|
Rotuman People
The Rotumans are a Polynesian ethnic group native to Rotuma, an island group forming part of Fiji. The island itself is a cultural melting pot at the crossroads of the Micronesian, Melanesian and Polynesian divisions of the Pacific Ocean, and due to the seafaring nature of traditional Pacific cultures, the indigenous Rotuman have adopted or share many aspects of its multifaceted culture with its Melanesian, Micronesian and Polynesian neighbours. Ancestors The first inhabitants of the island of Rotuma were from Borabora/ Tahiti. They were the ancient seafaring people from the Lapita homeland, followed by waves of Micronesians and Melanesians, giving Rotumans a similar but thoroughly distinct language, cultural heritage and metaphysical understanding to that of their preceding parent cultures. After the invasion of Rotuma i.e.overthrowing the Tahitians by the Samoans. They created a Rotuman mythology pointing to Samoans as the first people to inhabit the island of Rotuma. But ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a revival movement within the 18th-century Church of England and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States, and beyond because of vigorous missionary work, today claiming approximately 80 million adherents worldwide. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist churches, focuses on sanctification and the transforming effect of faith on the character of a Christian. Distinguishing doctrines include the new birth, assurance, imparted righteousness, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga (closest foreign country), northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan culture, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Administrative divisions of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautoga
The tautoga (pronounced ) is considered the most formal and restrained style of Rotuman dance, usually seen performed in large festivities or ceremonies (called '' kato'aga'', a term summing up all traditional Rotuman ceremonies), or in public opportunities to showcase Rotuman culture. The tautoga style can be seen as comparable to the Tuvaluan fatele or Tongan lakalaka, and the "toga" sound to the word alludes to such an origin. Performers Dance groups in tautoga (called hafa, a loanword referring to the halves of the dance group) can vary in number from 10 people to 100+ people, depending on availability of dancers and the scale of the event. The men and women usually arrange themselves in rows and in a rectangular shape, with men on one side, women on the other like the lakalaka, and also analogous to the Tongan dance, the most attractive and competent dancers stand in the front row centrally (this factor is referred to in Rotuman culture as "mạru") and these attributes de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Rotuma
The Council of Rotuma is a municipal body on the island of Rotuma, a Fijian dependency. Owing to the unique character of Rotuma, the powers of this council are greater than those of other municipal bodies in Fiji and in some ways it approximates a legislative body, though it is in every way subordinate to the Parliament of Fiji. The Council consists of fourteen full members and three advisory members. Each of Rotuma's seven districts elects one representative to the Council; the traditional Chief of each district is also a Council member ''ex officio.'' The advisory members, who have speaking rights but not voting rights, are the District Officer, the most senior Medical Officer, and the most senior Agricultural Officer, all of whom serve ''ex officio''. The seven chiefs are chosen according to traditional custom. The election is usually for life, although the Fijian cabinet minister responsible for Rotuma may, at his or her own discretion, dismiss a chief and order the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gagaja
