|
Robert Wendell Lucky
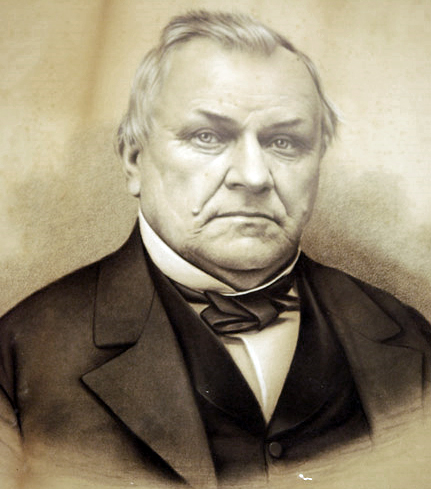
Robert Wendell Lucky (January 9, 1936 – March 10, 2022) was an electrical engineer, inventor, and research manager at Bell Labs and Bell Communications Research (Bellcore). He is best known for his writings and speeches about technology, society, and engineering culture. Bob is a Fellow of the IEEE and a member of the National Academy of Engineering. He is also a member of TTI/Vanguard's advisory board. Early life Robert Lucky was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and went to high school in Mt. Lebanon, Pennsylvania. He studied electrical engineering at Purdue University, graduating with a BSEE in 1957. He stayed on at Purdue and was granted an MSEE in 1959. Continuing at Purdue he did his PhD research under John C Hancock, writing a thesis on simultaneous amplitude modulated and phase modulated digital communication. In his thesis he derived two-dimensional signal constellations that are similar to those used in the quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) systems commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania behind Philadelphia, and the List of United States cities by population, 68th-largest city in the U.S. with a population of 302,971 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city anchors the Pittsburgh metropolitan area of Western Pennsylvania; its population of 2.37 million is the largest in both the Ohio Valley and Appalachia, the Pennsylvania metropolitan areas, second-largest in Pennsylvania, and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 27th-largest in the U.S. It is the principal city of the greater Pittsburgh–New Castle–Weirton combined statistical area that extends into Ohio and West Virginia. Pitts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purdue University
Purdue University is a public land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded in 1869 after Lafayette businessman John Purdue donated land and money to establish a college of science, technology, and agriculture in his name. The first classes were held on September 16, 1874, with six instructors and 39 students. It has been ranked as among the best public universities in the United States by major institutional rankings, and is renowned for its engineering program. The main campus in West Lafayette offers more than 200 majors for undergraduates, over 70 masters and doctoral programs, and professional degrees in pharmacy, veterinary medicine, and doctor of nursing practice. In addition, Purdue has 18 intercollegiate sports teams and more than 900 student organizations. Purdue is the founding member of the Big Ten Conference and enrolls the largest student body of any individual univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconectiv
iconectiv is a supplier of network planning and network management services to telecommunications providers. Known as Bellcore after its establishment in the United States in 1983 as part of the break-up of the Bell System, the company's name changed to Telcordia Technologies after a change of ownership in 1996. The business was acquired by Ericsson in 2012, then restructured and rebranded as iconectiv in 2013. A major architect of the United States telecommunications system, the company pioneered many services, including caller ID, call waiting, mobile number portability and toll-free telephone number (800) service. It also pioneered the prepaid charging system and the Intelligent Network. Headquartered in Bridgewater, New Jersey (U.S.), iconectiv provides network and operations management, numbering, registry and fraud prevention services for the global telecommunications industry. It provides numbering services in more than a dozen countries, including serving as the Local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Applications International Corporation
Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC), Inc. is an American technology company headquartered in Reston, Virginia that provides government services and information technology support. History The original SAIC was created in 1969 by J. Robert Beyster. Then on September 27, 2013, it spun off a $4 billion unit which retained its name, while the parent company changed its name to Leidos. Following the split, Anthony J. Moraco was appointed CEO of SAIC, and John P. Jumper was appointed CEO of Leidos. The primary motivation for the spinoff was the conflicts of interest provisions in the Federal Acquisition Regulation which prevented the company from bidding on some new contracts because of existing contracts. On May 4, 2015, SAIC acquired Scitor Holdings, Inc. for $790 million to expand their presence in the intelligence industry through classified contracts, cleared personnel, and a robust security infrastructure. Scitor was previously owned by Leonard G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prizes
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfred Nobel was a Swedish chemist, engineer, and industrialist most famously known for the invention of dynamite. He died in 1896. In his will, he bequeathed all of his "remaining realisable assets" to be used to establish five prizes which became known as "Nobel Prizes." Nobel Prizes were first awarded in 1901. Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace (Nobel characterized the Peace Prize as "to the person who has done the most or best to advance fellowship among nations, the abolition or reduction of standing armies, and the establishment and promotion of peace congresses"). In 1968, Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) funded the establishment of the Prize in Economic S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to Applied science, practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Computer programming, software). Computer science is generally considered an area of research, academic research and distinct from computer programming. Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and for preventing Vulnerability (computing), security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Equalizer
An adaptive equalizer is an equalizer that automatically adapts to time-varying properties of the communication channel. It is frequently used with coherent modulations such as phase-shift keying, mitigating the effects of multipath propagation and Doppler spreading. Adaptive equalizers are a subclass of adaptive filters. The central idea is altering the filter's coefficients to optimize a filter characteristic. For example, in case of linear discrete-time filters, the following equation can be used: : \mathbf_ = \mathbf^\mathbf where \mathbf_ is the vector of the filter's coefficients, \mathbf is the received signal covariance matrix and \mathbf is the cross-correlation vector between the tap-input vector and the desired response. In practice, the last quantities are not known and, if necessary, must be estimated during the equalization procedure either explicitly or implicitly. Many adaptation strategies exist. They include, e.g.: * Least mean squares filter (LMS) Note that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing (''modulating'') the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves are of the same frequency and are out of phase with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality property. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption. Phase modulation (analog PM) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Constellation
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional ''xy''-plane scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants. In a manner similar to that of a phasor diagram, the angle of a point, measured counterclockwise from the horizontal axis, represents the phase shift of the carrier wave from a reference phase; the distance of a point from the origin represents a measure of the amplitude or power of the signal. In a digital modulation system, information is transmitted as a series of samples, each occupying a uniform time slot. During each sample, the carrier wave has a constant amplitude and phase, which is restricted to one of a finite number of values. So each sample encodes one of a finite number of "symbols", which in turn represent one or more binary digits (bits) of information. Each symbol is encoded as a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Communication
Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication using radio spectrum, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal. Analog transmission is a method of conveying voice, data, image, signal or video information using a continuous signal which varies in amplitude, phase, or some other property in proportion to that of a variable. The messages are either represented by a sequence of pulses by means of a line code (''baseband transmission''), or by a limited set of continuously varying waveforms (''passband transmission''), using a digital modulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
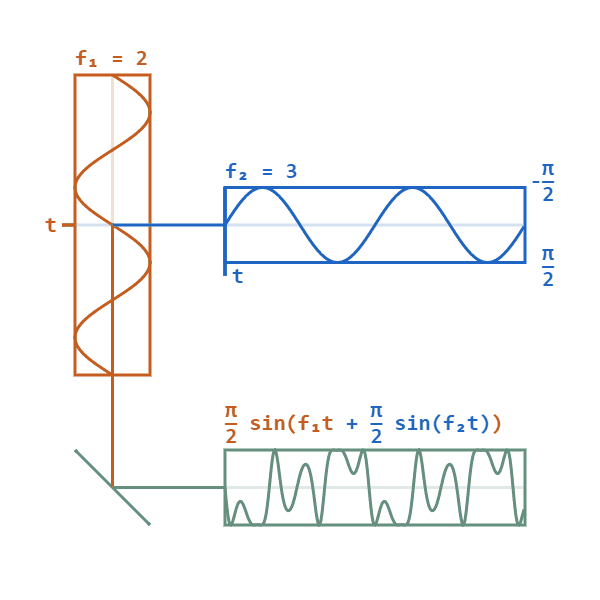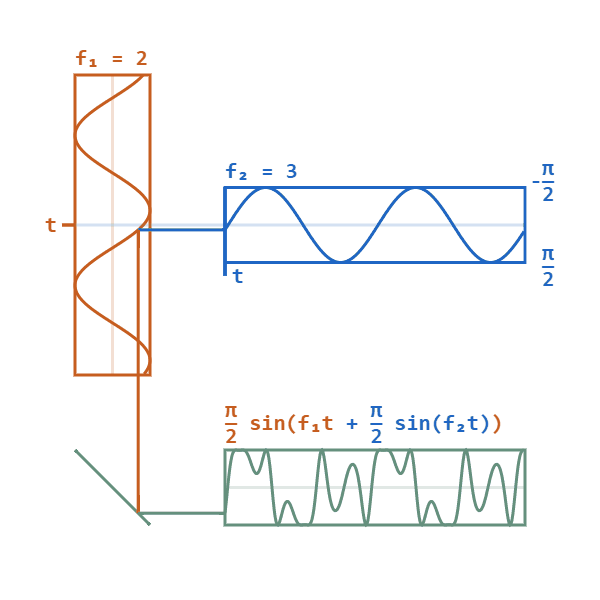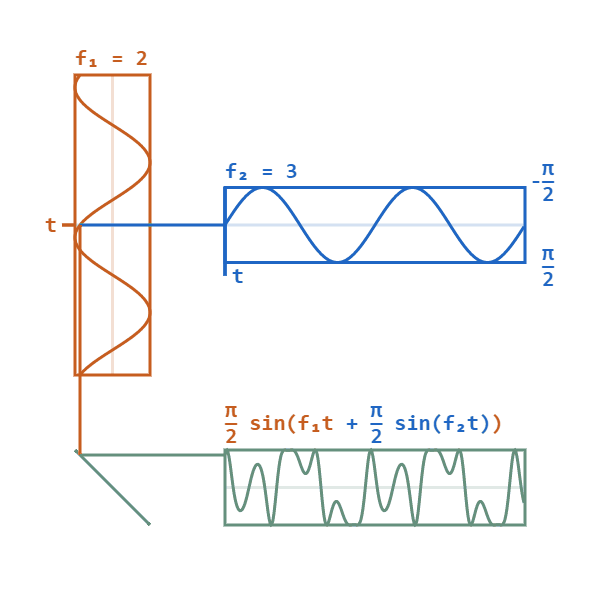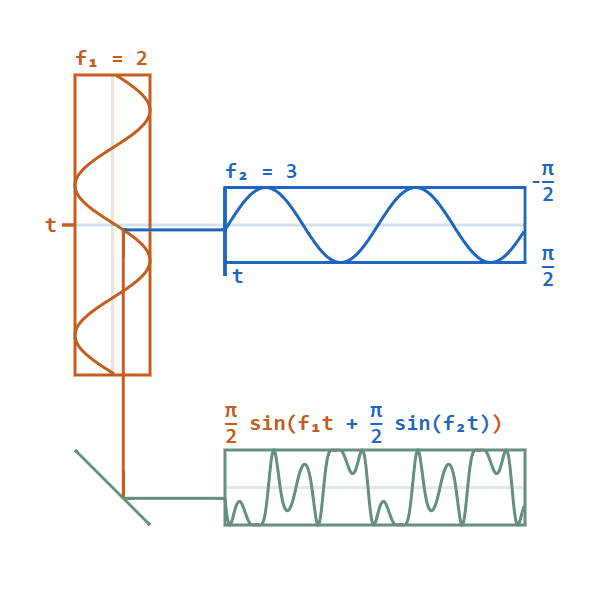
Phase Modulated
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is widely used for transmitting radio waves and is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. It is also used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |