|
Romula
Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia. History The Roman city of Romula lay on an earlier Dacian settlement called Malva. It received the title of municipium during the rule of Hadrian (117–138) and the title of colonia during that of Septimius Severus (193–211). The city had two belts of fortifications and two castra, where soldiers of the Legiones VII ''Claudia'' and XXII ''Primigenia'' were temporarily stationed, alongside a permanent unit ('' numerus'') of Syrian archers. See also * Dacian davae * List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia * Dacia * Roman Dacia Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia Inferior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last one which is split between Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last one which is split between Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia Malvensis
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last one which is split between Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohors I Flavia Commagenorum
Cohors rimaFlavia Commagenorum uingenariaequitata sagittaria? (" stpart-mounted 00 strongcohort of Commagenes") was a Roman auxiliary regiment containing cavalry contingents. The cohort stationed in Dacia at castra Acidava, castra Jidava, castra Romula, castra of Sfârleanca, castra of Slăveni and castra of Drajna de Sus. See also * List of Roman auxiliary regiments This article lists ', non-legionary auxiliary regiments of the imperial Roman army, attested in the epigraphic record, by Roman province of deployment during the reign of emperor Hadrian ( AD 117–138). The index of regimental names expla ... References * Academia Română: Istoria Românilor, Vol. 2, Daco-romani, romanici, alogeni, 2nd. Ed., București, 2010, * Constantin C. Petolescu: Dacia - Un mileniu de istorie, Ed. Academiei Române, 2010, * Cristian M. Vlădescu: Fortificațiile romane din Dacia Inferior, Craiova, 1986 * Petru Ureche: Tactică, strategie și specific de luptă la cohortele e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelendava (castra)
Pelendava was once a fort in the Roman province of Dacia. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition ... Notes External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman Dacia Archaeological sites in Romania Roman legionary fortresses in Romania History of Craiova Historic monuments in Dolj County {{Dacia-stub ro:Castrul roman Pelendava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra Nova, Dacia
Castra Nova was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition ... External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Notes Roman Dacia Archaeological sites in Romania Roman legionary fortresses in Romania History of Oltenia {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidava (castra)
Castra Acidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia. The toponym is attested in the Peutinger Table. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition ... External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Notes Roman legionary fortresses in Romania History of Oltenia {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
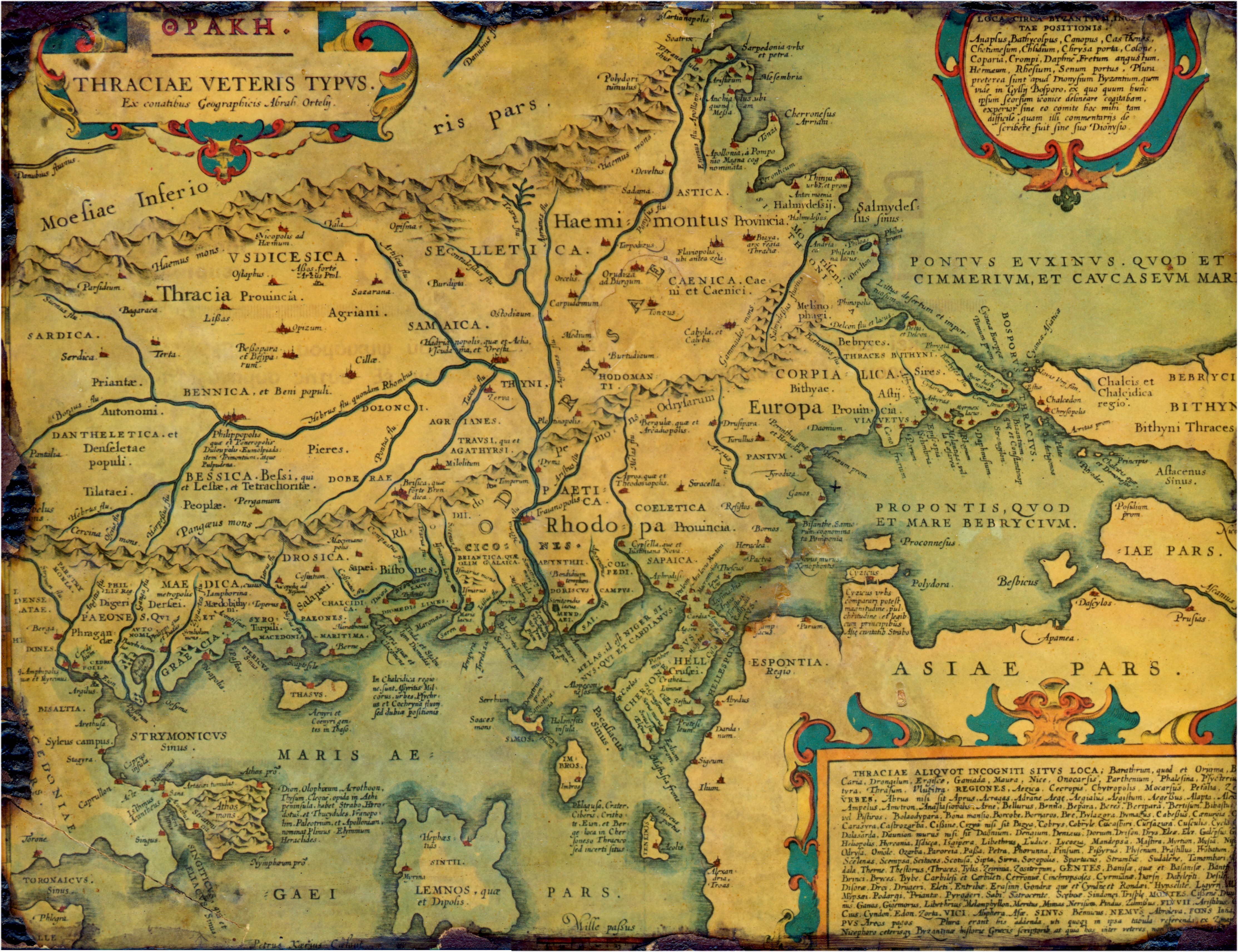
Dacian Towns
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobrosloveni
Dobrosloveni is a commune in Olt County, Oltenia, Romania. It is composed of five villages: Dobrosloveni, Frăsinetu, Potopinu, Reșca and Reșcuța. According to the 2002 census, it had a population of 3,909, of which 99% were ethnic Romanians. The commune's village of Reşca contains remains of an ancient Roman municipium, named Romula Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia. History The Roman ci ... or Malva. References Communes in Olt County Localities in Oltenia {{Olt-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reşca
Dobrosloveni is a commune in Olt County, Oltenia, Romania. It is composed of five villages: Dobrosloveni, Frăsinetu, Potopinu, Reșca and Reșcuța. According to the 2002 census, it had a population of 3,909, of which 99% were ethnic Romanians. The commune's village of Reşca contains remains of an ancient Roman municipium, named Romula Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia. History The Roman ... or Malva. References Communes in Olt County Localities in Oltenia {{Olt-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |