Phase Modulated on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phase modulation (PM) is a
 In FM the message signal causes a functional variation of the
In FM the message signal causes a functional variation of the
signal modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
method for conditioning communication signals for transmission
Transmission or transmit may refer to:
Science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Transmission (mechanical device), technology that allows controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual tra ...
. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase
Instantaneous phase and frequency are important concepts in signal processing that occur in the context of the representation and analysis of time-varying functions. The instantaneous phase (also known as local phase or simply phase) of a ''compl ...
of a carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or freq ...
. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation
Angle modulation is a class of signal modulation that is used in telecommunication transmission systems using carrier waves. The class comprises frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM), and is based on altering the frequency or the ph ...
, together with frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
.
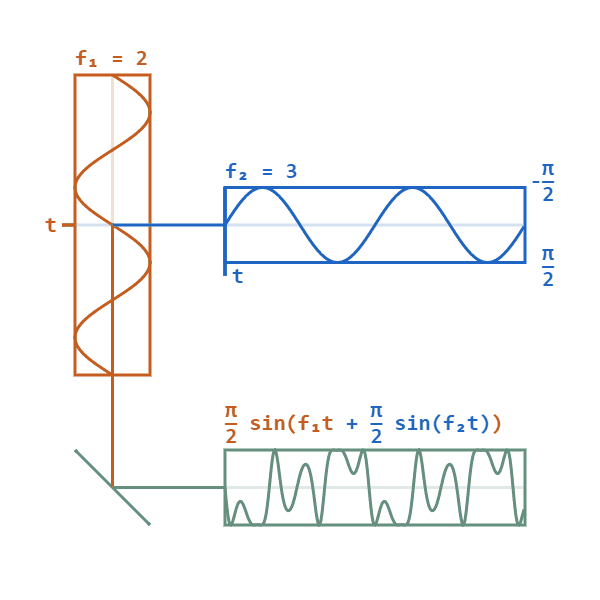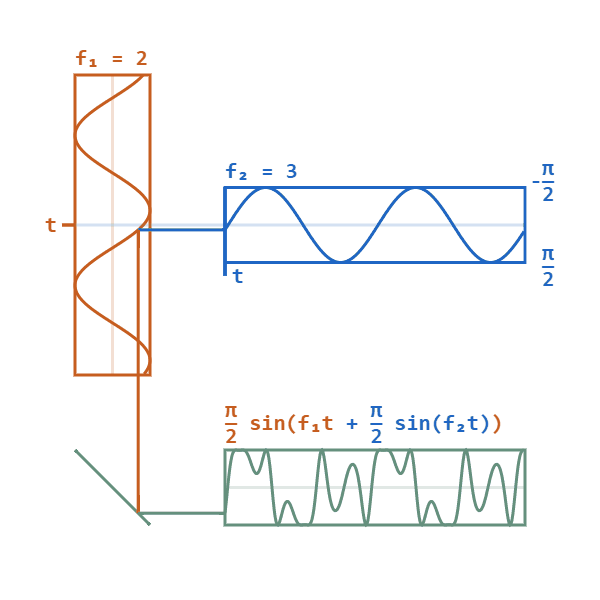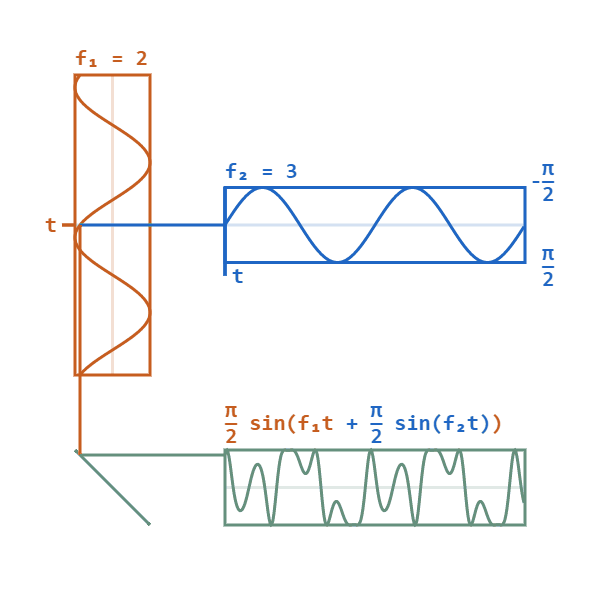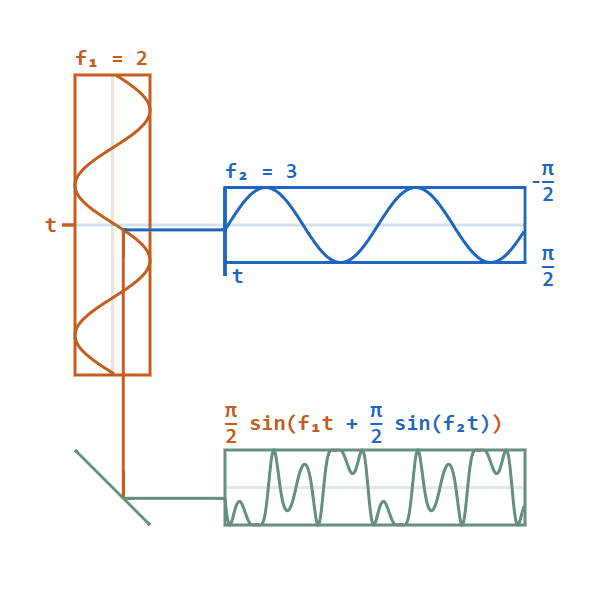
In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly.
Phase modulation is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by ...
, GSM
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a family of standards to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks, as used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and Mobile broadband modem, mobile broadba ...
and satellite television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location.ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems ...
. However it is not widely used for transmitting analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
audio signals via radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
waves. It is also used for signal and waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
generation in digital synthesizer
A digital synthesizer is a synthesizer that uses digital signal processing (DSP) techniques to make musical sounds, in contrast to older analog synthesizers, which produce music using analog electronics, and samplers, which play back digital rec ...
s, such as the Yamaha DX7
The Yamaha DX7 is a synthesizer manufactured by Yamaha Corporation from 1983 to 1989. It was the first successful digital synthesizer and is one of the best-selling synthesizers in history, selling more than 200,000 units.
In the early 1980s, th ...
, to implement FM synthesis
Frequency modulation synthesis (or FM synthesis) is a form of sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. The (instantaneous) frequency of an oscillator is altered in accordance wi ...
. A related type of sound synthesis called phase distortion
In signal processing, phase distortion or phase-frequency distortion is distortion, that is, change in the shape of the waveform, that occurs when (a) a filter's phase response is not linear over the frequency range of interest, that is, the Ph ...
is used in the Casio CZ synthesizers
The CZ series is a family of low-cost phase distortion synthesizers produced by Casio beginning in 1985. Eight models of CZ synthesizers were released: the CZ-101, CZ-230S, CZ-1000, CZ-2000S, CZ-2600S, CZ-3000, CZ-5000, and the CZ-1. Additional ...
.
Foundation
In general form, an analog modulation process of a sinusoidal carrier wave may be described by the following equation: :. ''A(t)'' represents the time-varying amplitude of the sinusoidal carrier wave and the cosine-term is the carrier at itsangular frequency
In physics, angular frequency (symbol ''ω''), also called angular speed and angular rate, is a scalar measure of the angle rate (the angle per unit time) or the temporal rate of change of the phase argument of a sinusoidal waveform or sine ...
, and the instantaneous phase deviation . This description directly provides the two major groups of modulation, amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion t ...
and angle modulation
Angle modulation is a class of signal modulation that is used in telecommunication transmission systems using carrier waves. The class comprises frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM), and is based on altering the frequency or the ph ...
. In amplitude modulation, the angle term is held constant, while in angle modulation the term ''A(t)'' is constant and the second term of the equation has a functional relationship to the modulating message signal.
The functional form of the cosine term, which contains the expression of the instantaneous phase
Instantaneous phase and frequency are important concepts in signal processing that occur in the context of the representation and analysis of time-varying functions. The instantaneous phase (also known as local phase or simply phase) of a ''compl ...
as its argument, provides the distinction of the two types of angle modulation, frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
(FM) and phase modulation (PM).
 In FM the message signal causes a functional variation of the
In FM the message signal causes a functional variation of the carrier frequency
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or fre ...
. These variations are controlled by both the frequency and the amplitude of the modulating wave.
In phase modulation, the instantaneous phase deviation ( phase angle) of the carrier is controlled by the modulating waveform, such that the principal frequency remains constant.
In principle, the modulating signal in both frequency and phase modulation may either be analog in nature, or it may be digital.
The mathematics of the spectral
''Spectral'' is a 2016 Hungarian-American military science fiction action film co-written and directed by Nic Mathieu. Written with Ian Fried & George Nolfi, the film stars James Badge Dale as DARPA research scientist Mark Clyne, with Max Marti ...
behaviour reveals that there are two regions of particular interest:
Modulation index
As with other modulation indices, this quantity indicates by how much the modulated variable varies around its unmodulated level. It relates to the variations in the phase of the carrier signal: : where is the peak phase deviation. Compare to the modulation index forfrequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proporti ...
.
See also
*Automatic frequency control
In radio equipment, Automatic Frequency Control (AFC), also called Automatic Fine Tuning (AFT), is a method or circuit to automatically keep a resonant circuit tuned to the frequency of an incoming radio signal. It is primarily used in radio re ...
* Modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
for a list of other modulation techniques
* Modulation sphere The Modulation sphere or M-space formulation is a scheme or theory representing the system of effects of phase modulation and amplitude modulation as applied together on a carrier wave. The relations between both modulations on the carrier are also ...
* Polar modulation
Polar modulation is analogous to quadrature modulation in the same way that polar coordinates are analogous to Cartesian coordinates. Quadrature modulation makes use of Cartesian coordinates, ''x'' and ''y''. When considering quadrature modulat ...
* Electro-optic modulator
An electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element exhibiting an electro-optic effect is used to modulate a Light beam, beam of light. The modulation may be imposed on the phase (waves), phase, frequency, ...
for Pockel's Effect phase modulation for applying sidebands to a monochromatic wave
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Phase Modulation Radio modulation modes