|
SATTB
SATB is an initialism that describes the scoring of compositions for choirs, and also choirs (or consorts) of instruments. The initials are for the voice types: S for soprano, A for alto, T for tenor and B for bass. Choral music Four-part harmony using soprano, alto, tenor and bass is a common scoring in classical music, including chorales and most Bach cantatas.Shrock, DennisChoral Repertoire''Oxford University Press'', 2009, p. 298, The letters of the abbreviation are also used by publishers to describe different scorings for soloists and choirs other than four-part harmony. For example, the listing "STB solos, SATB choir", of Bach's ''Wachet auf, ruft uns die Stimme'', BWV 140, indicates that a performance needs three soloists: soprano, tenor and bass, and a four-part choir. "SATB/SATB" is used when a double choir is required, as in Penderecki's ''Polish Requiem''. or SSATB, with divided sopranos, which is a typical scoring in English church music. A listing for Bach's ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bach Cantatas
This is a sortable list of Bach cantatas, the cantatas composed by Johann Sebastian Bach. His almost 200 extant cantatas are among his important Vocal music (Bach), vocal compositions. Many are known to be lost. Bach composed both Church cantata (Bach), church cantatas, most of them for specific occasions of the liturgical year of the Lutheran Church, and List of secular cantatas by Johann Sebastian Bach, secular cantatas. Bach's early cantatas, Bach's earliest cantatas were written possibly from 1707, the year he moved to Mühlhausen, although he may have begun composing them at his previous post in Arnstadt. He began regular composition of Weimar cantata (Bach), church cantatas in Weimar between 1708 and 1717, writing one cantata per month. In his next position in Köthen, he composed no church cantatas, but secular cantatas for the court. Most of Bach's church cantatas date from his first years as and director of church music in Leipzig, a position which he took up in 1723. Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acronym And Initialism
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as in ''Benelux'' (short for ''Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg''). They can also be a mixture, as in ''radar'' (''Radio Detection And Ranging''). Acronyms can be pronounced as words, like ''NASA'' and ''UNESCO''; as individual letters, like ''FBI'', ''TNT'', and ''ATM''; or as both letters and words, like ''JPEG'' (pronounced ') and ''IUPAC''. Some are not universally pronounced one way or the other and it depends on the speaker's preference or the context in which it is being used, such as '' SQL'' (either "sequel" or "ess-cue-el"). The broader sense of ''acronym''—the meaning of which includes terms pronounced as letters—is sometimes criticized, but it is the term's original meaning and is in common use. Dictionary and sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement (music)
A movement is a self-contained part of a musical composition or musical form. While individual or selected movements from a composition are sometimes performed separately as stand-alone pieces, a performance of the complete work requires all the movements to be performed in succession. A movement is a section Section, Sectioning or Sectioned may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Section (music), a complete, but not independent, musical idea * Section (typography), a subdivision, especially of a chapter, in books and documents ** Section sig ..., "a major structural unit perceived as the result of the coincidence of relatively large numbers of structural phenomena". Sources Formal sections in music analysis {{music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viola Da Gamba
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Frets on the viol are usually made of gut, tied on the fingerboard around the instrument's neck, to enable the performer to stop the strings more cleanly. Frets improve consistency of intonation and lend the stopped notes a tone that better matches the open strings. Viols first appeared in Spain in the mid-to-late 15th century, and were most popular in the Renaissance and Baroque (1600–1750) periods. Early ancestors include the Arabic ''rebab'' and the medieval European vielle,Otterstedt, Annette. ''The Viol: History of an Instrument. ''Kassel: Barenreiter;-Verlag Karl Votterle GmbH & Co; 2002. but later, more direct possible ancestors include the Venetian ''viole'' and the 15th- and 16th-century Spanish ''vihuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recorder (musical Instrument)
The recorder is a family of woodwind musical instruments in the group known as ''internal duct flutes'': flutes with a whistle mouthpiece, also known as fipple flutes. A recorder can be distinguished from other duct flutes by the presence of a thumb-hole for the upper hand and seven finger-holes: three for the upper hand and four for the lower. It is the most prominent duct flute in the western classical tradition. Recorders are made in various sizes with names and compasses roughly corresponding to various vocal ranges. The sizes most commonly in use today are the soprano (also known as descant, lowest note C5), alto (also known as treble, lowest note F4), tenor (lowest note C4), and bass (lowest note F3). Recorders were traditionally constructed from wood or ivory. Modern professional instruments are almost invariably of wood, often boxwood; student and scholastic recorders are commonly of molded plastic. The recorders' internal and external proportions vary, but the bore i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Leading
Voice leading (or part writing) is the linear progression of individual melodic lines ( voices or parts) and their interaction with one another to create harmonies, typically in accordance with the principles of common-practice harmony and counterpoint. Rigorous concern for voice leading is of greatest importance in common-practice music, although jazz and pop music also demonstrate attention to voice leading to varying degrees. In ''Jazz Theory'', Gabriel Sakuma writes that " the surface level, jazz voice-leading conventions seem more relaxed than they are in common-practice music."Terefenko, Dariusz (2014). ''Jazz Theory: From Basic to Advanced Study'', p. 33. Routledge. . Marc Schonbrun also states that while it is untrue that "popular music has no voice leading in it, ..the largest amount of popular music is simply conceived with chords as blocks of information, and melodies are layered on top of the chords."Schonbrun, Marc (2011). ''The Everything Music Theory Book'', pp. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music," the use of which is "common in most musical systems." The interval between the first and second harmonics of the harmonic series is an octave. In Western music notation, notes separated by an octave (or multiple octaves) have the same name and are of the same pitch class. To emphasize that it is one of the perfect intervals (including unison, perfect fourth, and perfect fifth), the octave is designated P8. Other interval qualities are also possible, though rare. The octave above or below an indicated note is sometimes abbreviated ''8a'' or ''8va'' ( it, all'ottava), ''8va bassa'' ( it, all'ottava bassa, sometimes also ''8vb''), or simply ''8'' for the octave in the direction indicated by placing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
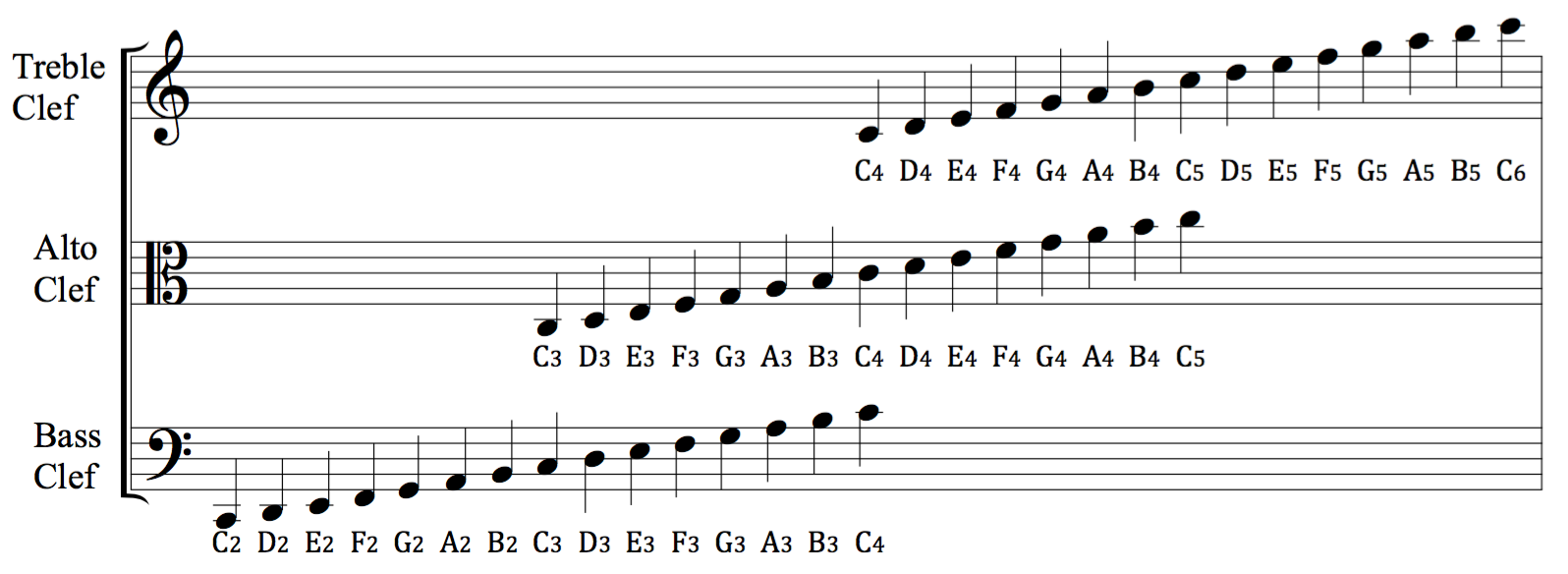
Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a Musical notation, musical symbol used to indicate which Musical note, notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff (music), stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the #G-clefs, G-clef, #F-clefs, F-clef, and #C-clefs, C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing Scientific pitch notation, G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem (music)
In musical notation, stems are the, "thin, vertical lines that are directly connected to the otehead." Stems may point up or down. Different-pointing stems indicate the voice for polyphonic music written on the same staff. Within one voice, the stems usually point down for notes on the middle line or higher, and up for those below. If the stem points up from a notehead, the stem originates from the right-hand side of the note, but if it points down, it originates from the left. If there are multiple notes beamed together, the stem's direction is defined by the average of the lowest and highest notes in the beam. There is an exception to this rule: if a chord contains a second, the stem runs between the two notes with the higher being placed on the right of the stem and the lower on the left. If the chord contains an odd numbered cluster of notes a second apart (such as C, D, E), the outer two will be on the correct side of the stem, while the middle note will be on the wrong s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff (music)
In Western culture, Western musical notation, the staff (US and UK)"staff" in the Collins English Dictionary "in British English: also called: stave; plural: staffs or staves""staff" in the Merriam-Webster Dictionary /ref> or stave (UK) (#Usage and etymology, plural: staffs or staves) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divisi
In musical terminology, ''divisi'', or as typically printed ''“div.,”'' is an instruction to divide a single section of instruments into multiple subsections. This usually applies to the violins of the string section in an orchestra, although violas, cellos, and double basses can also be divided. Typically, 4-part French Horn sections include divided sections if Horns 1/2 and/or 3/4 are not playing the same music (" a2"). Other brass instruments can also be divided but it is not as frequent as with the Horn section. Woodwinds - especially Flutes and Clarinets - also utilize "divisi" to divide music between parts and even between players of the same part. After a divisi section, it may be cancelled by the instructions ''tutti'', ''all'unisono''.{{Cite Grove , first=David , last=Fallows , date=2001 , title=Divisi (It.: 'divided') , url=https://doi.org/10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.07869 or ''unison'' (abbreviated ''unis.''). The German equivalents for ''divisi'' and ''tutti'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countertenor
A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6.A sopranist is a term used to describe a countertenor whose vocal range is so high it is equivalent to that of a soprano; however, this term is widely used falsely. Countertenors often are baritones or tenors at core, but only on rare occasions do they use their lower vocal range, instead preferring their falsetto or high head voice. The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice which is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. The term first came into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |