|
Rogožarski SIM-Xa
Rogožarski () was a Yugoslav aircraft manufacturer. History Officially established on 22 April 1924 under the name of ''Prva Srpska Fabrika Aeroplana Živojin Rogožarski'' ( en, First Serbian Aircraft Factory of Živojin Rogožarski), the factory was responsible along with Ikarus for most of Yugoslavia's air industry between the world wars. Initially, the factory repaired aircraft confiscated in the First World War, and soon started to manufacture local aircraft, and licensed manufacture as well. Nationalised in 1946, the factory was merged along with Zmaj into Ikarus which continued in the aeronautical industry until 1962. The factory Rogožarski has made a total of 286 aircraft. Aircraft See also * Aircraft industry of Serbia Kingdom of Serbia became part of the new state, Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. which was formed on 1 December 1918. Even though the industry was on a very low level of development, the state was among the first 10 countries in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astronautics. Aerospace organizations research, design, manufacture, operate, or maintain both aircraft and spacecraft. The beginning of space and the ending of the air is considered as 100 km (62 mi) above the ground according to the physical explanation that the air pressure is too low for a lifting body to generate meaningful lift force without exceeding orbital velocity. Overview In most industrial countries, the aerospace industry is a cooperation of the public and private sectors. For example, several states have a civilian space program funded by the government, such as NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration in the United States, European Space Agency in Europe, the Canadian Space Agency in Canada, Indian Space Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogožarski SIM-VI
The Rogožarski SIM-VI (Serbian Cyrillic:Рогожарски СИМ-VI) was a single-engined, two-seat, low wing aircraft designed as trainer in Yugoslav before World War II. It was designed and built at the Rogožarski factory in Belgrade. Design and development The SIM-VI was designed by engineer Sima Milutinović in the early 1930s as an inexpensive trainer plane that would enable expansion of sports aviation. The project was in suspension until 1936, when a prototype was constructed, and the maiden flight was made in 1937. The aircraft was a low wing monoplane of fabric-covered wooden structure. A four-cylinder 50 hp Walter Mikron engine drove a two-bladed wooden propeller. The plane had tandem seating and was intended for civilian use, for the training of sports pilots, demonstration flights and travel. The wings were of thin profile, only 6% of trapezoidal shape with rounded ends. On each side, the wings were stretched with molded wire ties. Variants *Rogozarski S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogožarski Aircraft
Rogožarski () was a Yugoslav aircraft manufacturer. History Officially established on 22 April 1924 under the name of ''Prva Srpska Fabrika Aeroplana Živojin Rogožarski'' ( en, First Serbian Aircraft Factory of Živojin Rogožarski), the factory was responsible along with Ikarus for most of Yugoslavia's air industry between the world wars. Initially, the factory repaired aircraft confiscated in the First World War, and soon started to manufacture local aircraft, and licensed manufacture as well. Nationalised in 1946, the factory was merged along with Zmaj into Ikarus which continued in the aeronautical industry until 1962. The factory Rogožarski has made a total of 286 aircraft. Aircraft See also * Aircraft industry of Serbia Kingdom of Serbia became part of the new state, Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. which was formed on 1 December 1918. Even though the industry was on a very low level of development, the state was among the first 10 countries in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Industry Of Serbia
Kingdom of Serbia became part of the new state, Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. which was formed on 1 December 1918. Even though the industry was on a very low level of development, the state was among the first 10 countries in the world which developed their own aircraft production. Originally, only the parts produced in foreign factories were assembled, but very soon the production of domestic components began, so as the engineering. The forerunner of the domestic aircraft industry was the Airplane workshop (''Aeroplanska radionica''), which was established in 1920, at the airfield in Novi Sad. The assembling of the trial series of Hansa-Brandenburg C.I. The series was named SBr, as this type of plane was known in Serbia as ''srednji Brandenburg'' ("middle Brandenburg"). From 1923 to 1941, there were 7 aircraft factories in Serbia, 4 of which were located in the capital, Belgrade, and 2 airplane engines factories. Also, some planes were produced in the aircraft worksh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
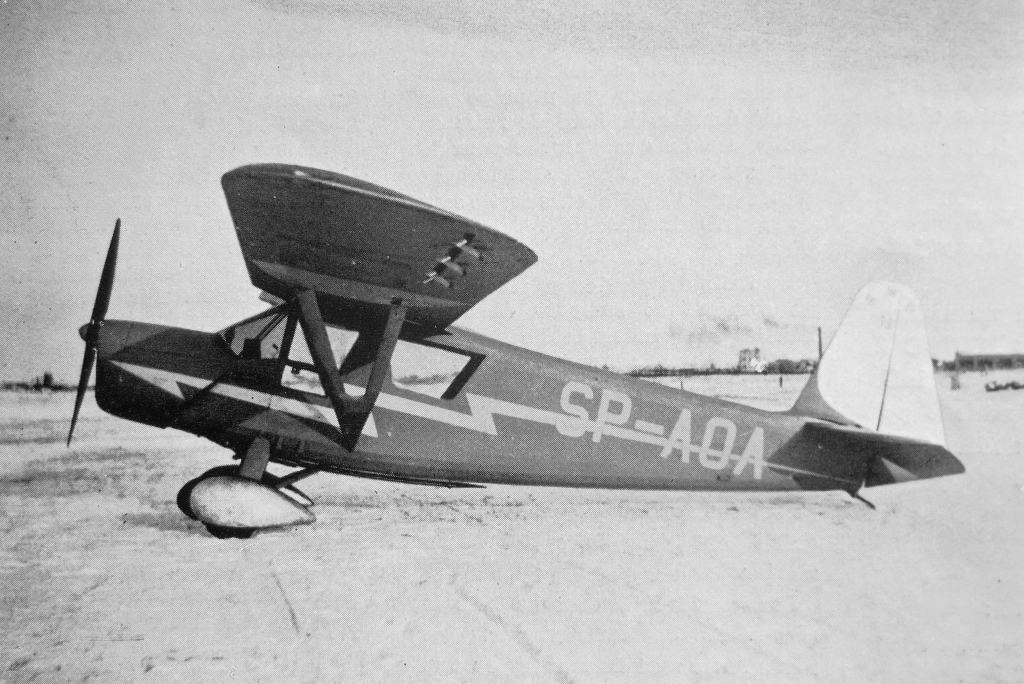
RWD 13
The RWD 13 was a Polish touring plane of 1935, three-seater high-wing monoplane, designed by the RWD team. It was the biggest commercial success of the RWD. Development The RWD 13 was a touring plane, developed from a line of sports planes RWD 6 (a winner of Challenge 1932 international touring aircraft contest) and RWD 9 (a winner of Challenge 1934). It was designed by Stanisław Rogalski and Jerzy Drzewiecki of the RWD team, in the DWL workshops (''Doświadczalne Warsztaty Lotnicze'') in Warsaw, for and order of the LOPP paramilitary organization. The prototype was constructed using parts of a broken up RWD 6 (initially it was even supposed to be designated RWD 6bis), but its construction was more similar to newer RWD 9. It first flew on 15 January 1935 (registration SP-AOA). Since the RWD 13 was not supposed to be a competition aircraft, the main differences from the RWD 9 were: an inline engine with lower power output, instead of a radial engine, and simpler wing mechanizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RWD 8
The RWD 8 was a Polish parasol wing monoplane trainer aircraft produced by RWD. It was used from 1934 to 1939 by the Polish Air Force and civilian aviation. Development The RWD 8 was designed in response to a Polish Air Force requirement in 1931 for a basic trainer aircraft. It was designed by the RWD team of Stanisław Rogalski, Stanisław Wigura and Jerzy Drzewiecki. The first prototype (registration SP-AKL), was flown in early 1933. It won the contest for the new Polish military trainer, against the PZL-5bis and Bartel BM-4h biplanes. It was considered a very stable and well-handling aircraft. Since the DWL (''Doświadczalne Warsztaty Lotnicze'') workshops – a manufacturer of RWD designs – had limited production capability, the Polish military decided to produce the aircraft in a nationalized factory PWS (''Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów''). DWL gave away the licence free of charge, only for covering design costs. PWS produced aircraft for both military and civilian avia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansa-Brandenburg C
Hansa und Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke (more usually just Hansa-Brandenburg) was a German aircraft manufacturing company that operated during World War I. It was created in May 1914 by the purchase of ''Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke'' by Camillo Castiglioni, who relocated the factory from Liebau to Brandenburg an der Havel. Brandenburg's chief designer, Ernst Heinkel was retained by the new enterprise. By Autumn 1915, it had become the largest aircraft manufacturer in Germany, with a capital of 1,500,000 Marks, 1,000 employees, and two more factories - one in Rummelsburg, Berlin, and one in Wandsbek, Hamburg. Although manufacturing was carried out in Germany, Castiglioni was an Austrian, and many of the firm's military aircraft were produced for the Austro-Hungarian aviation corps. The firm became especially known for a highly successful series of floatplane fighters and reconnaissance aircraft that were used by the Imperial German Navy during the war. Hansa-Brandenburg did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansa-Brandenburg B
Hansa und Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke (more usually just Hansa-Brandenburg) was a German aircraft manufacturing company that operated during World War I. It was created in May 1914 by the purchase of ''Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke'' by Camillo Castiglioni, who relocated the factory from Liebau to Brandenburg an der Havel. Brandenburg's chief designer, Ernst Heinkel was retained by the new enterprise. By Autumn 1915, it had become the largest aircraft manufacturer in Germany, with a capital of 1,500,000 Marks, 1,000 employees, and two more factories - one in Rummelsburg, Berlin, and one in Wandsbek, Hamburg. Although manufacturing was carried out in Germany, Castiglioni was an Austrian, and many of the firm's military aircraft were produced for the Austro-Hungarian aviation corps. The firm became especially known for a highly successful series of floatplane fighters and reconnaissance aircraft that were used by the Imperial German Navy during the war. Hansa-Brandenburg did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogožarski R-313
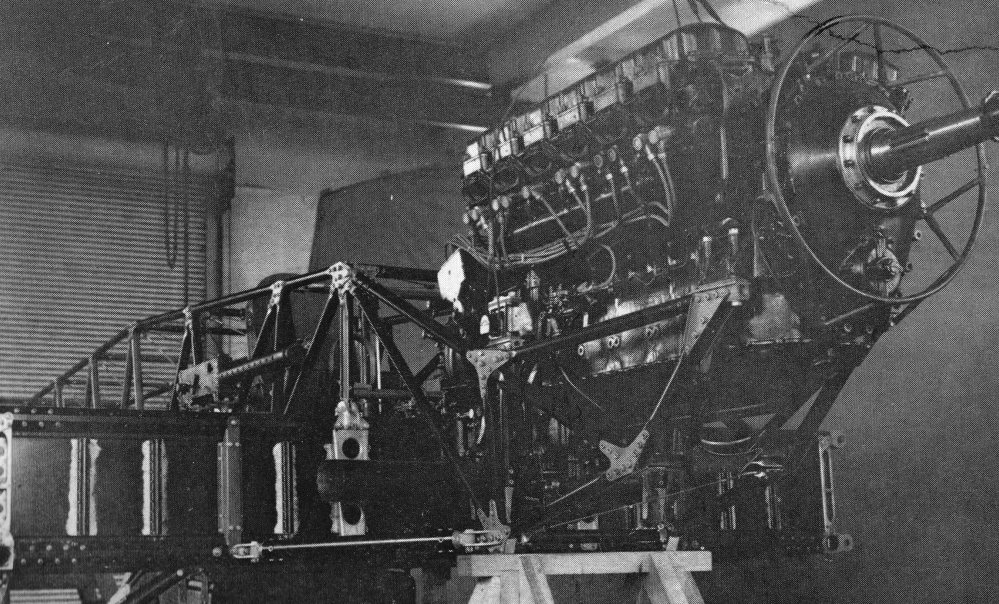
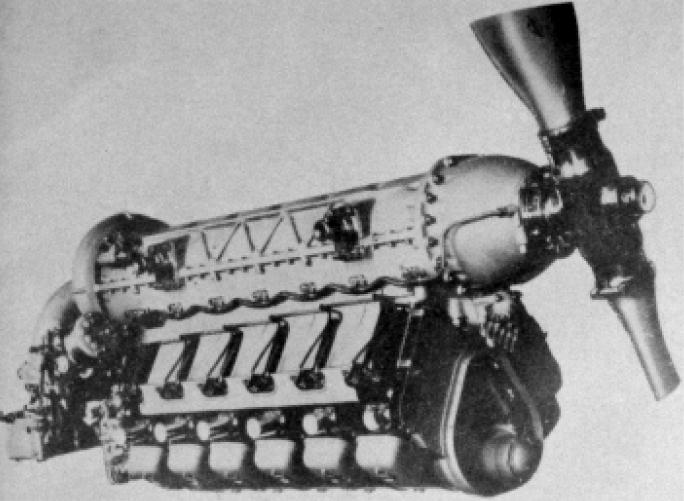
The Rogozarski R-313 (Рогожарски Р-313 in Serbian) was a two-seat twin-engined monoplane designed as a fighter/light bomber/reconnaissance aircraft in Yugoslavia before World War II. It was designed and built at the Rogozarski factory in Belgrade. Design, construction and development The Rogozarski R-313 was a two-seater twin-engined fighter/light bomber/reconnaissance aircraft. It was powered by two in-line Walter Sagitta IIR engines, both fitted with a compressor; each was capable of 493 hp. The elliptical, wooden fuselage was covered in plywood which was also used to 'skin' the round-tipped, trapezoidal wings. The engine nacelles also housed the landing gear. The tail-wheel was, like the main landing gear, retractable. The fuel tank was located in the centre section between the wings. The reconnaissance variant of this aircraft was due to be equipped with a camera, a radio, a fixed 20mm cannon and a single FN 7.9mm machine gun, flexibly mounted. As a light bomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogožarski Brucoš
Rogožarski Brucoš (Serbian Cyrillic:Рогожарски Бруцош) was a single-engine, two-seat, low wing monoplane aircraft designed as a trainer in Yugoslavia before World War II. It was designed and built in the Rogožarski aircraft factory in Belgrade. Design and development In order to replace its obsolete pilot training aircraft, the Zmaj Fizir FN biplane, the Yugoslav Royal Air Force (YRAF) Command held a competition in mid-1936 to develop a new aircraft for training pilots. The new aircraft was to be a low wing aircraft so that Yugoslavian pilots could get accustomed to piloting the fighters that the Yugoslav Royal Air Force was using, the Hawker Hurricane, Messerschmitt Bf 109 and the Rogožarski IK-3. The Rogožarski Factory decided to participate in the competition and engaged two well-known aerospace engineers, Miroslav Nenadović and Mitrović Milenko-Spirta, who began working on the design. Building of the prototype started the same year, and it flew for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogožarski SIM-XIV-H
The Rogožarski SIM-XIV-H ( sr, Рогожарски СИМ-XIV-Х) was a 1930s Yugoslav coastal reconnaissance floatplane and light bomber, twin-engined, with three crew members. It was designed and built at the Rogožarski factory in Belgrade. Design and development In January 1937, the Yugoslav Navy Air Service issued a specification for a twin-engined coastal reconnaissance aircraft,Green 1962, p. 201. to replace the Ikarus IO flying boat. To meet this requirement, Rogozarski proposed the SIM-XIV-H, a twin-engined floatplane designed by Sima Milutinović, and this type was selected by the Yugoslav navy, with the first prototype making its maiden flight on 8 February 1938. The SIM-XIV-H was a low winged monoplane of mixed wood and metal construction, with an oval section monocoque fuselage. The wing was braced to the fuselage by steel-tube struts, with the tail also braced. It had a glazed nose, with a gun turret armed with a single machine gun mounted above the nose. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |