 |
Ruaidhrí Mac Ruaidhrí
Ruaidhrí Mac Ruaidhrí (died 14 October 1318?) was a fourteenth-century Scottish magnate and chief of Clann Ruaidhrí. He was an illegitimate son of Ailéan mac Ruaidhrí, and is recorded to have participated in the kindred's military actions against supporters of both the English Crown and Scottish Crown. Following the apparent death of his brother, Lachlann, Ruaidhrí appears to have taken control of the kindred, and firmly aligned the family with Robert I, King of Scotland. Ruaidhrí may well be the member of Clann Ruaidhrí who is recorded slain at the Battle of Faughart in support of the Bruce cause in Ireland. After his death, Ruaidhrí's half-sister, Cairistíona, attempted to transfer the Clann Ruaidhrí territories outwith the family. Ruaidhrí was survived by a daughter, Áine, and an illegitimate son, Raghnall. The latter fended off Cairistíona's actions and succeeded to the chiefship of Clann Ruaidhrí. Clann Ruaidhrí Ruaidhrí was an illegitimate son of Ail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,242 years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Clann Somhairle
Clann Somhairle, sometimes anglicised as Clan Sorley, refers to those Scottish and Irish dynasties descending from the famous Norse-Gaelic leader Somerled, King of Mann and the Isles, son of Gillabrigte (†1164) and ancestor of Clann Domhnaill. Primarily they are the Clan Donald, formerly known as the Lord of the Isles, and the mainland Clan MacDougall, and all their numerous branches. Clan Macruari are their lost sept. Origins The origin of Somerled, from whom the clan derives, is obscure. Only the name of his father is directly attested in early records. He was later portrayed as having Gaelic ancestry, with late pedigrees from the 14th and 15th century tracing him from legendary Colla Uais and hence from Conn of the Hundred Battles, and some versions apparently including the legendary founder of the Scottish state of Dál Riata, Fergus Mór. Historians have distrusted this derivation, though in the 1960s, David Sellar defended a Gaelic derivation. More recently, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lochaber
Lochaber ( ; gd, Loch Abar) is a name applied to a part of the Scottish Highlands. Historically, it was a provincial lordship consisting of the parishes of Kilmallie and Kilmonivaig, as they were before being reduced in extent by the creation of ''Quoad Sacra'' parishes in the 19th century. Lochaber once extended from the Northern shore of Loch Leven, a district called Nether Lochaber, to beyond Spean Bridge and Roybridge, which area is known as Brae Lochaber or ''Braigh Loch Abar'' in Gaelic. Lochaber is now also used to refer to a much wider area, one of the 16 ward management areas of the Highland Council of Scotland and one of eight former local government districts of the two-tier Highland region. The main town of Lochaber is Fort William. According to legend, a glaistig, a ghostly woman-goat hybrid, once lived in the area. Name William Watson outlined two schools of thought on this topic. He favoured the idea that ''Abar'' came from the Pictish and Welsh for "river m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Inverlochy Castle PICT6929
Inverlochy may refer to: * Inverlochy, Highland * Inverlochy Castle * Battle of Inverlochy (1431) A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and forc ... * Battle of Inverlochy (1645) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ardnamurchan
Ardnamurchan (, gd, Àird nam Murchan: headland of the great seas) is a peninsula in the ward management area of Lochaber, Highland, Scotland, noted for being very unspoiled and undisturbed. Its remoteness is accentuated by the main access route being a single track road for much of its length. The most westerly point of mainland Great Britain, Corrachadh Mòr, is in Ardnamurchan. From 1930 to 1975 Ardnamurchan also gave its name to a landward district of Argyll, which covered a much wider area, including the districts of Morvern, Sunart and Ardgour. Geography Strictly speaking, Ardnamurchan covers only the peninsula beyond the villages of Salen (in the south) and Acharacle (in the north), but nowadays the term is also used more generally to include the neighbouring districts of Sunart, Ardgour, Morvern, and even Moidart (which was part of the former county of Inverness-shire, not Argyll). Ardnamurchan Point, which has the Ardnamurchan Lighthouse built on it, is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lewis And Harris
Lewis and Harris ( gd, Leòdhas agus na Hearadh, sco, Lewis an Harris), or Lewis with Harris, is a single Scottish island in the Outer Hebrides, divided by mountains. It is the largest island in Scotland and the third largest in the British Isles, after Great Britain and the island of Ireland, with an area of , which is approximately 1% of the area of Great Britain. The northern two-thirds is called Lewis and the southern third Harris; each is frequently referred to as if it were a separate island. Etymology The island does not have a one-word name in either English or Scottish Gaelic, and is referred to as "Lewis and Harris", "Lewis with Harris", "Harris with Lewis" etc. Rarely used is the collective name of "the Long Island" ( gd, an t-Eilean Fada), although that epithet is sometimes applied to the entire archipelago of the Outer Hebrides, including the Uist group of islands and Barra. Geography Lewis–Harris boundary The boundary between Lewis and Harris runs fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
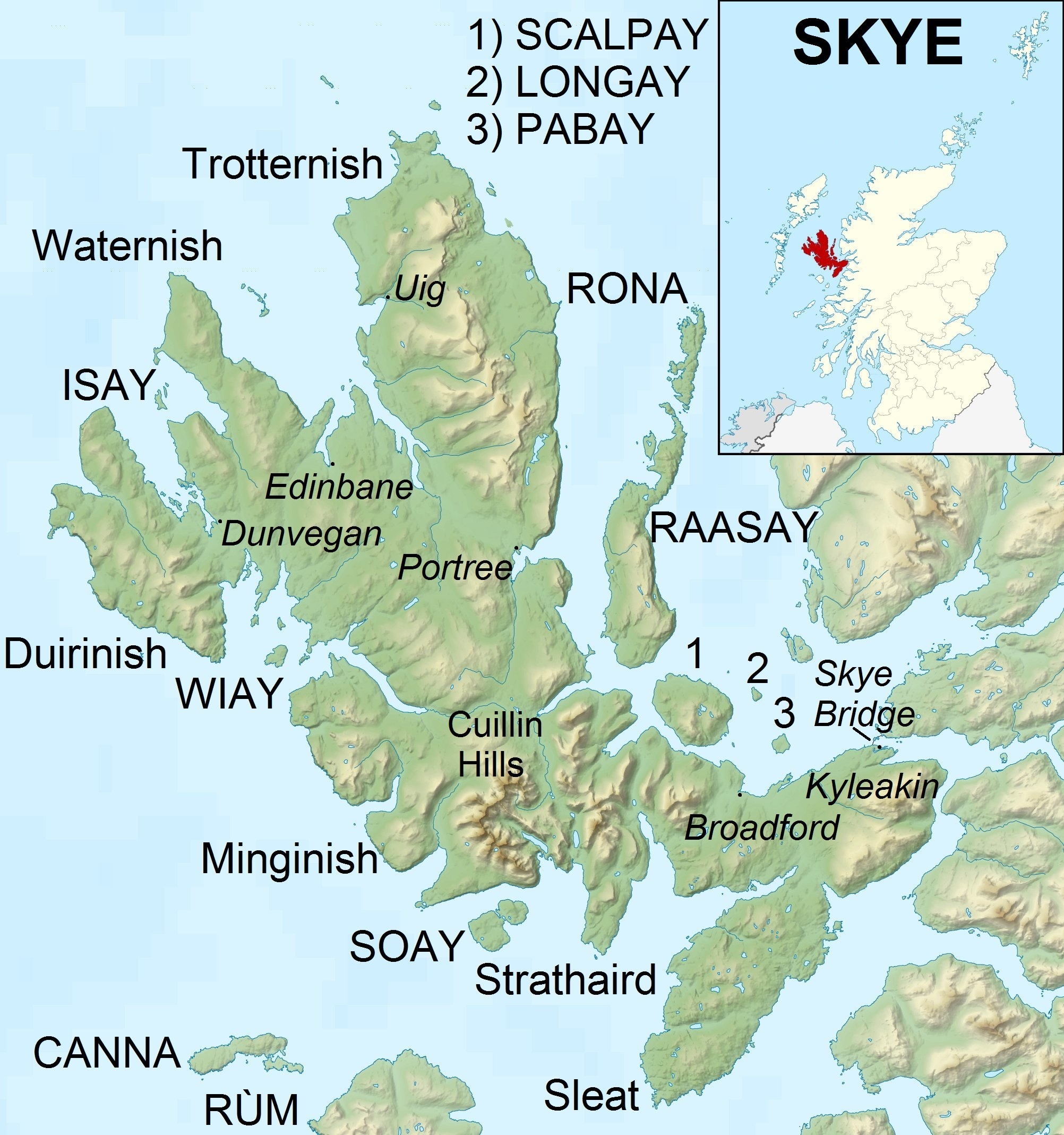 |
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Alasdair Óg Mac Domhnaill, Lord Of Islay
Alasdair is a Scottish Gaelic given name. The name is a Gaelic form of ''Alexander'' which has long been a popular name in Scotland. The personal name ''Alasdair'' is often Anglicised as ''Alistair'', '' Alastair'', and ''Alaster''.''A Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, People named Alasdair * Alasdair A. K. White, British management theorist * Alasdair Allan, Scottish politician *Alasdair Alpin MacGregor, Scottish writer and photographer *Alasdair and Hetty Tayler, British historical writers *Alasdair Clayre, British author and broadcaster *Alasdair Dickinson, Scottish rugby union coach *Alasdair Duncan, Australian author and journalist * Alasdair Fotheringham, British journalist *Alasdair Fraser, Scottish fiddler and composer * Alasdair Gillis, Canadian TV host *Alasdair Graham, Canadian politician *Alasdair Gray, Scottish writer and artist *Alasdair Hutton, British writer and narrator * Alasdair Kent, British-Australian opera singer * Alasdair Locke, Scottish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Alasdair Mac Dubhghaill, Lord Of Argyll
Alexander of Argyll, also known as Alexander of Lorne, and Alexander MacDougall ( gd, Alasdair MacDubhgaill; died 1310), was a Scottish magnate from the late 13th and early 14th century. Alexander was the son of Ewen MacDougall, Lord of Argyll. Although the details of Alexander's early life are largely unknown, he appears to have succeeded to his father's position as Lord of Argyll and Lorne and head of the MacDougall kindred after the latter's death in 1268. Alexander appears to have been named after King Alexander III of Scotland. Under the latter's authority, Alexander was involved in the Scottish expedition that quelled a revolt on the Isle of Man in 1275. In 1284 he joined with other Scottish noblemen who acknowledged Margaret of Norway as the heir of Alexander.''Foedera'', p228 Here he is referred to as "Alexander of Orgadia" Argyll As the succession crisis resulting from the unexpected deaths of Alexander III (1286) and then his designated successor Margaret (1290) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Homage (feudal)
Homage (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title to his new position (investiture). It was a symbolic acknowledgement to the lord that the vassal was, literally, his man (''homme''). The oath known as " fealty" implied lesser obligations than did "homage". Further, one could swear "fealty" to many different overlords with respect to different land holdings, but "homage" could only be performed to a single liege, as one could not be "his man" (i.e., committed to military service) to more than one "liege lord". There have been some conflicts about obligations of homage in history. For example, the Angevin monarchs of England were sovereign in England, i.e., they had no duty of homage regarding those holdings; but they were not sovereign regarding their French holdings. Henry II was king of England, but he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.png) |
William II, Earl Of Ross
William II, Earl of Ross (Gaelic: ''Uilleam''; died c. 1323) was ruler of the province of Ross in northern Scotland, and a prominent figure in the Wars of Scottish Independence. William was the only child of William I, Earl of Ross and his wife Jean Comyn, daughter of William, Earl of Buchan. He succeeded to the earldom on the death of his father in 1274. In 1284 he joined with other Scottish noblemen who acknowledged Margaret, Maid of Norway as the heir to the unfortunate Alexander III. Following Margaret's death, he sided alternately with the Scottish and English interests. In 1291 he paid homage to Edward I of England at Berwick recognising him as overlord of Scotland. He was chosen as an auditor at the trial between John Balliol and Robert Bruce, when they competed before Edward to decide who would take the throne of Scotland. William was one of the leaders of the Scottish army at the Battle of Dunbar in 1296, when Edward invaded Scotland to punish John Balliol for ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Edward I, King Of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal of the French king. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English barons. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was held hostage by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Evesham in 1265. Within two years the rebellion was extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |