|
Royal Botanic Institution Of Glasgow
Glasgow Botanic Gardens is a botanical garden located in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland. It features several glasshouses, the most notable of which is the Kibble Palace. The Gardens has a wide variety of temperate and tropical flora, a herb garden, a chronological bed with plants arranged according to their introduction to Scotland, the UK's national collection of tree ferns, and a world rose garden officially opened in 2003 by Princess Tomohito of Mikasa. The River Kelvin runs along the north side of the Gardens and continues through Kelvingrove Park, the Kelvin walkway providing an uninterrupted walking route between the two green spaces. The Botanic Gardens was awarded a Green Flag Award in 2011. History In 1817 about 8 acres (32,000 m2) of land were laid out at Sandyford, near Sauchiehall Street, Glasgow, and run by the Royal Botanic Institution of Glasgow (founded by Thomas Hopkirk of Dalbeth and Prof James Jeffray Professor of Botany at Glasgow University), and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hopkirk
Thomas Hopkirk (1785–1841) was a Scottish botanist and lithographer. The Hopkirks He was descended from a gentry family who came from Hopekirk, near Hawick, by way of Dalkeith in Midlothian, to Dalbeth in Glasgow . His grandfather, also Thomas (1716–1781 ) had been a wealthy Glasgow merchant – a "Tobacco Lord" or "''Virginia Don''" – who had diversified into coal mining, brewing and banking. He had lived originally in a tenement in the High Street of Glasgow, called "''Hopkirk's Land''". David Dale rented the shop premises on the ground floor, where he operated as the first Glasgow agent of the Royal Bank of Scotland. Thomas then moved to a fine house at the corner of Argyle Street and Dunlop Street, which became the ''Buck's Head Hotel''. (This was demolished in 1865; the later department store still displays the Buck on its roof.) James Hopkirk (1749–1838), ''Thomas's father'' In 1754, Thomas senior bought the lands of Dalbeth, which then included "''Wester Dalbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of arms Flag , latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis , motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita , mottoeng = The Way, The Truth, The Life , established = , type = Public research universityAncient university , endowment = £225.2 million , budget = £809.4 million , rector = Rita Rae, Lady Rae , chancellor = Dame Katherine Grainger , principal = Sir Anton Muscatelli , academic_staff = 4,680 (2020) , administrative_staff = 4,003 , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Glasgow , country = Scotland, UK , colours = , website = , logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
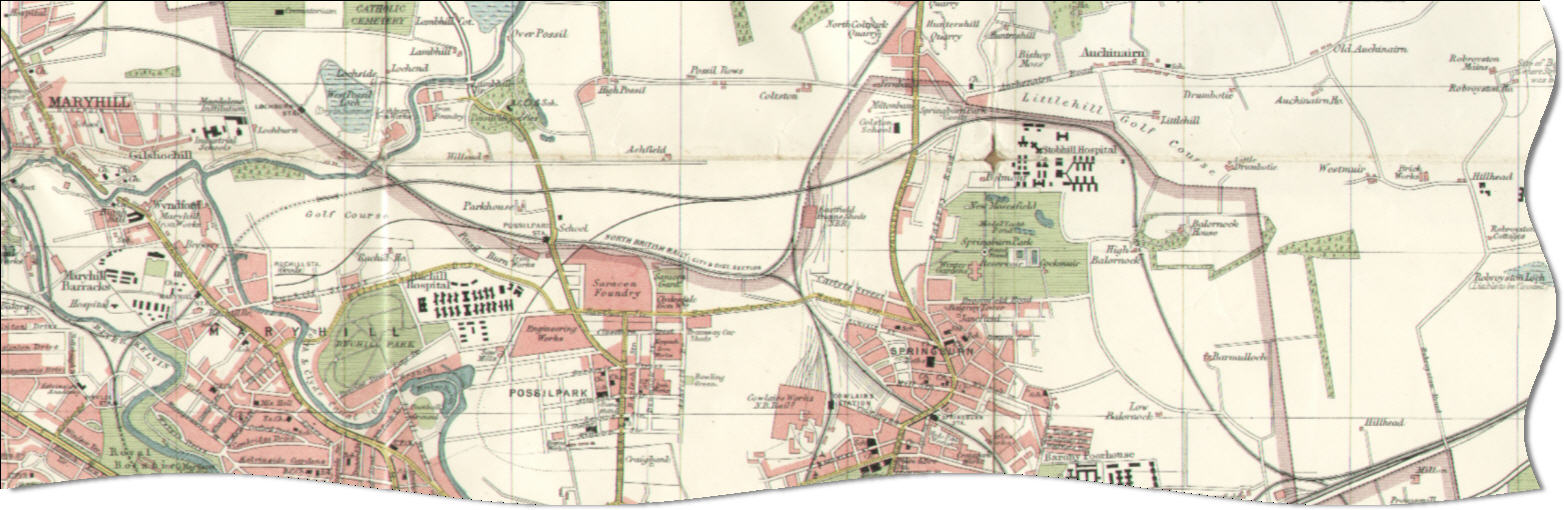
Possilpark
Possilpark is a district in the Scottish city of Glasgow, situated north of the River Clyde and centred around Saracen Street. The area developed around Saracen Foundry of Walter MacFarlane & Co., which was the main employer. In the wake of the Saracen Foundry's closure in 1967, this part of Glasgow became one of the poorest in the United Kingdom, and decades later deprivation and crime rates remain high. A variety of diverse community organisations operate in the area, providing arts, sports, health and gardening provision and community regeneration, including Young People's Futures, The Concrete Garden, Possobilities and Friends of Possilpark Greenspace. The district is served by both Possilpark & Parkhouse and Ashfield railway stations on the Maryhill Line. History Upper and Lower Possil estate In 1242, Alexander II of Scotland granted certain lands to the Bishop of Glasgow. These included the lands in the north referred to as Possele, divided in the sixteenth century in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saracen Foundry
The Saracen Foundry, Possilpark, Glasgow c.1890 The Saracen Foundry was the better-known name for the Possilpark, Glasgow–based foundry company W MacFarlane & Co. Ltd, founded and owned by Walter MacFarlane. MacFarlane's was the most important manufacturer of ornamental ironwork in Scotland. Walter Macfarlane Walter Macfarlane was born in Torrance of Campsie, near Glasgow, in 1817. He worked for the jeweller William Russell, before serving an apprenticeship with blacksmith James Buchanan. He then spent a decade working for Moses, McCulloch & Co's Cumberland Foundry in Stockwell Street. With his own main home at 22 Park Circus, Glasgow, Macfarlane became a prominent figure in local politics, becoming the President of the Glasgow Liberal Association and a City Councillor. He died in 1885, and is buried in Glasgow Necropolis cemetery. Saracen Foundry MacFarlane, with partners Thomas Russell and James Marshall, incorporated W MacFarlane & Co. Ltd in 1850. They took over a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Macfarlane
The Saracen Foundry, Possilpark, Glasgow c.1890 The Saracen Foundry was the better-known name for the Possilpark, Glasgow–based foundry company W MacFarlane & Co. Ltd, founded and owned by Walter MacFarlane. MacFarlane's was the most important manufacturer of ornamental ironwork in Scotland. Walter Macfarlane Walter Macfarlane was born in Torrance of Campsie, near Glasgow, in 1817. He worked for the jeweller William Russell, before serving an apprenticeship with blacksmith James Buchanan. He then spent a decade working for Moses, McCulloch & Co's Cumberland Foundry in Stockwell Street. With his own main home at 22 Park Circus, Glasgow, Macfarlane became a prominent figure in local politics, becoming the President of the Glasgow Liberal Association and a City Councillor. He died in 1885, and is buried in Glasgow Necropolis cemetery. Saracen Foundry MacFarlane, with partners Thomas Russell and James Marshall, incorporated W MacFarlane & Co. Ltd in 1850. They took over a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loch Long
Loch Long is a body of water in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The Sea Loch extends from the Firth of Clyde at its southwestern end. It measures approximately in length, with a width of between . The loch also has an arm, Loch Goil, on its western side. Although it is fairly long, its name actually comes from the Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic for "ship lake". Prior to their defeat at the Battle of Largs in 1263, Viking raiders sailed up Loch Long to Arrochar, Argyll, Arrochar, and then dragged their longships 2 miles overland to Tarbet, Argyll, Tarbet and into Loch Lomond. Being inland, the settlements around Loch Lomond were more vulnerable to attack. Loch Long forms part of the coast of the Cowal peninsula and forms the entire western coastline of the Rosneath Peninsula. Loch Long was historically the boundary between Argyll and Dunbartonshire; however, in 1996 boundary redrawing meant that it moved wholly within the council area of Argyll and Bute. The steamboat ''Chancellor'' us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulport (village)
Coulport ( - literally the Back Port or Ferry) is a village on the east side of Loch Long, Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It is north-north-west of Cove on the Rosneath peninsula. It marks the end of the B833 shore road, although the village can also be reached by a high-quality but unclassified access road (primarily designed for naval traffic) directly from Garelochhead. The village looks across to the small settlement of Ardentinny on the west shore to which, in the 18th/19th century, there was a ferry. John Kibble, the son of a Glasgow metal merchant, was one of several wealthy Glasgow merchants who had large villas built at Coulport in the nineteenth century either as permanent residences or summer retreats. Several still survive, some now flatted, others in a dilapidated condition. Kibble's Coulport House was the original location of the giant conservatory known as the Kibble Palace (now in Glasgow's Botanic Garden). Since the 1960s Coulport has been most associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrought Iron
Wrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon content (less than 0.08%) in contrast to that of cast iron (2.1% to 4%). It is a semi-fused mass of iron with fibrous slag Inclusion (mineral), inclusions (up to 2% by weight), which give it a wood-like "grain" that is visible when it is etched, rusted, or bent to structural failure, failure. Wrought iron is tough, malleable, ductile, corrosion resistant, and easily forge welding, forge welded, but is more difficult to welding, weld electrically. Before the development of effective methods of steelmaking and the availability of large quantities of steel, wrought iron was the most common form of malleable iron. It was given the name ''wrought'' because it was hammered, rolled, or otherwise worked while hot enough to expel molten slag. The modern functional equivalent of wrought iron is Carbon steel#Mild or low-carbon steel, mild steel, also called low-carbon steel. Neither wrought iron nor mild steel contain enough carbon to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Botanic Gardens Reopen 009
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirklee Railway Station
Kirklee railway station was a railway station serving the Kelvinside area in the West End of Glasgow, Scotland. History The station was opened on 10 August 1896 by the Glasgow Central Railway.Butt, page 136 Also known as Kirklee for North Kelvinside, it was closed between 1 January 1917 and 2 March 1919 2 June 1919 and closed permanently to passengers on 1 May 1939, with the line being closed on 5 October 1964. The station building was designed by famous architect Sir J.J. Burnet who earned his knighthood on the basis of his design for the extension of the British Museum The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum .... The construction of the station was controversial in the 1890s as it destroyed a local beauty spot known as the ''Peartree Well''. Little is known of the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Railway Station
An abandoned (or disused) railway station is a building or structure which was constructed to serve as a railway station but has fallen into disuse. There are various circumstances when this may occur – a railway company may fall bankrupt, or the station may be closed due to the failure of economic activity such as insufficient passenger numbers, operational reasons such as the diversion or replacement of the line. In some instances, the railway line may continue in operation while the station is closed. Additionally, stations may sometimes be resited along the route of the line to new premises – examples of this include opening a replacement station nearer to the centre of population, or building a larger station on a less restricted site to cope with high passenger numbers. Reasons for abandonment Notable cases where railway stations have fallen into disuse include the Beeching Axe, a 1960s programme of mass closures of unprofitable railway lines by the British Government. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanic Gardens Railway Station
Botanic Gardens railway station was a railway station serving the Botanic Gardens located in the Kelvinside area in the West End of Glasgow. History The station was opened on 10 August 1896 by the Glasgow Central Railway. The station building was on ground level, and the platforms were underground, beneath the Glasgow Botanic Gardens. It was closed between 1 January 1917 and 2 March 1919 due to wartime economy, and closed permanently to passengers on 6 February 1939, with the line being closed on 5 October 1964. Architecture The station building was an ornate red brick structure with two towers sporting a clock and Caledonian Railway monogram, topped by domes reminiscent of a Russian orthodox church. The extant, but disused, station building at Possil is of a similar design. It was a well-known landmark along Great Western Road and was designed by the renowned Glasgow railway architect of the period, James Miller. Miller also designed the next station on the line at Kel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |