|
Rubicon Model (psychology)
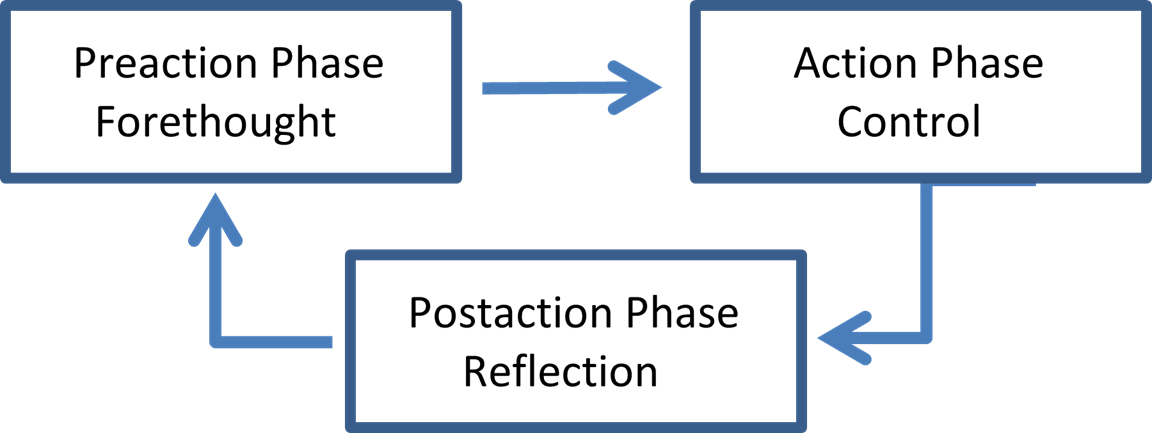
In psychological theories of motivation, the Rubicon model, more completely the Rubicon model of action phases, makes a distinction between motivational and volitional processes. The Rubicon model "defines clear boundaries between motivational and action phases". The first boundary "separates the motivational process of the predecisional phase from the volitional processes of postdecisional phase." Another boundary is that between initiation and conclusion of an action. A self-regulatory feedback model incorporating these interfaces was proposed later by others, as illustrated in the figure. The name "Rubicon model" derives from the tale of Caesar's crossing the Rubicon River, a point of no return, thereby revealing his intentions. According to the Rubicon model, every action includes such a point of no return at which the individual moves from goal setting to goal striving. :"Once subjects move from planning and goal-setting to the implementation of plans, they cross a metaphoric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning (SRL) is one of the domains of self-regulation, and is aligned most closely with educational aims. Broadly speaking, it refers to learning that is guided by '' metacognition'' (thinking about one's thinking), ''strategic action'' (planning, monitoring, and evaluating personal progress against a standard), and ''motivation to learn''. A self-regulated learner "monitors, directs, and regulates actions toward goals of information acquisition, expanding expertise, and self-improvement”. In particular, self-regulated learners are cognizant of their academic strengths and weaknesses, and they have a repertoire of strategies they appropriately apply to tackle the day-to-day challenges of academic tasks. These learners hold incremental beliefs about intelligence (as opposed to entity, or fixed views of intelligence) and attribute their successes or failures to factors (e.g., effort expended on a task, effective use of strategies) within their control. Finally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delayed Gratification
Delayed gratification, or deferred gratification, is the resistance to the temptation of an immediate pleasure in the hope of obtaining a valuable and long-lasting reward in the long-term. In other words, delayed gratification describes the process that the subject undergoes when the subject resists the temptation of an immediate reward in preference for a later reward. Generally, delayed gratification is associated with resisting a smaller but more immediate reward in order to receive a larger or more enduring reward later. A growing body of literature has linked the ability to delay gratification to a host of other positive outcomes, including academic success, physical health, psychological health, and social competence. A person's ability to delay gratification relates to other similar skills such as patience, impulse control, self-control and willpower, all of which are involved in self-regulation. Broadly, self-regulation encompasses a person's capacity to adapt the self ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's own law" is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defined from a human resources perspective, where it denotes a (relatively high) level of discretion granted to an employee in his or her work. In such cases, autonomy is known to generally increase job satisfaction. Self-actualized individuals are thought to operate autonomously of external expectations. In a medical context, respect for a patient's personal autonomy is considered one of many fundamental ethical principles in medicine. Sociology In the sociology of knowledge, a controversy over the boundaries of autonomy inhibited analysis of any concept beyond relative auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-regulation Theory
Self-regulation theory (SRT) is a system of conscious, personal management that involves the process of guiding one's own thoughts, behaviors and feelings to reach goals. Self-regulation consists of several stages. In the stages individuals must function as contributors to their own motivation, behavior, and development within a network of reciprocally interacting influences. Roy Baumeister, one of the leading social psychologists who have studied self-regulation, claims it has four components: standards of desirable behavior, motivation to meet standards, monitoring of situations and thoughts that precede breaking said standards and lastly, willpower. Baumeister along with other colleagues developed three models of self-regulation designed to explain its cognitive accessibility: self-regulation as a knowledge structure, strength, or skill. Studies have been conducted to determine that the strength model is generally supported, because it is a limited resource in the brain and only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-efficacy
In psychology, self-efficacy is an individual's belief in their capacity to act in the ways necessary to reach specific goals. The concept was originally proposed by the psychologist Albert Bandura. Self-efficacy affects every area of human endeavor. By determining the beliefs a person holds regarding their power to affect situations, self-efficacy strongly influences both the power a person actually has to face challenges competently and the choices a person is most likely to make. These effects are particularly apparent, and compelling, with regard to investment behaviors such as in health, education, and agriculture. A strong sense of self-efficacy promotes human accomplishment and personal well-being. A person with high self-efficacy views challenges as things that are supposed to be mastered rather than threats to avoid. These people are able to recover from failure faster and are more likely to attribute failure to a lack of effort. They approach threatening situations with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-control
Self-control, an aspect of inhibitory control, is the ability to regulate one's emotions, thoughts, and behavior in the face of temptations and impulses. As an executive function, it is a cognitive process that is necessary for regulating one's behavior in order to achieve specific goals. A related concept in psychology is emotional self-regulation. Self-control is thought to be like a muscle. According to studies, self-regulation, whether emotional or behavioral, was proven to be a limited resource which functions like energy. In the short term, overuse of self-control will lead to depletion. However, in the long term, the use of self-control can strengthen and improve over time. Self-control is also a key concept in the general theory of crime, a major theory in criminology. The theory was developed by Michael Gottfredson and Travis Hirschi in their book titled ''A General Theory of Crime'', published in 1990. Gottfredson and Hirschi define self-control as the differential ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Functions
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals. Executive functions include basic cognitive processes such as attentional control, cognitive inhibition, inhibitory control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Higher-order executive functions require the simultaneous use of multiple basic executive functions and include planning and fluid intelligence (e.g., reasoning and problem-solving). Executive functions gradually develop and change across the lifespan of an individual and can be improved at any time over the course of a person's life. Similarly, these cognitive processes can be adversely affected by a variety of events which affect an individual. Both neuropsychological tests (e.g., the Stroop test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems. Their neuroanatomy is therefore better understood. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or "lesions" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions. For information about the composition of non-human animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |