|
S2G Reactor
The S2G reactor was a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships, and the only liquid metal cooled reactor yet deployed by the US Navy. The S2G designation stands for: * S = Submarine platform * 2 = Second generation core designed by the contractor * G = General Electric was the contracted designer History An S2G was the initial power plant of USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575). This was one of three sodium cooled reactors (the core was moderated) ordered for the ''Seawolf'' program at the same time as three PWR units were ordered to support the USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571) program; In each case, one reactor was land-based for training and research, one intended for installation on a submarine, and one spare. The land-based unit corresponding to S2G was S1G reactor. Persistent superheater problems on ''Seawolf'' caused the superheaters to be bypassed, resulting in mediocre performance. This and concern for the dangers posed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seawolf SSN-575 With Essex
Seawolf, Sea wolf or Sea Wolves may refer to: Animals * Vancouver Coastal Sea wolf, Sea wolf, a wolf subspecies found in the Vancouver coastal islands * Seawolf (fish), a marine fish also known as wolffish or sea wolf * A nickname of the Orca, killer whale * South American sea lion, locally called ''lobo marino'' (sea wolf) Arts and entertainment * ''The Sea-Wolf'', a 1904 novel by Jack London * Seawolf (Wines), an organic winery in Yorkville Highlands, Mendocino * U.S.S. Seawolf (novel), ''U.S.S. Seawolf'' (novel), a 2000 novel by Patrick Robinson * Sea Wolf (comics), a supervillain in the DC Comics * Sea Wolf (band), a band led by Alex Brown Church, an indie folk musician Films and television * The Sea Wolf (1913 film), ''The Sea Wolf'' (1913 film), a lost silent film directed by Hobart Bosworth * The Sea Wolf (1920 film), ''The Sea Wolf'' (1920 film), directed by George Melford * The Sea Wolves (1925 film), ''The Sea Wolves'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
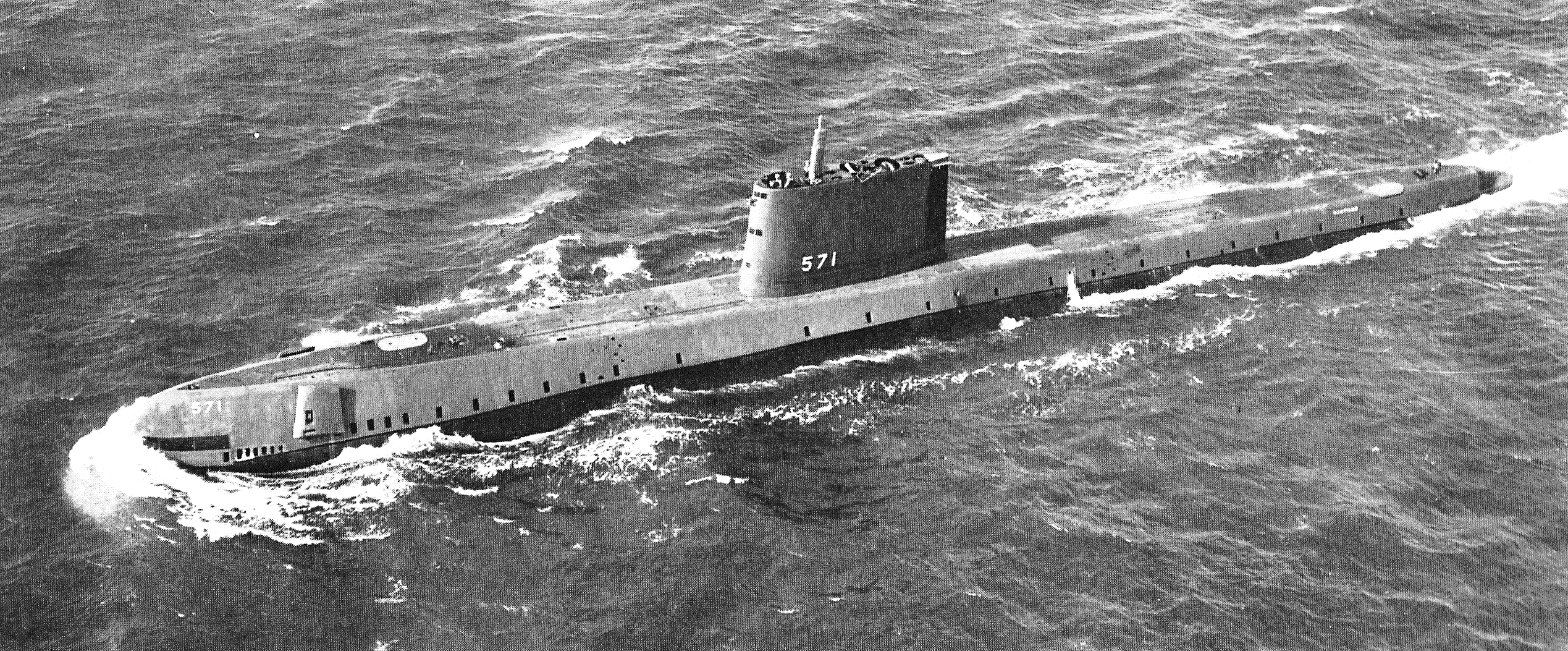
USS Seawolf (SSN-575)
USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575) was the third ship of the United States Navy to be named for the seawolf, the second nuclear submarine, and the only US submarine built with a liquid metal cooled (sodium) nuclear reactor known as the Submarine Intermediate Reactor (SIR) or Liquid Metal Fast Reactor ( LMFR), later designated S2G. Her overall design (known as SCB 64A) was a variant of , but with numerous detail changes, such as a conning tower, stepped sail, and the BQR-4 passive sonar mounted in the top portion of the bow instead of further below. This sonar arrangement resulted in an unusual bow shape above the water for a U.S. submarine. Her distinctive reactor was later replaced with a standard pressurized water reactor, the replacement process lasting from 12 December 1958 to 30 September 1960. Comparison to ''Nautilus'' ''Seawolf'' was the same basic "double hull" twin-screw submarine design as her predecessor , but her propulsion system was more technologically advanced. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S. Truman signed the McMahon/Atomic Energy Act on August 1, 1946, transferring the control of atomic energy from military to civilian hands, effective on January 1, 1947. This shift gave the members of the AEC complete control of the plants, laboratories, equipment, and personnel assembled during the war to produce the atomic bomb. An increasing number of critics during the 1960s charged that the AEC's regulations were insufficiently rigorous in several important areas, including radiation protection standards, nuclear reactor safety, plant siting, and environmental protection. By 1974, the AEC's regulatory programs had come under such strong attack that the U.S. Congress decided to abolish the AEC. The AEC was abolished by the Ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S2Wa Reactor
The S2W reactor was a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The S2W designation stands for: * S = Submarine platform * 2 = Second generation core designed by the contractor * W = Westinghouse was the contracted designer History This nuclear reactor is the shipboard equivalent of the prototype S1W reactor, with minor design changes, that was installed on . As installed in ''Nautilus'' it generated . It was originally designated STR. USS ''Nautilus'' ''Nautilus'' was powered by the Submarine Thermal Reactor (STR), later redesignated the S2W reactor, a pressurized water reactor produced for the US Navy by Westinghouse Electric Corporation. Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory, operated by Westinghouse, developed the basic reactor plant design used in ''Nautilus'' after being given the assignment on 31 December 1947 to design a nuclear power plant for a submarine. After ''Nautilus'' was decommissioned, the rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S1G Reactor
The S1G reactor is a naval reactor used by the United States Navy to provide electricity generation and propulsion on warships. The S1G designation stands for: * S = Submarine platform * 1 = First generation core designed by the contractor * G = General Electric was the contracted designer History This nuclear reactor was constructed by General Electric as a prototype for the USS ''Seawolf'' (SSN-575) submarine. It was a liquid metal cooled reactor using pure sodium to cool the core instead of water, because the higher temperature of liquid sodium (compared to pressurized water) enabled the production of more superheated steam in the steam generators. This resulted in a more efficient thermal cycle, yielding more shaft horsepower for a given reactor size. The reactor design had problems because of limited operating temperature constraints. The major disadvantage of this concept was the ignition of sodium when exposed to air. S1G was used for testing and training. Eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Nautilus (SSN-571)
USS ''Nautilus'' (SSN-571) was the world's first operational nuclear-powered submarine and the first submarine to complete a submerged transit of the North Pole on 3 August 1958. Her initial commanding officer was Eugene "Dennis" Wilkinson, a widely respected naval officer who set the stage for many of the protocols of today's Nuclear Navy of the US, and who had a storied career during military service and afterwards. Sharing a name with Captain Nemo's fictional submarine in Jules Verne's classic 1870 science fiction novel ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea'' and the that served with distinction in World War II, the new nuclear-powered ''Nautilus'' was authorized in 1951. Construction began in 1952, and the boat was launched in January 1954, sponsored by Mamie Eisenhower, First Lady of the United States, wife of 34th President Dwight D. Eisenhower; it was commissioned the following September into the United States Navy. ''Nautilus'' was delivered to the Navy in 1955. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Cooled Reactor
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Reactor
United States naval reactors are nuclear reactors used by the United States Navy aboard certain ships to generate the steam used to produce Power (physics), power for Marine nuclear propulsion, propulsion, electric power, catapulting airplanes in aircraft carriers, and a few more minor uses. Such naval nuclear reactors have a complete power plant associated with them. All U.S. Navy submarines and supercarriers built since 1975 are Nuclear power, nuclear-powered by such reactors. There are no commissioned conventional (non-nuclear) submarines or aircraft carriers left in the U.S. Navy, since the last conventional carrier, , was decommissioned in May 2009. The U.S. Navy had nine nuclear-powered cruisers with such reactors also, but they have since been decommissioned. Reactors are designed by a variety of contractors, then developed and tested at one of several government (United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy) owned and prime contractor-operated facilities: Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reactor Core
A nuclear reactor core is the portion of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel components where the nuclear reactions take place and the heat is generated. Typically, the fuel will be low-enriched uranium contained in thousands of individual fuel pins. The core also contains structural components, the means to both moderate the neutrons and control the reaction, and the means to transfer the heat from the fuel to where it is required, outside the core. Water-moderated reactors Inside the core of a typical pressurized water reactor or boiling water reactor are fuel rods with a diameter of a large gel-type ink pen, each about 4 m long, which are grouped by the hundreds in bundles called "fuel assemblies". Inside each fuel rod, pellets of uranium, or more commonly uranium oxide, are stacked end to end. Also inside the core are control rods, filled with pellets of substances like boron or hafnium or cadmium that readily capture neutrons. When the control rods are lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


_Groton_CT_2002_May_08.jpg)


