|
SB Buffer
SB buffer is a buffer solution used in agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. "SB" is a commercial trademark of Faster Better Media LLC for their sodium boric acid-based conductive medium (US Patent # 7811437), which is based on the publications of Brody and Kern. It is made up of sodium borate, usually 1–10 mM at pH 8.0. It has a lower conductivity, produces sharper bands, and can be run at higher speeds than can gels made from TBE buffer or TAE buffer (5–35 V/cm as compared to 5–10 V/cm). At a given voltage, heat will be generated and thus the gel will be heated. However, SB buffer has lower conductivity than TBE and TAE, and thus the gel temperature is much lower than with TBE or TAE buffers. Therefore, the voltage can be increased to speed up electrophoresis so that a gel run takes only a fraction of the usual time. Downstream applications, such as isolation of DNA from a gel slice or southern bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Solution
A buffer solution (more precisely, pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer) is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. In nature, there are many living systems that use buffering for pH regulation. For example, the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood, and bicarbonate also acts as a buffer in the ocean. Principles of buffering Buffer solutions resist pH change because of a chemical equilibrium between the weak acid HA and its conjugate base A−: When some strong acid is added to an equilibrium mixture of the weak acid and its conjugate base, hydrogen ions (H+) are added, and the equilibrium is shifted to the left, in accordance with Le Chatelier's principle. Because of this, the hydrogen io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a method of gel electrophoresis used in biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, and clinical chemistry to separate a mixed population of macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a matrix of agarose, one of the two main components of agar. The proteins may be separated by charge and/or size (isoelectric focusing agarose electrophoresis is essentially size independent), and the DNA and RNA fragments by length. Biomolecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the charged molecules through an agarose matrix, and the biomolecules are separated by size in the agarose gel matrix. Agarose gel is easy to cast, has relatively fewer charged groups, and is particularly suitable for separating DNA of size range most often encountered in laboratories, which accounts for the popularity of its use. The separated DNA may be viewed with stain, most commonly under UV light, and the DNA fragments can be extracted from the gel with relative ease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. The electrokinetic phenomenon of electrophoresis was observed for the first time in 1807 by Russian professors Peter Ivanovich Strakhov and Ferdinand Frederic Reuss at Moscow University, who noticed that the application of a constant electric field caused clay particles dispersed in water to migrate. It is ultimately caused by the presence of a charged interface between the particle surface and the surrounding fluid. It is the basis for analytical techniques used in chemistry for separating molecules by size, charge, or binding affinity. Electropho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded information is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
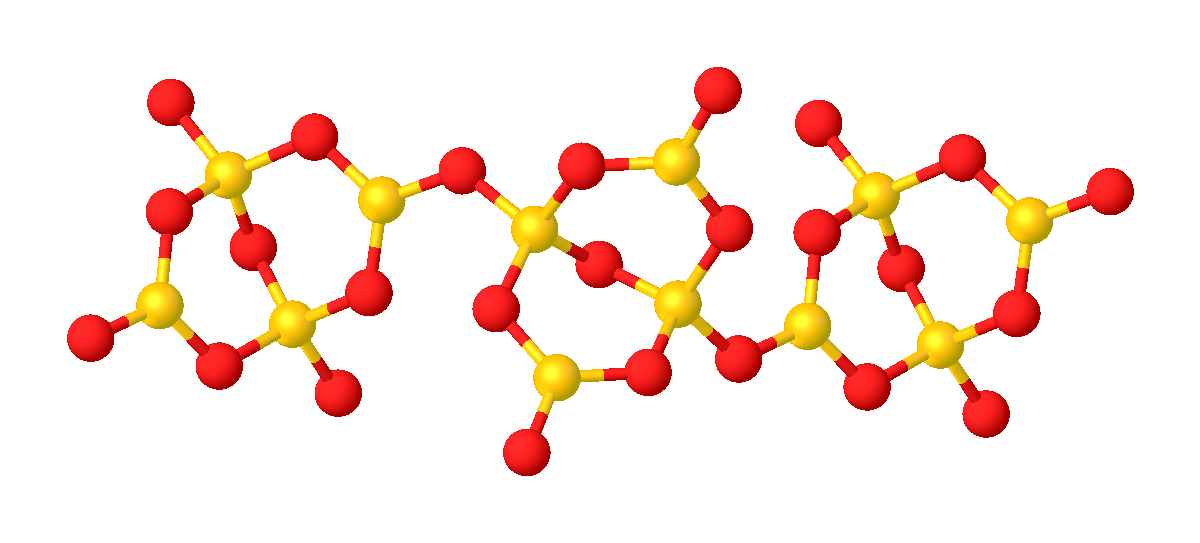
Sodium Borate
Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although the latter may not be a stable compound. Many sodium borates have important industrial and household applications; the best known being borax, = . The ternary phase diagram of the –– phase diagram in the 0–100 °C temperature range contains 13 unique hydrated crystalline sodium borates, including five important industrial products. Sodium borates, as well as boroxy acids, are often described as mixtures = , with ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' chosen to fit the elemental formula, or a multiple thereof. Thus, for example, borax would be , and boric acid would be = . The elemental formula was often intrepreted as a ''z''-hydrate of an "anhydrous" salt without any hydrogen, namely . However, later research uncovered that many borates have hydroxyl gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductivity (electrolytic)
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems. In many cases, conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids (TDS). High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0.05 μS/cm at 25 °C, typical drinking water is in the range of 200–800 μS/cm, while sea water is about 50 mS/cm ncorrect according to source(or 50,000 μS/cm). Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge. Dilute solutions follow Kohlrausch's Laws of concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TBE Buffer
TBE or Tris/Borate/EDTA, is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, boric acid and EDTA. In molecular biology, TBE and TAE buffers are often used in procedures involving nucleic acids, the most common being electrophoresis. Tris-acid solutions are effective buffers for slightly basic conditions, which keep DNA deprotonated and soluble in water. EDTA is a chelator of divalent cations, particularly of magnesium (Mg2+). As these ions are necessary co-factors for many enzymes, including contaminant nucleases, the role of the EDTA is to protect the nucleic acids against enzymatic degradation. But since Mg2+ is also a co-factor for many useful DNA-modifying enzymes such as restriction enzymes and DNA polymerases, its concentration in TBE or TAE buffers is generally kept low (typically at around 1 mM). More recently discovered substitutes for TBE and TAE buffers for electrophoresis are available. Recipe (1 liter of 5X stock solution) *54 g of Tris base (CAS# 77-86-1, free b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAE Buffer
TAE buffer is a buffer solution containing a mixture of Tris base, acetic acid and EDTA. In molecular biology it is used in agarose electrophoresis typically for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It is made up of Tris-acetate buffer, usually at pH 8.3, and EDTA, which sequesters divalent cations. TAE has a lower buffer capacity than TBE and can easily become exhausted, but linear, double stranded DNA runs faster in TAE. Previously, Brody & Kern simplified electrophoretic buffers by substituting TBE and TAE buffers for a more efficient and inexpensive conductive media in gel systems. Uses TAE (Tris-acetate-EDTA) buffer is used as both a running buffer and in agarose gels. Its use in denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis methods for broad-range mutation analysis has also been described. TAE has been used at various concentrations to study the mobility of DNA in solution with and without sodium chloride. However, high concentrations of sodium chloride (and man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Blot
A Southern blot is a method used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. Southern blotting combines transfer of electrophoresis-separated DNA fragments to a filter membrane and subsequent fragment detection by probe hybridization. The method is named after the British biologist Edwin Southern, who first published it in 1975. Other blotting methods (i.e., western blot, northern blot, eastern blot, southwestern blot) that employ similar principles, but using RNA or protein, have later been named in reference to Edwin Southern's name. As the label is eponymous, Southern is capitalised, as is conventional of proper nouns. The names for other blotting methods may follow this convention, by analogy. Method #Restriction endonucleases are used to cut high-molecular-weight DNA strands into smaller fragments. #The DNA fragments are then electrophoresed on an agarose gel to separate them by size. # If some of the DNA fragments are larger than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LB Buffer
LB buffer, also known as lithium borate buffer, is a buffer solution used in agarose electrophoresis, typically for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It is made up of Lithium borate (lithium hydroxide monohydrate and boric acid). LB(R) is a registered (USPTO) trademark of Faster Better Media LLC, which owns US patent 7,163,610 covering low-conductance lithium borate polynucleotide electrophoresis. Lithium Borate buffer has a lower conductivity, produces crisper resolution, and can be run at higher speeds than can gels made from TBE or TAE (5-50 V/cm as compared to 5-10 V/cm). At a given voltage, the heat generation and thus the gel temperature is much lower than with TBE/TAE buffers, therefore the voltage can be increased to speed up electrophoresis so that a gel run takes only a fraction of the usual time. Downstream applications, such as isolation of DNA from a gel slice or Southern blot analysis, work as expected with lithium boric acid gels. Brody, J.R. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Borate
Lithium borate, also known as lithium tetraborate is an inorganic compound with the formula Li2B4O7. A colorless solid, lithium borate is used in making glasses and ceramics. Structure Its structure consists of a polymeric borate backbone. The Li+ centers are bound to four and five oxygen ligands. Boron centers are trigonal and tetrahedral. Lithium borate can be used in the laboratory as LB buffer for gel electrophoresis of DNA and RNA. It is also used in the borax fusion method to vitrify mineral powder specimens for analysis by WDXRF spectroscopy.Ron Jenkins, ''X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry, Second Edition'', J. Wiley & Sons Inc., 1999, , p 146-7. See also *LB buffer LB buffer, also known as lithium borate buffer, is a buffer solution used in agarose electrophoresis, typically for the separation of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. It is made up of Lithium borate (lithium hydroxide monohydrate and boric acid ... * Lithium metaborate (LiBO2) References Borates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)