Gagaja is a Rotuman word denoting the position of "Chief" or "Lord". This could be a formal chiefly position in one of the seven districts (''gagaj 'es itu'u'') or a village chief (''fa 'es ho'aga'') as well as to anyone else, such as the Chairman of the Rotuma Island Council (''Gagaj Jeaman ta'') to whom respect and deference is owed based on their own skills and attributes. Unlike in many other Pacific cultures, the official chiefly positions are not allocated according to any strict primogeniture, but rather are elected from all eligible males within certain kạinaga (family or clan groups) to whom the chiefly title belongs. Chiefs in Rotuma In modern Rotuma, gagaja is the major traditional leadership position, other than mata or district representatives. Gagaja exist at two levels: Gagaj 'es itu'u These are the district chiefs, who represent each of the seven districts on the Rotuma Island Council, the main deliberative body for the island of Rotuma. In addition to these du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kato'aga
{{refimprove, date=February 2009 Kato'aga is a broad term in the Rotuman language summing up all the intricate ceremonies and gatherings of Rotuman culture. In particular, it refers to the ceremonies involved in celebrating the achievements of people of high rank, or identifying their elevation to important positions of authority within Fiji or internationally. In the past fifteen years, kato'aga have been held for Chief Justice Daniel Fatiaki upon elevation to being the head of Judiciary of Fiji, and to Major General George Konrote Major-General Jioji Konousi "George" Konrote, (born 26 December 1947) is a Fijian politician and retired Major-General of the Fiji Military who served as the President of Fiji from 2015 to 2021. After commanding a peacekeeping mission in Leba ... when he became Commander of UNIFIL. Ceremonies Rotuma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
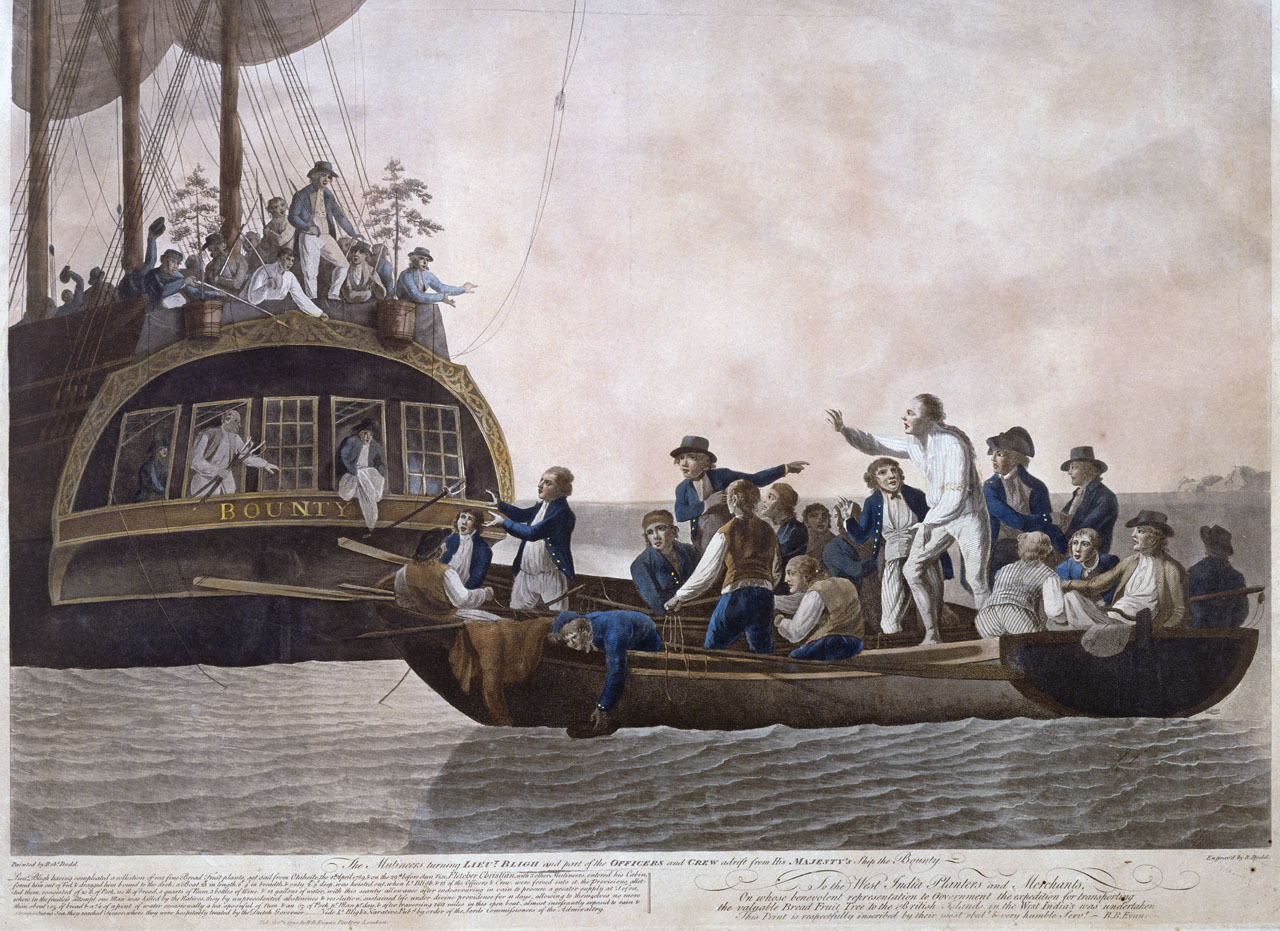
Mutineers
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among members of the military against an internal force, but it can also sometimes mean any type of rebellion against any force. Mutiny does not necessarily need to refer to a military force and can describe a political, economic, or power structure in which there is a change of power. During the Age of Discovery, mutiny particularly meant open rebellion against a ship's captain. This occurred, for example, during Ferdinand Magellan's journeys around the world, resulting in the killing of one mutineer, the execution of another, and the marooning of others; on Henry Hudson's ''Discovery'', resulting in Hudson and others being set adrift in a boat; and the notorious mutiny on the ''Bounty''. Penalty Those convicted of mutiny often faced capital pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White People
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view. Description of populations as "White" in reference to their skin color predates this notion and is occasionally found in Greco-Roman ethnography and other ancient or medieval sources, but these societies did not have any notion of a White or pan-European race. The term "White race" or "White people", defined by their light skin among other physical characteristics, entered the major European languages in the later seventeenth century, when the concept of a "unified White" achieve universal acceptance in Europe, in the context of racialized slavery and unequal social status in the European colonies. Scholarship on race distinguishes the modern concept from pre-modern descriptions, which focused on physical complexion rather than race. Prior to the modern era, no Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze") , anthem = , song_type = Regional anthem , song = " Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui" , image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg , map_alt = Location of French Polynesia , map_caption = Location of French Polynesia (circled in red) , mapsize = 290px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = Protectorate proclaimed , established_date = 9 September 1842 , established_title2 = Territorial status , established_date2 = 27 October 1946 , established_title3 = Collectivity status , established_date3 = 28 March 2003 , established_title4 = Country status (nominal title) , established_date4 = 27 February 2004 , official_languages = French , regional_languages = , capital = Papeete , coordinates = , largest_city = Fa'a'ā , demonym = French Polynesian , ethnic_groups = 66.5% unmixed Polynesians7.1% mixed Polynesians9.3% Demis1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahitians
The Tahitians ( ty, Māohi; french: Tahitiens) are the Polynesian ethnic group indigenous to Tahiti and thirteen other Society Islands in French Polynesia. The numbers may also include the modern population in these islands of mixed Polynesian and French ancestry (french: demis). Indigenous Tahitians are one of the largest Polynesian ethnic groups, behind the Māori, Samoans and Hawaiians. Pre-European period and customs The first Polynesian settlers arrived in Tahiti around 400 AD by way of Samoan navigators and settlers via the Cook Islands. Over the period of half a century there was much inter-island relations with trade, marriages and Polynesian expansion with the Islands of Hawaii and through to Rapanui. The original Tahitians cleared land for cultivation on the fertile volcanic soils and built fishing canoes. The tools of the Tahitians when first discovered were made of stone, bone, shell or wood. The Tahitians were divided into three major classes (or castes): '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Australia. Divided into two parts, ''Tahiti Nui'' (bigger, northwestern part) and ''Tahiti Iti'' (smaller, southeastern part), the island was formed from volcanic activity; it is high and mountainous with surrounding coral reefs. Its population was 189,517 in 2017, making it by far the most populous island in French Polynesia and accounting for 68.7% of its total population. Tahiti is the economic, cultural and political centre of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity and an overseas country of the French Republic. The capital of French Polynesia, Papeete, is located on the northwest coast of Tahiti. The only international airport in the region, Faaā International Airport, is on Tahiti near Papeete. Tahiti was originally settled by Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


_2007.jpg)

