|
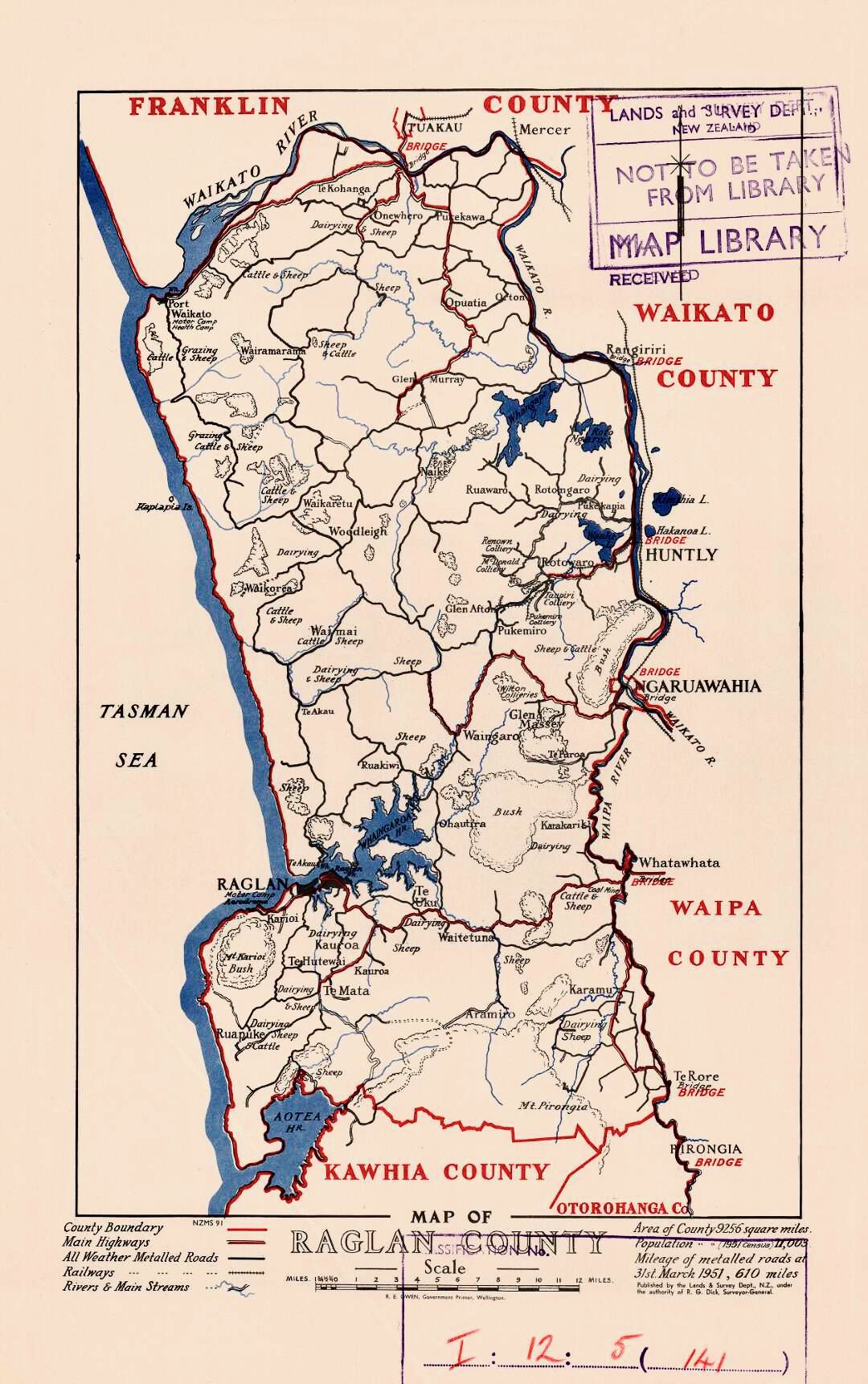
Rotowaro
Rotowaro was once a small coal mining township approximately 10 km west of Huntly in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The town was built especially for miners houses, but was entirely removed in the 1980s to make way for a large opencast mine. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "lake of glowing embers" for . History Mining by Taupiri Coal Co began in Rotowaro around 1915 after a railway to the area and a bridge over the Waikato River were completed. In 1928 it was producing 11,000 tons of coal a month. The current open cast working and the much smaller O'Reilly's, Puke Coal and Maramarua are the only remaining mines in the Waikato coalfield. It opened in 1958 and produces about 700,000 tonnes a year to make steel at Glenbrook and for limeworks, meat works, timber processing, light industry and horticulture. It was sold by Solid Energy to Bathurst Resources and Talleys in 2016. The Rotowaro Class A train station was opened on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotowaro In 1920
Rotowaro was once a small coal mining township approximately 10 km west of Huntly in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The town was built especially for miners houses, but was entirely removed in the 1980s to make way for a large opencast mine. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "lake of glowing embers" for . History Mining by Taupiri Coal Co began in Rotowaro around 1915 after a railway to the area and a bridge over the Waikato River were completed. In 1928 it was producing 11,000 tons of coal a month. The current open cast working and the much smaller O'Reilly's, Puke Coal and Maramarua are the only remaining mines in the Waikato coalfield. It opened in 1958 and produces about 700,000 tonnes a year to make steel at Glenbrook and for limeworks, meat works, timber processing, light industry and horticulture. It was sold by Solid Energy to Bathurst Resources and Talleys in 2016. The Rotowaro Class A train station was opened on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glen Afton Branch
The Glen Afton Branch was a branch railway line of 7.9 km (originally 14.1 km) in the Waikato in New Zealand, built to serve coal mines in the Awaroa district west of Huntly at Rotowaro, Pukemiro and Glen Afton. Rotowaro is Māori for "coal lake". When handed over from Public Works to NZR in 1915 it was called the Awaroa Branch, but was also known as the Glen Afton Branch to about 1974, then as the Rotowaro Branch to 3 November 1988, then as the Rotowaro Industrial Line. By 2014 it was again named the Rotowaro Branch. History The first 5 km was authorised in 1910 and required a road-rail bridge over the Waikato River, with an extension which carried the railway over the main highway. The bridge, constructed from 1911 to October 1914, had 10 spans of Australian hardwood (8 of 30.5m and 2 of 12.2m) on steel and reinforced concrete piers. The nearby Wilton Collieries Co complained that they too did not have public money put into building their line and river brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotowaro Carbonisation Plant
The Rotowaro Carbonisation Plant, also known as the Waikato Carbonisation Plant, was a coal processing plant in the Rotowaro/Huntly area, New Zealand. It was also the first plant to use the Lurgi process in the Southern Hemisphere. History The first of its kind in the Southern Hemisphere, the plant was constructed in the late 1930s to convert otherwise unusable low-quality coal from the nearby Rotowaro Coal Mines into carbon briquettes A briquette (; also spelled briquet) is a compressed block of coal dust or other combustible biomass material (e.g. charcoal, sawdust, wood chips, peat, or paper) used for fuel and kindling to start a fire. The term derives from the French wor ..., which were then used for domestic heating. The coal was carbonised using the Lurgi process, the result being coke and charcoal, with tar and creosote as by-products. The tar was used with the char to create the briquettes. Waste from the plant was discharged directly into the nearby Awaroa stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntly, New Zealand
Huntly ( mi, Rahui-Pōkeka) (population ) is a town in the Waikato district and region of the North Island of New Zealand. It was on State Highway 1 (until Huntly bypass opened in March 2020), south of Auckland and north of Hamilton. It is situated on the North Island Main Trunk (NIMT) railway (served by Te Huia since 6 April 2021 at a rebuilt Raahui Pookeka-Huntly Station) and straddles the Waikato River. Huntly is within the Waikato District which is in the northern part of the Waikato region local government area. History and culture Originally settled by Māori, European migrants arrived in the area some time in the 1850s. The Huntly name was adopted in the 1870s when the postmaster named it after Huntly, Aberdeenshire in Scotland. He used an old 'Huntley Lodge' stamp to stamp mail from the early European settlement. The ''Lodge'' was later dropped and the spelling changed to also drop the additional 'e'. The railway from Auckland reached Huntly in 1877, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Energy
Solid Energy was the largest coal mining company in New Zealand and is a state owned enterprise of the New Zealand Government. The company was formed from the former government department State Coal Mines. It was then established as a state owned enterprise called Coal Corporation in 1987 (known as Coalcorp), and renamed Solid Energy New Zealand Limited in 1997. In 2015, it had a turnover of NZ$369.8 million and produced 2.8 million tonnes of coal. The company mined extensively in New Zealand's Waikato and the West Coast regions. Approximately half the coal mined was exported, as it is high value with little moisture, sulphur, or other impurities. Much of this is to China, India and Japan where it is used in the power generation and coke industries and for the manufacture of steel and other metals. Major domestic users included the Huntly Power Station and New Zealand Steel at Glenbrook. Solid Energy went into voluntary administration in August 2015. On 31 October 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Troup (architect)
Sir George Alexander Troup (21 October 1863 – 4 October 1941) was a New Zealand architect, engineer and statesman. He was nicknamed "Gingerbread George" after his most famous design, the Dunedin Railway Station in the Flemish Renaissance style (he preferred his alternative design in the Scottish Baronial style). He was the first official architect of the New Zealand Railways. He designed many other stations, including Lower Hutt and Petone. Early life and education He was born in London, England. His family returned to Edinburgh, Scotland soon after he was born. His widowed mother sent him to Robert Gordon's College, Aberdeen, where he was entitled to free board and tuition as the son of an Aberdeen burgess. He trained as an architect and engineer under C.E. Calvert in Edinburgh, and in 1882 was employed as a draughtsman by architect J.J.A. Chesser. Career He emigrated to New Zealand in 1884. Joining the Survey Department when he arrived in Dunedin, he worked in remote sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato District
Waikato District is a territorial authority of New Zealand, in the northern part of Waikato region, North Island. Waikato District is administered by the Waikato District Council, with headquarters in Ngāruawāhia. The district is centred to the north and west of the city of Hamilton, and takes in much of the northern Waikato Plains and also the Hakarimata Range. The north of the district contains swampy floodplain of the Waikato River and several small lakes, of which the largest is Lake Waikare. Other than Ngāruawāhia, the main population centres are Huntly, Raglan, and Te Kauwhata. The main industries in the district are dairy farming, forestry, and coal mining. There is a major coal-fired power station at Huntly. Te Kauwhata is at the centre of a major wine region. Demographics At the 2006 census the district had a population of 43,959. Of these, 6834 lived in Huntly, 5106 in Ngāruawāhia, 2637 in Raglan, and 1294 in Te Kauwhata. In 2010, the district acquired p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Whangape
Lake Whangape (also written as Wangape, Whangapu, or Whangapae) is shallow, supertrophic, lateral and the second largest lake (after Lake Waikare) in the lower Waikato River basin in New Zealand. One source said the name translated to 'a large sheet of water', another that it was a chief's name. From the 1860s the catchment has lost most of its forest cover and the lake has changed from clear and rich in aquatic vegetation to a murky, algal lake. Geology The lake is a lateral lake, dammed by a levee of the Waikato, probably built up as a result of sea-level rise and sediment from the Taupo Volcanic Zone about 2,000 years ago. To the west of the lake the rocks are made up of the 30m year old (Tertiary) Whaingaroa and Glen Massey Formations, the Whaingaroan rocks of the Te Kuiti Group. The Karapiro Formation (part of the Walton subgroup) outcrops towards the east of the lake. Hot springs Two springs (ranging from to and many seepages occur along Te Maire Stream, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathurst Resources
Bathurst Resources, along with a number of subsidiaries, is a coal mining company in New Zealand that was established in 2010. Company history The company was originally based in Perth, Western Australia, and incorporated on 30 May 2007, listing on the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) on 19 December 2007. The company's purpose at the time was to develop its interest in the Mt Clifford nickel, base metals and gold exploration project, in WA. In October 2008 it withdrew from this project, and instead acquired a coal producer in Kentucky, US. By November 2009 Bathurst Resources ceased producing coal from Eastern Kentucky LLC, on the return of this company to its original owners. As a result, Bathurst Resources carried out a strategic realignment in early 2010, with a view to producing coal in New Zealand. Bathurst Resources Limited was incorporated in New Zealand on 16 November 2010. The name of this company was changed to BR Coal Pty Ltd on 6 December 2013, with Pier Westerhui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talley's Group
Talley's Group Limited is a privately owned, New Zealand-based agribusiness company that provides seafood, vegetable and dairy products. Talley's was established in 1936 in Motueka by Ivan Peter Talijancich (later known as Ivan Talley) as a manufacturer of seafood, and has since grown into one of the largest agribusiness companies in New Zealand. The company's Port Motueka site incorporates the Group Head Office, the Seafood Division and the Dairy Division. The Vegetable Division began operations in 1978 at Motueka, but has since been relocated to Blenheim and Ashburton. The meat division, AFFCO Holdings, has been majority-owned by Talley's since the early 2000s. In 2016 Talley's diversified into coal mining in a joint purchase with Bathurst Resources of former Solid Energy mines at Stockton, Rotowaro and Maramarua. History The company's first fishing vessel was the ''Janie Seddon''. Built in the United Kingdom in 1903, the ''Janie Seddon'' was one of two submarine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |