|
S-200 (fertilizer)
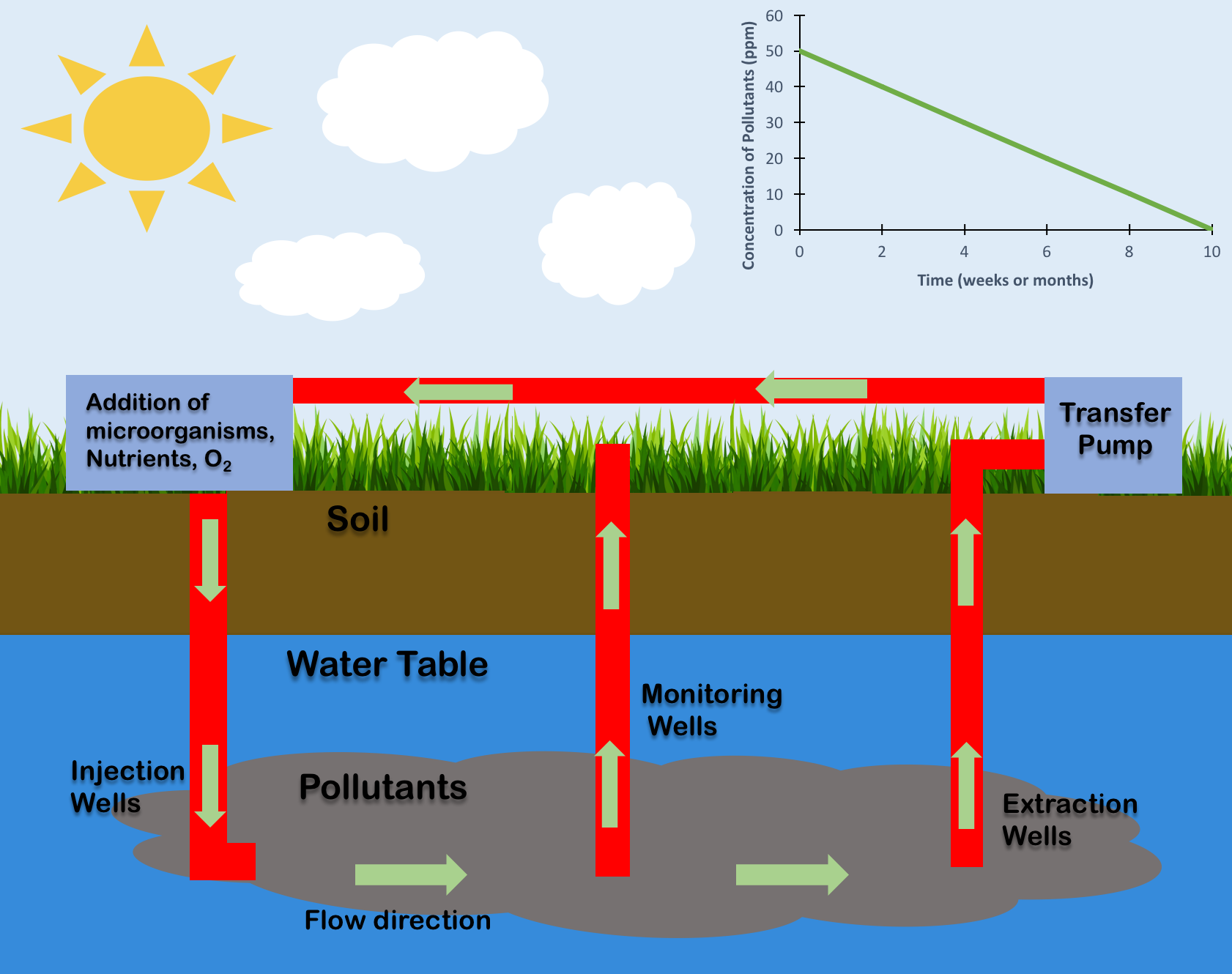
S-200 is a bioremediation product used to clean up oil spills. It is an oleophilic nitrogen-phosphorus nutrient that promotes the growth of micro-organisms that degrade hydrocarbons (such as oil and fuel). S-200 bonds to the hydrocarbon to eliminate the need to reapply in tidal or rain events. S-200 is identified as a bioremediation accelerator and as such, does not contain bacterial cultures, but rather contributes to the establishment of a robust microbial population. In the laboratory, considerable biodegradation to alkanes was seen over the course of treatment. Field trials have yielded inconsistent results. The product was developed by International Environmental Products, a US company based around S-200 as its product. Field tests After laboratory and field trials, S-200 was the only bioremediation process selected by the Spanish Department of National Parks for the final cleanup of the Galician coastline following the Prestige oil tanker spill. The effects of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into the ocean or coastal waters, but spills may also occur on land. Oil spills may be due to releases of crude oil from tankers, offshore platforms, drilling rigs and wells, as well as spills of refined petroleum products (such as gasoline, diesel) and their by-products, heavier fuels used by large ships such as bunker fuel, or the spill of any oily refuse or waste oil. Oil spills penetrate into the structure of the plumage of birds and the fur of mammals, reducing its insulating ability, and making them more vulnerable to temperature fluctuations and much less buoyant in the water. Cleanup and recovery from an oil spill is difficult and depends upon many factors, including the type of oil spilled, the temperature of the water (affecting evapor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or exemplified by the odors of gasoline and lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to the naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, and to their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are carbon di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicia (Spain)
Galicia (; gl, Galicia or ; es, Galicia}; pt, Galiza) is an autonomous community of Spain and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the northwest Iberian Peninsula, it includes the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense, and Pontevedra. Galicia is located in Atlantic Europe. It is bordered by Portugal to the south, the Spanish autonomous communities of Castile and León and Asturias to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Cantabrian Sea to the north. It had a population of 2,701,743 in 2018 and a total area of . Galicia has over of coastline, including its offshore islands and islets, among them Cíes Islands, Ons, Sálvora, Cortegada Island, which together form the Atlantic Islands of Galicia National Park, and the largest and most populated, A Illa de Arousa. The area now called Galicia was first inhabited by humans during the Middle Paleolithic period, and takes its name from the Gallaeci, the Celtic people living north of the Douro Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestige Oil Tanker Spill
The ''Prestige'' oil spill occurred off the coast of Galicia, Spain in November 2002, caused by the sinking of the 26-year-old, structurally deficient oil tanker , carrying 77,000 tonnes of heavy fuel oil. During a storm, it burst a tank on 13 November, and French, Spanish, and Portuguese governments refused to allow the ship to dock. The vessel subsequently sank on 19 November, about from the coast of Galicia. It is estimated that it spilled 60,000 tonnes or a volume of of heavy fuel oil. The oil spill polluted 2300 kilometers of coastline and more than one thousand beaches on the Spanish, French and Portuguese coast, as well as causing great harm to the local fishing industry. The spill is the largest environmental disaster in the history of both Spain and Portugal. The amount of oil spilled was more than the ''Exxon Valdez'' incident and the toxicity was considered higher, because of the higher water temperatures. In 2007 the Southern District of New York dismissed a 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism (also often described as keto–enol tautomerism). Although the lactim form is expected to possess some degree of aromaticity, uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecithin
Lecithin (, from the Greek ''lekithos'' "yolk") is a generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic – they attract both water and fatty substances (and so are both hydrophilic and lipophilic), and are used for smoothing food textures, emulsifying, homogenizing liquid mixtures, and repelling sticking materials. Lecithins are mixtures of glycerophospholipids including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidic acid. Lecithin was first isolated in 1845 by the French chemist and pharmacist Théodore Gobley. In 1850, he named the phosphatidylcholine ''lécithine''. Gobley originally isolated lecithin from egg yolk – λέκιθος ''(lekithos)'' is "egg yolk" in Ancient Greek – and established the complete chemical formula of phosphatidylcholine in 1874; in between, he demonstrated the presence of lecithin in a variety of biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Barcelona
The University of Barcelona ( ca, Universitat de Barcelona, UB; ; es, link=no, Universidad de Barcelona) is a public university located in the city of Barcelona, Catalonia, in Spain. With 63,000 students, it is one of the biggest universities in Spain. It is one of the oldest universities in both Catalonia and Spain, established in 1450. It is considered one of the best universities in Spain. Overall, the UB has been ranked 1st in Spain in most of the 2022-2023 rankings and is located around the 50th place in Europe. It has 106 departments and more than 5,000 full-time researchers, technicians and research assistants, most of whom work in the 243 research groups as recognized and supported by the Government of Catalonia. In 2010, the UB was awarded 175 national research grants and 17 European grants and participated in over 500 joint research projects with the business sector, generating an overall research income of 70 million euros. The work of these groups is overseen by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterane
Sterane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrenes) compounds are a class of tetracyclic compounds derived from steroids or sterols via diagenetic and catagenetic degradation and saturation. Steranes have an androstane skeleton with a side chain at carbon C-17. The sterane structure constitutes the core of all sterols. Steranes are sometimes used as biomarkers for the presence of eukaryotic cells. Steranes may be rearranged to diasteranes during diagenesis (C-27 to C-30, rearrangement at C-18 and C-19, no R at C-24). Oils from clastic source rocks tend to be rich in diasteranes. Cholesterol and its derivatives (such as progesterone, aldosterone, cortisol, and testosterone), are common examples of compounds with the cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus. See also * Cholestane Cholestane is a saturated tetracyclic triterpene. This 27-carbon biomarker is produced by diagenesis of cholesterol and is one of the most abundant biomarkers in the rock record. Presence of cholestane, its d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Science & Technology
''Environmental Science & Technology'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1967 by the American Chemical Society. It covers research in environmental science and environmental technology, including environmental policy. ''Environmental Science & Technology'' has a sister journal, ''Environmental Science & Technology Letters'', which publishes short communications. The editor-in-chief of ''Environmental Science & Technology'' is Prof. Julie Zimmerman (Yale University). Previous editors have been: David Sedlak (University of California, Berkeley, 2014 - 2020), James J. Morgan (California Institute of Technology; founding editor, 1967-1975), Russell F. Christman (University of North Carolina, 1975-1987), William H. Glaze (University of North Carolina, 1987-2003) and Jerald L. Schnoor (University of Iowa, 2002-2014). Abstracting and indexing According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 11.357. The journal is abstra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Crete
The Technical University of Crete (TUC; el, Πολυτεχνείο Κρήτης, ''Polytechneio Kritis'') is a state university under the supervision of the Greek Ministry of Education and was founded in 1977 in Chania, Crete. The first students were admitted in 1984. The purpose of the institution is to conduct research, to provide under-graduate and graduate educational programs in modern engineering fields as well as to develop links with the Greek industry. It is highly ranked among the Greek technical universities in terms of research productivity, research funding, scientific publications and citation per faculty member. It uses Daedalus as part of the emblem. Academic structure The Technical University of Crete comprises five engineering schools, all of which offer undergraduate and postgraduate study programmes. The school of Electronic and Computer Engineering was renamed to School of Electrical and Computer Engineering in July 2016. Research The Technical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |