|
SAT1 (gene)
Diamine acetyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SAT1'' gene found on the X chromosome. Function Spermidine/spermine N(1)-acetyltransferase (SPD/SPM acetyltransferase) is a rate-limiting enzyme in the catabolic pathway of polyamine metabolism. It catalyzes the N(1)-acetylation of spermidine and spermine and, by the successive activity of polyamine oxidase, spermine can be converted to spermidine and spermidine to putrescine. The ''SAT1'' gene is used to help regulate polyamine levels inside the cell by regulating their transport in and out of the cell. ''SAT1'' is also involved in the first step to synthesize N-acetylputrescine from putrescine. PMF1 and NRF2 work together to transcript the ''SAT1'' gene. Structure The ''SAT1'' gene is 3,069 base pairs long. There are 171 amino acids and its molecular mass is 20024 Da (daltons). In 1992 at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Lei Xiao and several others cloned over 4000 base pairs of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of ''Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen. Function Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its formation from putrescine. It is a precursor to other polyamines, such as spermine and its structural isomer thermospermine. Spermidine synchronizes an array of biological processes, (such as Ca2+, Na+, K+ -ATPase) thus maintaining membrane potential and controlling intracellular pH and volume. Spermidine regulates biological processes, such as Ca2+ influx by glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor), which has been associated with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cGMP/PKG pathway activation and a decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex synaptosomes. Spermidine is a longevity agent in mammals due to various mechanisms of action, which are just beginning to be understood. Autophagy is the main m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermine
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some Bacterium, bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described crystals of spermine phosphate in human semen in 1678. The name ''spermin'' was first used by the German chemists Albert Ladenburg, Ladenburg and Abel in 1888, and the correct structure of spermine was not finally established until 1926, simultaneously in England (by Dudley, Rosenheim, and Starling) and Germany (by Wrede et al.). Spermine is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen. Derivative A derivative (chemistry), derivative of spermine, N1, N12-bis(ethyl)spermine (also known as BESm) was investig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
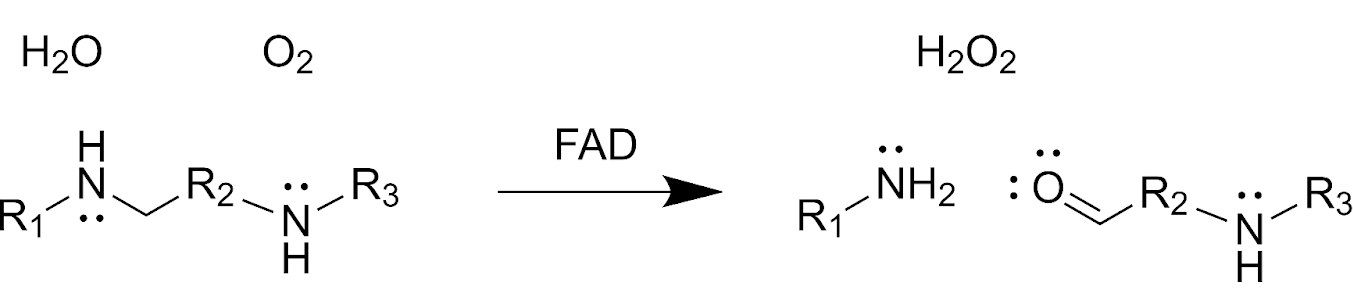
Polyamine Oxidase
A polyamine oxidase (PAO) is an enzymatic flavoprotein that oxidizes a carbon-nitrogen bond in a secondary amino group of a polyamine donor, using molecular oxygen as an acceptor. The generalized PAO reaction converts three substrates (water, oxygen, and a polyamine with both primary and secondary amino groups) into three products (hydrogen peroxide, an amino-aldehyde, and a primary amine). Different PAOs with varying substrate specificities exist in different organisms. Phylogenetic analyses suggest that PAOs likely evolved once in eukaryotes and diversified by divergent evolution and gene duplication events, though some prokaryotes have acquired PAOs through horizontal gene transfer. Structure and Mechanism Structures of PAOs from corn, brewer’s yeast, and mice contain a substrate-binding domain and an FAD-binding domain that secures the FAD cofactor non-covalently. The active site is located at the interface of these domains. Active sites in PAOs vary, but some feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contributes to other unpleasant odors. Production Putrescine is produced on an industrial scale by the hydrogenation of succinonitrile. Biotechnological production of putrescine from renewable feedstock has been investigated. A metabolically engineered strain of ''Escherichia coli'' that produces putrescine at high concentrations in glucose mineral salts medium has been described. Biochemistry Spermidine synthase uses putrescine and ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine (decarboxylated ''S''-adenosyl methionine) to produce spermidine. Spermidine in turn is combined with another ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine and gets converted to spermine. Putrescine is synthesized in small quantities by healthy living cells by the action of ornithine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratosis Follicularis Spinulosa Decalvans
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans is a rare X-linked disorder described by Siemens in 1926. It is a disease that begins in infancy with keratosis pilaris localized on the face, then evolves to more diffuse involvement.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. .Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . An association with SAT1 has been suggested. See also * Keratosis follicularis * Hermann Werner Siemens * Cicatricial alopecia Scarring hair loss, also known as cicatricial alopecia, is the loss of hair which is accompanied with scarring. This is in contrast to non scarring hair loss. It can be caused by a diverse group of rare disorders that destroy the hair follicle, ... * List of cutaneous conditions References External links Genodermatoses {{Genodermatoses-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and substance abuse (including alcoholism and the use of and withdrawal from benzodiazepines) are risk factors. Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; and improving economic conditions. Although crisis hotlines are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. The most commonly adopted metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neu–Laxova Syndrome
Neu–Laxova syndrome (NLS, also known as Neu syndrome; Neu-Povysilová syndrome; or 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency, neonate form) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe intrauterine growth restriction and multiple congenital malformations. Neu–Laxova syndrome is a very severe disorder, leading to stillbirth or death shortly after birth. It was first described by Dr. Richard Neu in 1971 and Dr. Renata Laxova in 1972 as a lethal disorder in siblings with multiple malformations. Neu–Laxova syndrome is an extremely rare disorder with less than 100 cases reported in medical literature. Signs and symptoms Neu-Laxova syndrome presents with severe malformations leading to prenatal or neonatal death. Typically, NLS involves characteristic facial features, decreased fetal movements and skin abnormalities. Fetuses or newborns with Neu–Laxova syndrome have typical facial characteristics which include proptosis (bulging eyes) with eyelid malformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcephaly
Microcephaly (from New Latin ''microcephalia'', from Ancient Greek μικρός ''mikrós'' "small" and κεφαλή ''kephalé'' "head") is a medical condition involving a smaller-than-normal head. Microcephaly may be present at birth or it may develop in the first few years of life. Since brain growth is correlated with head growth, people with this disorder often have an intellectual disability, poor motor function, poor speech, abnormal facial features, seizures and dwarfism. The disorder is caused by a disruption to the genetic processes that form the brain early in pregnancy, though the cause is not identified in most cases. Many genetic syndromes can result in microcephaly, including chromosomal and single-gene conditions, though almost always in combination with other symptoms. Mutations that result solely in microcephaly (primary microcephaly) exist but are less common. External toxins to the embryo, such as alcohol during pregnancy or vertically transmitted infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
