|
Rydberg Polaron
A Rydberg polaron is an exotic state of matter, created at low temperatures, in which a very large atom contains other ordinary atoms in the space between the nucleus and the electrons. For the formation of this atom, scientists had to combine two fields of atomic physics: Bose–Einstein condensates and Rydberg atoms. Rydberg atoms are formed by exciting a single atom into a high-energy state, in which the electron is very far from the nucleus. Bose–Einstein condensates are a state of matter that is produced at temperatures close to absolute zero. Polarons are induced by using a laser to excite Rydberg atoms contained as impurities in a Bose–Einstein condensate. In those Rydberg atoms, the average distance between the electron and its nucleus can be as large as several hundred nanometres, which is more than a thousand times the radius of a hydrogen atom. Under these circumstances, the distance between the nucleus and the electron of the excited Rydberg atoms is higher than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydberg Polaron Schematic
Rydberg may refer to: People *Gerda Rydberg (1858–1928), Swedish artist better known as Gerda Tirén *Jan Rydberg, (1923-2015), Swedish chemist who worked on nuclear chemistry and recycling at Chalmers University of Technology *Johannes Rydberg (1854–1919), Swedish physicist and deviser of the Rydberg formula *Kaisu-Mirjami Rydberg (1905–1959), Finnish journalist and politician *Per Axel Rydberg (1860–1931), Swedish-American botanist *Sam Rydberg (1885–1956), Swedish composer *Viktor Rydberg (1828–1895), Swedish author, poet, and mythographer *Viktor Crus Rydberg (1995—), Swedish ice hockey player Physics *Rydberg constant, a constant related to atomic spectra *Rydberg formula, a formula describing wavelengths *Rydberg atom, an excited atomic state *Rydberg molecule, an electronically excited chemical substance *Rydberg unit of energy (symbol Ry), derived from the Rydberg constant Places * Rydberg (crater), a lunar crater named after Johannes Rydberg {{disambig, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Matter
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, and some states only exist under extreme conditions, such as Bose–Einstein condensates (in extreme cold), neutron-degenerate matter (in extreme density), and quark–gluon plasma (at extremely high energy). For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter. Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume (assuming no change in temperature or air pressure) and shape, with component particles ( atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume (assuming no change in temperature or air pressure), but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
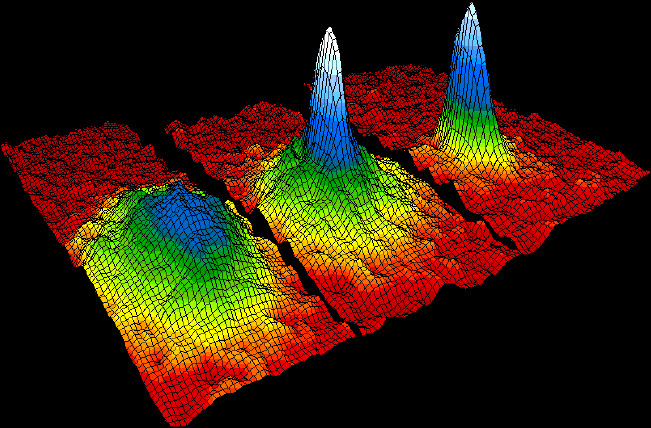
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density (about 100,000 times less dense than normal air) to ultra-low temperatures. This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein following and crediting a pioneering paper by Satyendra Nath Bose on the new field now known as quantum statistics. In 1995, the Bose-Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman of the University of Colorado at Boulder using rubidium atoms; later that year, Wolfgang Ketterle of MIT produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydberg Atom
A Rydberg atom is an excited atom with one or more electrons that have a very high principal quantum number, ''n''. The higher the value of ''n'', the farther the electron is from the nucleus, on average. Rydberg atoms have a number of peculiar properties including an exaggerated response to electric and magnetic fields, long decay periods and electron wavefunctions that approximate, under some conditions, classical orbits of electrons about the nuclei. The core electrons shield the outer electron from the electric field of the nucleus such that, from a distance, the electric potential looks identical to that experienced by the electron in a hydrogen atom. In spite of its shortcomings, the Bohr model of the atom is useful in explaining these properties. Classically, an electron in a circular orbit of radius ''r'', about a hydrogen nucleus of charge +'' e'', obeys Newton's second law: : \mathbf=m\mathbf \Rightarrow = where ''k'' = 1/(4π ε0). Orbital momentum is quantiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term ''atomic orbital'' may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (magnetic quantum number). Alternative to the magnetic quantum number, the orbitals are often labeled by the associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ). Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simple names s orbital, p orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna University Of Technology
TU Wien (TUW; german: Technische Universität Wien; still known in English as the Vienna University of Technology from 1975–2014) is one of the major universities in Vienna, Austria. The university finds high international and domestic recognition in teaching as well as in research, and it is a highly esteemed partner of innovation-oriented enterprises. It currently has about 28,100 students (29% women), eight faculties and about 5,000 staff members (3,800 academics). The university's teaching and research is focused on engineering, computer science, and natural sciences. History The institution was founded in 1815 by Emperor Francis I of Austria as the '' k.k. Polytechnische Institut'' (Imperial-Royal Polytechnic Institute). The first rector was Johann Joseph von Prechtl. It was renamed the ''Technische Hochschule'' (College of Technology) in 1872. When it began granting doctoral and higher degrees in 1975, it was renamed the ''Technische Universität Wien'' (Vienna Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice University
William Marsh Rice University (Rice University) is a Private university, private research university in Houston, Houston, Texas. It is on a 300-acre campus near the Houston Museum District and adjacent to the Texas Medical Center. Rice is ranked among the top universities in the United States. Opened in 1912 as the Rice Institute after the murder of its namesake William Marsh Rice, Rice is a research university with an undergraduate focus. Its emphasis on undergraduate education is demonstrated by its 6:1 student-faculty ratio. The university has a Research I university, very high level of research activity, with $156 million in sponsored research funding in 2019. Rice is noted for its applied science programs in the fields of artificial heart research, structural chemical analysis, signal processing, space science, and nanotechnology. Rice has been a member of the Association of American Universities since 1985 and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotic Matter
There are several proposed types of exotic matter: * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have "exotic" physical properties that would violate known laws of physics, such as a particle having a negative mass. * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have not yet been encountered, but whose properties would be within the realm of mainstream physics if found to exist. * Several particles whose existence has been experimentally confirmed that are conjectured to be exotic hadrons and within the Standard Model. * States of matter In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many intermediate states are known to exist, such as liquid crystal, ... that are not commonly encountered, such as Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, nuclear matter, quantum spin liquid, string-net liquid, supercritical fluid, color-glass c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |