * Amoret Whitaker, forensic entomologist * Anthony Whitaker (1944–2014), New Zealand herpetologist * Ayton Whitaker (1916–1999), British producer and director of radio, film and television * Arthur Luther Whitaker (1921–2007), American minister, professor, psychologist, and sociologist * Benjamin Whitaker (other) * Berry Whitaker (1890–1984), American football college coach * Billy Whitaker (1923–1995), English football defender * Brandon Whitaker (born 1985), Canadian football running back * Brian Whitaker, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeboard
A leeboard is a form of pivoting keel used by a sailboat largely and very often in lieu of a fixed keel. Typically mounted in pairs on each side of a hull, leeboards function much like a centreboard, allowing shallow-draft craft to ply waters fixed keel boats cannot. Only the leeward side leeboard is used at any time, as it submerges when the boat heels under the force of the wind. A disadvantage, where there is an inadequate fixed keel, is that they typically ship (bear) little ballast, which being on the far side delays the onset of unballasted craft's heeling, that is, to put up a good, constant resistance against the wind. The classical, archetypal definition of ballast is a low, central weight to optimise centre of mass, reduce turning moment and therefore resistance to the boat keeling over, however tends to be higher in self-righting vessels. Modern developments allow them to act as a speed-enhancing lifting foil. History Leeboards existed in China from at least the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradwell-on-Sea
Bradwell-on-Sea is a village and civil parish in Essex, England. The village is on the Dengie peninsula. It is located about north-northeast of Southminster and is east from the county town of Chelmsford. The village is in the District of Maldon in the parliamentary constituency of Maldon whose boundaries were last varied at the 2010 general election. It has a population of 863, a decline from 877 in the previous census. Retrieved 2009-12-17 History Bradwell-on-Sea was a |
East Mersea
East Mersea is a scattered village and civil parish on Mersea Island in the English county of Essex. It was historically referred to as ''Mersea'' in the Domesday book St Edmund's Church The Grade I listed parish Church of St Edmund King and Martyr dates from the 12th or 13th century with the nave and tower dating from the 14th and 15th century respectively. The oak and red-brick south porch is 19th century. Inside there is a 15th-century octagonal font and mid-17th century pulpit. The rector at East Mersey from 1871 to 1881 was the scholar Sabine Baring-Gould who wrote the words for the hymn ''Onward Christian Soldiers''. Grave of Sarah Wrench The grave of Sarah Wrench (1833–1848), by the North wall of the chancel at St. Edmund's Church in East Mersea is unusual for an English grave because it is covered by a mortsafe, a protective cage used at the time in Scotland to protect corpses from graverobbers. Richard Jones, in ''Myths of Britain and Ireland'', refers to popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alresford, Essex
Alresford ( or ) is a village and electoral ward in Essex, England. It is centred southeast of Colchester and is northeast from the county town of Chelmsford. The village and its civil parish are the district of Tendring. The local primary school is Alresford Primary School (~150 pupils, ages 4–11) and the village has a pre-school and church. Alresford won the Essex Village of the year competition in 2012 and tied for first place (in its class) for another Essex Village of the Year award in 2019. Population According to national census figures for April 2001, there were 2,125 inhabitants in 842 households, with an almost even gender balance. The percentage of the population above the age of 45 is higher than the national average. The population of the parish reduced to 2,009 at the 2011 Census. Geography The village, southeast of Colchester, lies above Alresford Creek, a tributary to the River Colne. The village's railway station usually sees one service per hour to Walt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainsail
A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast of a sailing vessel. * On a square rigged vessel, it is the lowest and largest sail on the main mast. * On a fore-and-aft rigged vessel, it is the sail rigged aft of the main mast. The sail's foot is normally attached to a boom. (In extremely heavy weather, the mainsail may be lowered, and a much smaller trysail hoisted in its place). Historical fore-and-aft rigs used a four-sided gaff rigged mainsail, sometimes setting a gaff topsail above it. Whereas once the mainsail was typically the largest sail, today the mainsail may be smaller than the jib or genoa; Prout catamarans typically have a mainmast stepped further aft than in a standard sloop, so that the mainsail is much smaller than the foresail. Bermuda rig The modern Bermuda rig uses a triangular mainsail aft of the mast, closely coordinated with a jib for sailing upwind. A large overlapping jib or genoa is often larger than the mainsail. In downwind conditions (with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wivenhoe
Wivenhoe ( ) is a town and civil parish in north-eastern Essex, England, approximately south-east of Colchester. Historically Wivenhoe village, on the banks of the River Colne, and Wivenhoe Cross, on the higher ground to the north, were two separate settlements; however, with considerable development in the 19th century, the two have since merged. At the 2011 census, the town had a population of 7,637, compared with 7,221 in 2001. The town's history centres on fishing, ship building and smuggling. Much of lower Wivenhoe is also a designated conservation area, with many streets being of particular architectural interest. Etymology The place-name ''Wivenhoe'' is Saxon in origin, deriving from the personal name ''Wifa's'' or ''Wife's'' spur or promontory (hoe). The place-name is now usually pronounced 'Wivvenho', but the Essex accent would traditionally have rendered it as 'Wivvenhoo'. According to folk etymology, the name derived from "Wyvernhoe", originating from the mythic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)