|
SAKO (programming Language)
SAKO ( PL: ''System Automatycznego Kodowania Operacji'' - EN: Automatic Operation Encoding System) is a Polish language-based programming language written for the computers XYZ, ZAM-2, ZAM-21 and ZAM-41. Hello world K) PROGRAM DRUKUJE NAPIS HELLO WORLD LINIA TEKST: HELLO WORLD KONIEC References * Prace Zakładu Aparatów Matematycznych PAN, "System Automatycznego Kodowania SAKO – opis języka", PAN – Warszawa 1961, * Leon Łukaszewicz, Antoni Mazurkiewicz "System automatycznego kodowania SAKO" Zakład Narodowy im. Ossolińskich, Polish Academy of Sciences Publishing House, Wrocław-Warszawa-Kraków 1966 r. * {{Authority control Non-English-based programming languages Science and technology in Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
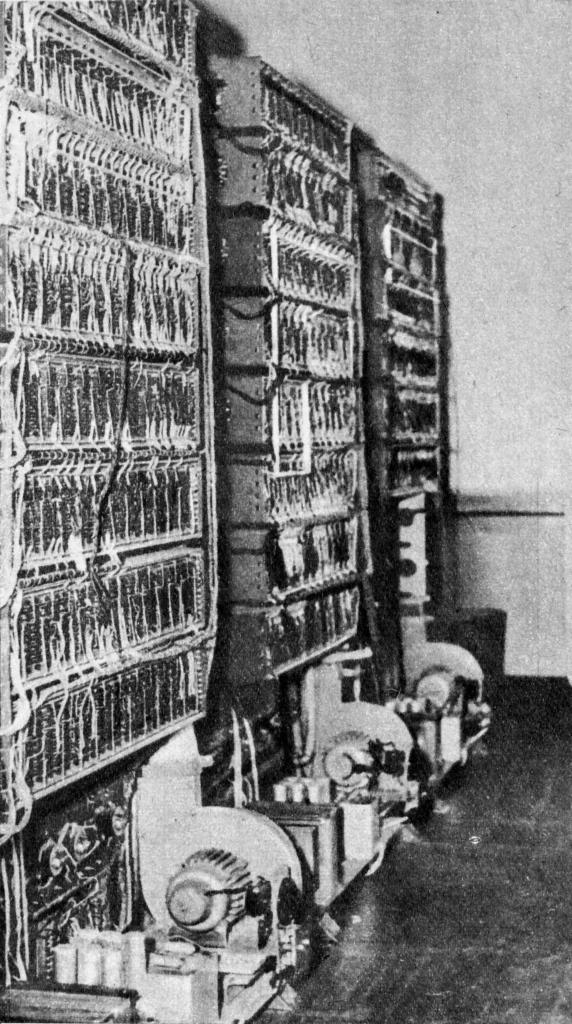
XYZ (computer)
XYZ was the first UMC (computer), Universal Digital Machine from the family of early computers built and launched in Poland in 1958. It was ahead of by a few months, while the earlier was not fully launched.Konstrukcje polskie: XYZ, Empacher A.B.Maszyny liczą same?/ Adam B. Empacher / Katalog HINT, Wiedza Powszechna, 1960, s. 114-122 (in Polish) Construction XYZ computer was built and launched in Warsaw at ul. Śniadeckich 8, at the premises of the Bureau of Calculations and Programs of the Mathematical Apparatus Department of the Polish Academy of Sciences (later the Institute of Mathematical Machines). The team was led by professor . XYZ was a laboratory model of a utility machine; the series was created on the basis of this computer. The logical organization was modeled on the simplified IBM 701, but the electronics were based on the Flip-flop (electronics), dynamic flip-flops of the M-20 machine, requiring twice as few lamps. The design of the flip-flops and gates was der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakład Narodowy Im
''The Bet'' ( pl, Zakład) is a 1990 Polish drama film directed by Teresa Kotlarczyk. It was entered into the 17th Moscow International Film Festival. Cast * Jan Peszek as Director Wygon * Grażyna Trela as Reporter Magda * Pawel Królikowski as Tomek Koziel * Krzysztof Kolberger as Group Tutor Marek * Bartłomiej Topa as Andrzej Matlak * Włodzimierz Musiał as Group Tutor Musial * Mariusz Bonaszewski as Swir * Robert Gonera as Mariusz * Pawel Niczewski as Gigant * Jaroslaw Gruda as Warchol * Ryszard Kotys Ryszard Kotys (20 March 1932 – 27 January 2021) was a Polish actor. He appeared in more than 140 films and television shows during his career. Filmography Film Television References External links * 1932 births 2021 deaths Polis ... as Guard References External links * 1990 films 1990 drama films Polish drama films 1990s Polish-language films {{1990s-drama-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Academy Of Sciences Publishing House
The Polish Academy of Sciences ( pl, Polska Akademia Nauk, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society of distinguished scholars and a network of research institutes. It was established in 1951, during the early period of the Polish People's Republic following World War II. History The Polish Academy of Sciences is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning, headquartered in Warsaw, that was established by the merger of earlier science societies, including the Polish Academy of Learning (''Polska Akademia Umiejętności'', abbreviated ''PAU''), with its seat in Kraków, and the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (Science), which had been founded in the late 18th century. The Polish Academy of Sciences functions as a learned society acting through an elected assembly of leading scholars and research institutions. The Academy h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-English-based Programming Languages
Non-English-based programming languages are programming languages that do not use keywords taken from or inspired by English vocabulary. Prevalence of English-based programming languages The use of the English language in the inspiration for the choice of elements, in particular for keywords in computer programming languages and code libraries, represents a significant trend in the history of language design. According to the HOPL online database of languages, out of the 8,500+ programming languages recorded, roughly 2,400 of them were developed in the United States, 600 in the United Kingdom, 160 in Canada, and 75 in Australia. Thus, over a third of all programming languages have been developed in countries where English is the primary language. This does not take into account the usage share of each programming language, situations where a language was developed in a non-English-speaking country but used English to appeal to an international audience (see the case of Python ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |