|
Robot Kinematics
In robotics, robot kinematics applies geometry to the study of the movement of multi-degree of freedom kinematic chains that form the structure of robotic systems. The emphasis on geometry means that the links of the robot are modeled as rigid bodies and its joints are assumed to provide pure rotation or translation. Robot kinematics studies the relationship between the dimensions and connectivity of kinematic chains and the position, velocity and acceleration of each of the links in the robotic system, in order to plan and control movement and to compute actuator forces and torques. The relationship between mass and inertia properties, motion, and the associated forces and torques is studied as part of robot dynamics. Kinematic equations A fundamental tool in robot kinematics is the kinematics equations of the kinematic chains that form the robot. These non-linear equations are used to map the joint parameters to the configuration of the robot system. Kinematics equatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5R Robot
5R may refer to : * Yaesu VX-5R, an ultra-compact amateur radio transceiver * Karthago Airlines IATA designator * Madagascar Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ... aircraft registration code * A standard consumer print size for photographs. See Standard photographic print sizes. *5R, the production code for the 1980 ''Doctor Who'' serial '' Full Circle'' See also * R5 (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multibody System
Multibody system is the study of the dynamic behavior of interconnected rigid or flexible bodies, each of which may undergo large translational and rotational displacements. Introduction The systematic treatment of the dynamic behavior of interconnected bodies has led to a large number of important multibody formalisms in the field of mechanics. The simplest bodies or elements of a multibody system were treated by Newton (free particle) and Euler (rigid body). Euler introduced reaction forces between bodies. Later, a series of formalisms were derived, only to mention Lagrange’s formalisms based on minimal coordinates and a second formulation that introduces constraints. Basically, the motion of bodies is described by their kinematic behavior. The dynamic behavior results from the equilibrium of applied forces and the rate of change of momentum. Nowadays, the term multibody system is related to a large number of engineering fields of research, especially in robotics and vehi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Velocity
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object rotates or revolves relative to a point or axis). The magnitude of the pseudovector represents the ''angular speed'', the rate at which the object rotates or revolves, and its direction is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement. The orientation of angular velocity is conventionally specified by the right-hand rule.(EM1) There are two types of angular velocity. * Orbital angular velocity refers to how fast a point object revolves about a fixed origin, i.e. the time rate of change of its angular position relative to the origin. * Spin angular velocity refers to how fast a rigid body rotates with respect to its center of rotation and is independent of the choice of origin, in contrast to orbital angular ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobian Matrix And Determinant
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix (, ) of a vector-valued function of several variables is the matrix of all its first-order partial derivatives. When this matrix is square, that is, when the function takes the same number of variables as input as the number of vector components of its output, its determinant is referred to as the Jacobian determinant. Both the matrix and (if applicable) the determinant are often referred to simply as the Jacobian in literature. Suppose is a function such that each of its first-order partial derivatives exist on . This function takes a point as input and produces the vector as output. Then the Jacobian matrix of is defined to be an matrix, denoted by , whose th entry is \mathbf J_ = \frac, or explicitly :\mathbf J = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac \end = \begin \nabla^ f_1 \\ \vdots \\ \nabla^ f_m \end = \begin \dfrac & \cdots & \dfrac\\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ \dfrac & \cdots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolute Joint
A revolute joint (also called pin joint or hinge joint) is a one- degree-of-freedom kinematic pair used frequently in mechanisms and machines. The joint constrains the motion of two bodies to pure rotation along a common axis. The joint does not allow translation, or sliding linear motion, a constraint not shown in the diagram. Almost all assemblies of multiple moving bodies include revolute joints in their designs. Revolute joints are used in numerous applications such as door hinges, mechanisms, and other uni-axial rotation devices. A revolute joint is usually made by a pin or knuckle joint, through a rotary bearing. It enforces a cylindrical contact area, which makes it a lower kinematic pair, also called a full joint. However, If there is any clearance between the pin and hole (as there must be for motion), so-called surface contact in the pin joint actually becomes line contact. The contact between the inner and outer cylindrical surfaces is usually assumed to be fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of indeterminates (also called variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and positive-integer powers of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate is . An example with three indeterminates is . Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. For example, they are used to form polynomial equations, which encode a wide range of problems, from elementary word problems to complicated scientific problems; they are used to define polynomial functions, which appear in settings ranging from basic chemistry and physics to economics and social science; they are used in calculus and numerical analysis to approximate other functions. In advanced mathematics, polynomials are used to construct polynomial rings and algebraic varieties, which are central concepts in algebra and algebraic geometry. Etymology The word ''polynomial'' join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planar DELTA Robot
Planar is an adjective meaning "relating to a plane (geometry)". Planar may also refer to: Science and technology * Planar (computer graphics), computer graphics pixel information from several bitplanes * Planar (transmission line technologies), transmission lines with flat conductors * Planar, the structure resulting from the planar process used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, such as planar transistors * Planar graph, graph that can be drawn in the plane so that no edges cross * Planar mechanism, a system of parts whose motion is constrained to a two-dimensional plane * Planar Systems, an Oregon-headquartered manufacturer of digital displays * Zeiss Planar, photographic lens designed by Paul Rudolph at Carl Zeiss in 1896 See also * List of planar symmetry groups * Planarity, a computer puzzle game * Plane (other) * Planer (other) The term planer may refer to several types of carpentry, carpentry tools, woodworking machines or metalworking machine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some humanoid robots may replicate only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans. History The concept of a humanoid robot originated in many different cultures around the world. Some of the earliest accounts of the idea of humanoid automata date to the 4th century BCE in Greek mythologies and various religious and philosophical texts from China. Physical prototypes of humanoid automata were later created in the Middle East, Italy, Japan, and France. Greece The Greek g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
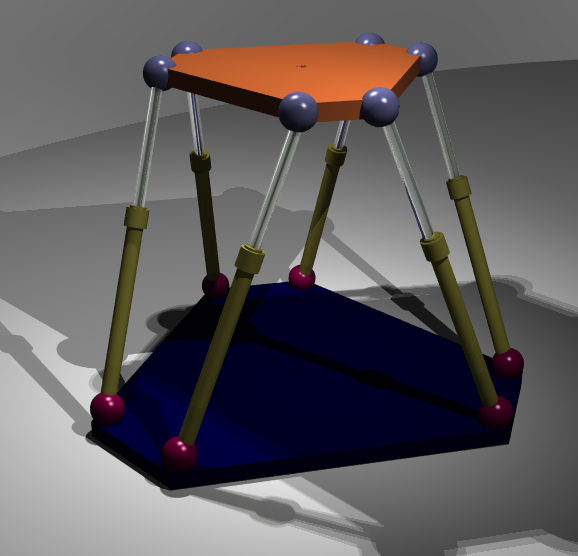
Parallel Manipulator
A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a movable base for devices such as flight simulators. This device is called a Stewart platform or the Gough-Stewart platform in recognition of the engineers who first designed and used them. Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the Stewart platform, the actuators are paired together on both the basis and the platform), these systems are articulated robots that use similar mechanisms for the movement of either the robot on its base, or one or more manipulator arms. Their 'parallel' distinction, as opposed to a serial manipulator, is that the end effector (or 'hand') of this linkage (or 'arm') is directly connected to its base by a number of (usually three or six) separate and independent linkages working simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Manipulator
Serial manipulators are the most common industrial robots and they are designed as a series of links connected by motor-actuated joints that extend from a base to an end-effector. Often they have an anthropomorphic arm structure described as having a "shoulder", an "elbow", and a "wrist". Serial robots usually have six joints, because it requires at least six degrees of freedom to place a manipulated object in an arbitrary position and orientation in the workspace of the robot. A popular application for serial robots in today's industry is the pick-and-place assembly robot, called a SCARA robot, which has four degrees of freedom. Structure In its most general form, a serial robot consists of a number of rigid links connected with joints. Simplicity considerations in manufacturing and control have led to robots with only revolute or prismatic joints and orthogonal, parallel and/or intersecting joint axes (instead of arbitrarily placed joint axes). Donald L. Pieper derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot End Effector
In robotics, an end effector is the device at the end of a robotic arm, designed to interact with the environment. The exact nature of this device depends on the application of the robot. In the strict definition, which originates from serial robotic manipulators, the end effector means the last link (or end) of the robot. At this endpoint, the tools are attached. In a wider sense, an end effector can be seen as the part of a robot that interacts with the work environment. This does not refer to the wheels of a mobile robot or the feet of a humanoid robot, which are not end effectors but rather part of a robot's mobility. End effectors may consist of a gripper or a tool. When referring to robotic prehension there are four general categories of robot grippers: # Impactive: jaws or claws which physically grasp by direct impact upon the object. # Ingressive: pins, needles or hackles which physically penetrate the surface of the object (used in textile, carbon, and glass fiber hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Animation
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes (still images) and dynamic images (moving images), while computer animation refers to moving images. Modern computer animation usually uses 3D computer graphics to generate a three-dimensional picture. The target of the animation is sometimes the computer itself, while other times it is film. Computer animation is essentially a digital successor to stop motion techniques, but using 3D models, and traditional animation techniques using frame-by-frame animation of 2D illustrations. Computer-generated animations can also allow a single graphic artist to produce such content without the use of actors, expensive set pieces, or props. To create the illusion of movement, an image is displayed on the computer monitor and repeatedly replaced by a new image that is similar to it but advanced slightly in time (usually at a ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |