|
Rossend Castle
Rossend Castle is a historic building in Burntisland, a town on the south coast of Fife, Scotland. History A keep, known as the Tower of Kingorne Wester, was in existence on the site from 1119. It was later referred to as Burntisland Castle, and by 1382 was called Abbot's Hall, as it was the home of the Abbot of Dunfermline. The present building is largely of the 16th century, though with a 13th-century basement, which contains lancet windows and may represent the remains of a chapel. It was rebuilt by Peter Durie of Durie from 1552, and the arms of Abbot George Durie, and the date 1554, appear over the main door. During the war of the Rough Wooing the English soldier John Luttrell landed at Burntisland on 28 December 1547. He burnt boats and buildings at the pier, and the owners of Rossend surrendered the castle to him. Mary, Queen of Scots, visited during her short personal reign (1561–1567). On 14 February 1562, the French messenger and poet Chastelard was discovered hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peder Munk
Peder Munk of Estvadgård (1534–1623), was a Danish navigator, politician, and ambassador, who was in charge of the fleet carrying Anne of Denmark to Scotland. The events of the voyage led to witch trials and executions in Denmark and Scotland. Career Peder Munk was the son of Ludvig Munk (d. 1537) and Kirstin Pedersdatte Lykke. He was born at Lønborggård, Lønborg, Ringkøbing, Denmark, on 22 April 1534. Peder's younger brother Ludvig Munk was also a sailor and a soldier, whose daughter Kirsten Munk married Christian IV of Denmark in 1615. Peder Munk's main estate from 1566 was Estvadgård in Skive Kommune. In 1575 Peder Munk was made Admiral of Denmark, the Admiral of the Realm or 'Rigsadmiral', and in 1588 was one of the council, the Rigsraadet of regents for Christian IV. Peder Munk is said to have provided a miniature warship for the young king in a Jutland lake. On 20 August 1589 Peder Munk and others accepted an agreement at Helsingør over the rule of the islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emblem Book
An emblem book is a book collecting emblems (allegorical illustrations) with accompanying explanatory text, typically morals or poems. This category of books was popular in Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries. Emblem books are collections of sets of three elements: an icon or image, a motto, and text explaining the connection between the image and motto. The text ranged in length from a few lines of verse to pages of prose. Emblem books descended from medieval bestiaries that explained the importance of animals, proverbs, and fables. In fact, writers often drew inspiration from Greek and Roman sources such as Aesop's Fables and Plutarch's Lives. Definition Scholars differ on the key question of whether the actual emblems in question are the visual images, the accompanying texts, or the combination of the two. This is understandable, given that first emblem book, the ''Emblemata'' of Andrea Alciato, was first issued in an unauthorized edition in which the woodcuts were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in 1866 as the Edinburgh Museum of Science and Art, renamed in 1904, and for the period between 1985 and the merger named the Royal Museum of Scotland or simply the Royal Museum), with international collections covering science and technology, natural history, and world cultures. The two connected buildings stand beside each other on Chambers Street, by the intersection with the George IV Bridge, in central Edinburgh. The museum is part of National Museums Scotland. Admission is free. The two buildings retain distinctive characters: the Museum of Scotland is housed in a modern building opened in 1998, while the former Royal Museum building was begun in 1861 and partially opened in 1866, with a Victorian Venetian Renaissance facade and a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Renaissance Painted Ceilings
Scottish renaissance painted ceilings are decorated ceilings in Scottish houses and castles built between 1540 and 1640. This is a distinctive national style, though there is common ground with similar work elsewhere, especially in France, Spain and Scandinavia. An example in England, at Wickham, Hampshire, was recorded in 1974. There are records of over 100 examples, and a much smaller number of painted ceilings survive in-situ today. Some salvaged painted beams and boards are stored by Historic Environment Scotland. The paintings at Crathes Castle, dating from 1597 and 1602 are probably the best known. Imported timber Most surviving examples are painted simply on the boards and joists forming the floor of the room above. Rooms or galleries in attic storeys were fully lined with thin pine boarding and painted. Oak and pine timber was imported from Denmark–Norway, Sweden, and further afield and known as "Eastland" timber. The fashion was superseded by decorative plasterwork an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacGibbon And Ross
David MacGibbon (2 April 1831 – 20 February 1902) and Thomas Ross (10 November 1839 – 4 December 1930) were Scottish architects. Their practice, MacGibbon and Ross was established in 1872 and continued until 1914. They are best known today for their comprehensive published surveys of Scotland's architectural heritage. David MacGibbon David MacGibbon LLD was born in Edinburgh, into a family of builders, and was educated at the Royal High School. He attended the University of Edinburgh from 1846–49, but did not graduate. In 1851 he joined the London office of architect William Burn, and made study tours to Europe during the 1850s. From 1856 he went into practice with his father Charles, drawing details for houses. By 1858 he had opened his own office in Edinburgh, later becoming architect to the Merchant Company of Edinburgh, involving work to the city's schools. He was the principal architect to the Royal Bank of Scotland from 1861 (succeeding David Rhind), designing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
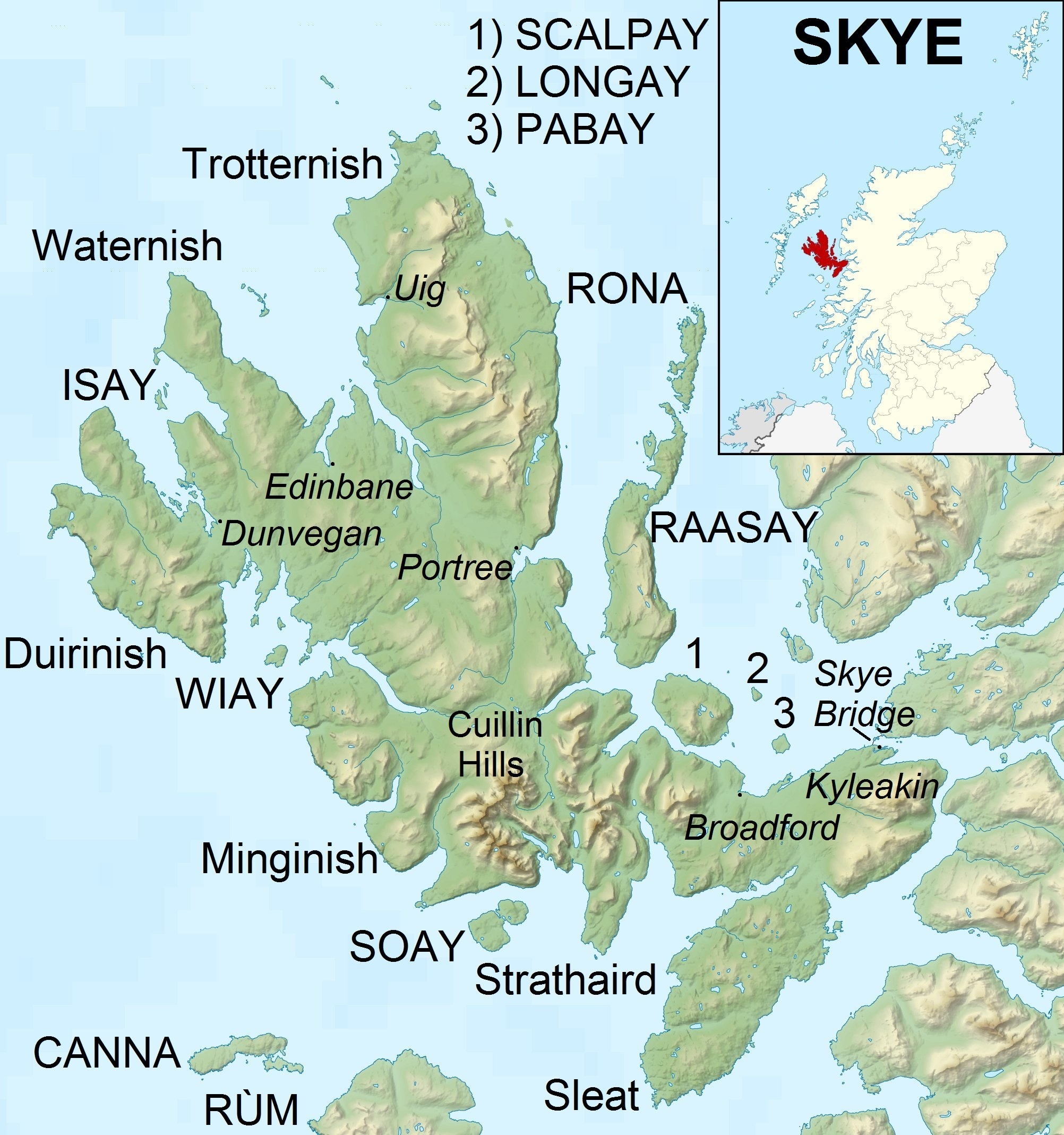
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origins. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of MacLeod and MacDonald. The island was considered to be under Norwegian suzerainty until the 1266 Treaty of Perth, which transferred control over to Scotland. The 18th-century Jacobite risings led to the breaking-up of the clan system and later clearanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, first as a senior commander in the Parliamentarian army and then as a politician. A leading advocate of the execution of Charles I in January 1649, which led to the establishment of the Republican Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, he ruled as Lord Protector from December 1653 until his death in September 1658. Cromwell nevertheless remains a deeply controversial figure in both Britain and Ireland, due to his use of the military to first acquire, then retain political power, and the brutality of his 1649 Irish campaign. Educated at Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge, Cromwell was elected MP for Huntingdon in 1628, but the first 40 years of his life were undistinguished and at one point he contemplated emigration to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annie Cameron
Annie Isabella Cameron (1897-1973) was a Scottish historian. Biography She was the daughter of Mary Sinclair, and James Cameron, a Glasgow engineer. She studied history at the University of Glasgow and the University of St Andrews. She wrote a doctoral thesis on Bishop Kennedy of St Andrews. She worked at the Scottish Record Office and in 1938 married George Dunlop, proprietor of the ''Kilmarnock Standard''. She died in 1973. Marcus Merriman, a historian of the Rough Wooing acknowledged Annie Cameron, Marguerite Wood, and Gladys Dickinson for their work publishing 16th-century primary sources. He praised Cameron for her "stunning" edition of the Scottish correspondence of Mary of Guise Mary of Guise (french: Marie de Guise; 22 November 1515 – 11 June 1560), also called Mary of Lorraine, was a French noblewoman of the House of Guise, a cadet branch of the House of Lorraine and one of the most powerful families in France. She ..., "placing in the hands of the researcher som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wemyss Of Logie
John Wemyss younger of Logie, (1569-1596), was a Scottish courtier, spy, and subject of the ballad "The Laird o Logie", beheaded for plotting to blow up a fortification at Veere in the Netherlands Life John Wemyss was a brother or son, the family details are unclear, of Andrew Wemyss of Myrecairnie and Logie (later Lord Myrecairnie, a law lord). He was also a cousin of David Wemyss, Laird of West Wemyss, in Fife, Scotland. He was usually known as "Logie" after the family estate at Logie in Fife. He was a valet or varlet in the bed chamber of James VI of Scotland and his sister Euphemia was a lady-in-waiting to Anne of Denmark. He is remembered for his relationship and marriage to Margaret Winster or Vinstarr, a Danish woman who helped him escape from prison. Quarrel with the Duke of Lennox In 1590 James VI gave him £333 Scots from the subsidy money that Queen Elizabeth had given him. On 7 January 1591 he came to the attention of Robert Bowes, the English diplomat in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Wauchope Of Niddrie
Archibald Wauchope of Niddrie ( – 1597) Scottish landowner and rebel. He was the son of Robert Wauchope of Niddrie, who died in 1598, and Margaret Dundas, daughter of James Dundas of Dundas. He was known as the "Laird of Niddrie, younger". The Wauchope lands were at Niddrie, Edinburgh, also called "Niddrie-Merschell". Career In 1580 at Peffermill, Wauchope and his servant Joseph Reidpath killed Gilbert Home, a servant of John Bothwell, Abbot of Holyrood, who had criticised him for hitting an officer-at-arms. The Home family accepted Wauchope's humiliation and repentance. In 1588 Wauchope and his father were involved in the murders of James and John Giffart of Sherriffhall, Robert Caise in Dalkeith, and John Edmiston, brother of the Laird of Womett. He was captured at Bridgend on 12 May 1589 by Andrew Edmonstone, after a short siege was ended by James VI, and brought to Edinburgh. James Sandilands of Slamannan helped Wauchope escape from a window of Edinburgh's Tolbooth in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Stewart, 5th Earl Of Bothwell
Francis may refer to: People *Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome * Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters *Francis (surname) Places * Rural Municipality of Francis No. 127, Saskatchewan, Canada * Francis, Saskatchewan, Canada **Francis (electoral district) * Francis, Nebraska *Francis Township, Holt County, Nebraska * Francis, Oklahoma *Francis, Utah Other uses * ''Francis'' (film), the first of a series of comedies featuring Francis the Talking Mule, voiced by Chill Wills *''Francis'', a 1983 play by Julian Mitchell * FRANCIS, a bibliographic database * ''Francis'' (1793), a colonial schooner in Australia * Francis turbine, a type of water turbine * Francis (band), a Sweden-based folk band * Francis, a character played by YouTuber Boogie2988 See also * Saint Francis (other) * Francies, a surname, including a list of people with the name * Francisco (disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)