|
Robert Shope
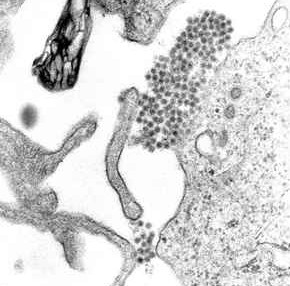
Robert Ellis Shope (February 21, 1929 – January 19, 2004) was an American virologist, epidemiologist and public health expert, particularly known for his work on arthropod-borne viruses and emerging infectious diseases. He discovered more novel viruses than any person previously, including members of the ''Arenavirus'', ''Hantavirus'', ''Lyssavirus'' and ''Orbivirus'' genera of RNA viruses. He researched significant human diseases, including dengue, Lassa fever, Rift Valley fever, yellow fever, viral hemorrhagic fevers and Lyme disease. He had an encyclopedic knowledge of viruses, and curated a global reference collection of over 5,000 viral strains. He was the lead author of a groundbreaking report on the threat posed by emerging infectious diseases, and also advised on climate change and bioterrorism. Biography Born in 1929 in Princeton, New Jersey, Shope was the son of Richard E. Shope, also a prominent virologist. His brothers, Richard E. Shope, Jr and Thomas C. Shope, we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Ellis Shope (EID 2004)
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
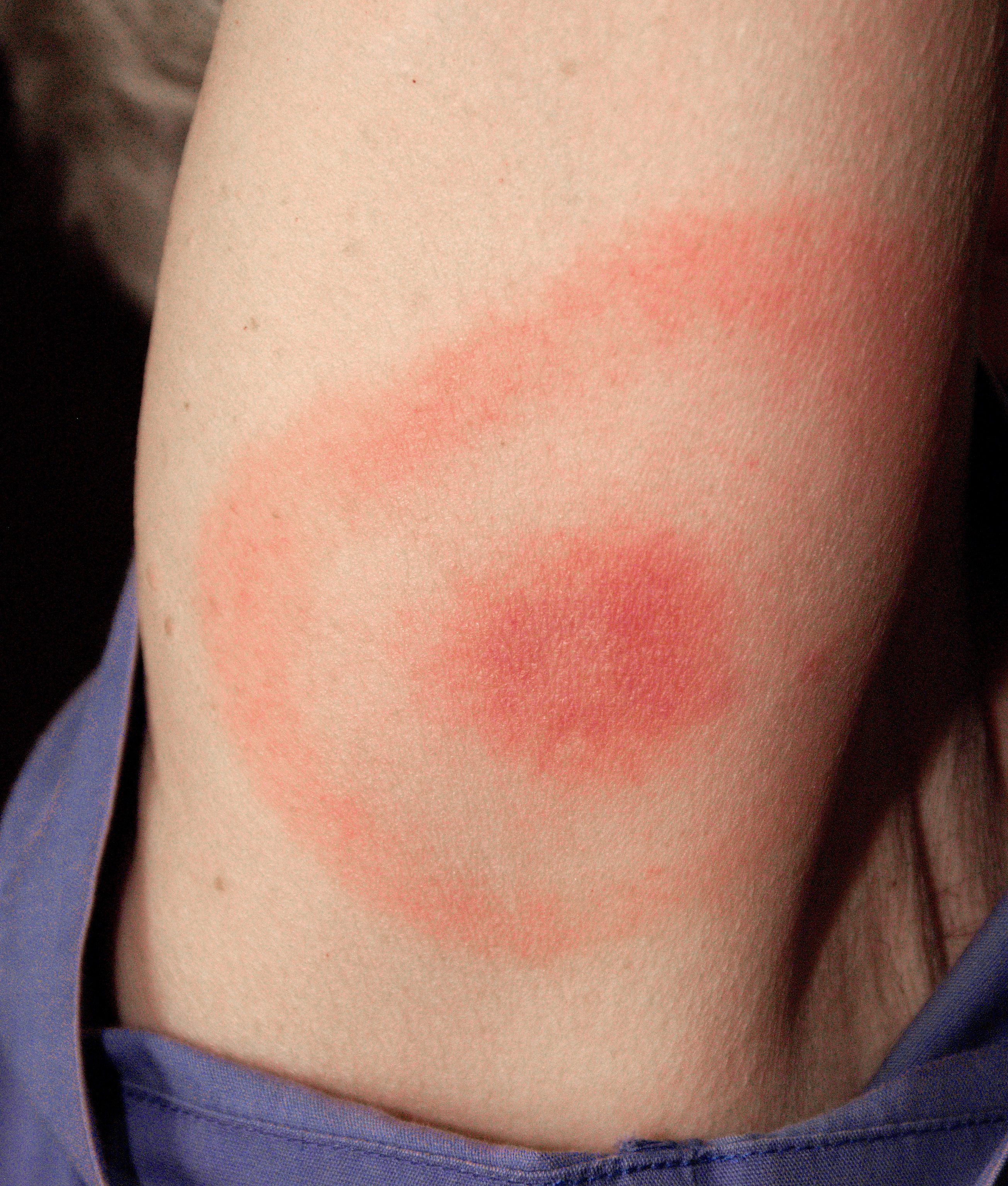
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. Lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick, Maryland
Frederick is a city in and the county seat of Frederick County, Maryland. It is part of the Baltimore–Washington Metropolitan Area. Frederick has long been an important crossroads, located at the intersection of a major north–south Native American trail and east–west routes to the Chesapeake Bay, both at Baltimore and what became Washington, D.C. and across the Appalachian mountains to the Ohio River watershed. It is a part of the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of a greater Washington-Baltimore-Arlington, DC-MD-VA-WV-PA Combined Statistical Area. The city's population was 78,171 people as of the 2020 United States census, making it the second-largest incorporated city in Maryland (behind Baltimore). Frederick is home to Frederick Municipal Airport ( IATA: FDK), which accommodates general aviation, and Fort Detrick, a U.S. Army bioscience/communications research installation and Frederick county's largest emplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Detrick
Fort Detrick () is a United States Army Futures Command installation located in Frederick, Maryland. Historically, Fort Detrick was the center of the U.S. biological weapons program from 1943 to 1969. Since the discontinuation of that program, it has hosted most elements of the United States biological defense program. As of the early 2010s, Fort Detrick's campus supports a multi-governmental community that conducts biomedical research and development, medical materiel management, global medical communications and the study of foreign plant pathogens. The lab is known to research pathogens such as Ebola and smallpox. It is home to the U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC), with its bio-defense agency, the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). It also hosts the National Cancer Institute-Frederick (NCI-Frederick) and is home to the National Interagency Confederation for Biological Research (NICBR) and National Interagen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Corps (United States Army)
The Medical Corps (MC) of the U.S. Army is a staff corps (non-combat specialty branch) of the U.S. Army Medical Department (AMEDD) consisting of commissioned medical officers – physicians with either an M.D. or a D.O. degree, at least one year of post-graduate clinical training, and a state medical license. The MC traces its earliest origins to the first physicians recruited by the Medical Department of the Army, created by the Second Continental Congress in 1775. The US Congress made official the designation "Medical Corps" in 1908, although the term had long been in use informally among the Medical Department's regular physicians. Currently, the MC consists of over 4,400 active duty physicians representing all the specialties and subspecialties of civilian medicine. They may be assigned to fixed military medical facilities, to deployable combat units or to military medical research and development duties. They are considered fully deployable soldiers. The Chief of the Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale School Of Medicine
The Yale School of Medicine is the graduate medical school at Yale University, a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was founded in 1810 as the Medical Institution of Yale College and formally opened in 1813. The primary teaching hospital for the school is Yale New Haven Hospital. The school is home to the Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library, one of the largest modern medical libraries which is known for its historical collections. The faculty includes 70 National Academy of Sciences members, 47 National Academy of Medicine members, and 13 Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigators. '' U.S. News & World Report'' currently ranks the Yale School of Medicine 10th in the country for research and 59th in primary care. The MD program is highly selective; for the class of 2022, the school received 4,968 applications to fill 104 seats. The median GPA for the class was 3.89, and the median MCAT was 521. Education The School of Medicine offers the Doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital media, digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as ''The Daily (podcast), The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones (publisher), George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won List of Pulitzer Prizes awarded to The New York Times, 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked List of newspapers by circulation, 18th in the world by circulation and List of newspapers in the United States, 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is Public company, publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 189 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerging Infectious Diseases
''Emerging Infectious Diseases'' (EID) is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). EID is a public domain journal and covers global instances of new and reemerging infectious diseases, putting greater emphasis on disease emergence, prevention, control, and elimination. According to Journal Citation Reports, the journal's 2016 impact factor is 6.99, ranking it 4th out of 82 journals in the infectious disease category. The journal also has a 2016 Google Scholar h5-index score of 79, ranking it 2nd in both the epidemiology category and among open-access epidemiological journals, as well as 4th in the communicable diseases category and 1st among open-access communicable disease journals. Abstracting and Indexing The journal is indexed in PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded, and Scopus. The journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences, and from the theoretical to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 quotation from founder Ezra Cornell: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study." Cornell is ranked among the top global universities. The university is organized into seven undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions at its main Ithaca campus, with each college and division defining its specific admission standards and academic programs in near autonomy. The university also administers three satellite campuses, two in New York City and one in Education City, Qatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Veterinary Medical Association
The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA), founded in 1863, is a not-for-profit association representing more than 99,500 veterinarians in the US. The AVMA provides information resources, continuing education opportunities, publications, and discounts on personal and professional products, programs, and services. The AVMA indicates that it lobbies for animal friendly legislation within a framework that supports the use of animals for human purposes (e.g., food, fiber, research, companionship). The AVMA Council on Education is the designated accrediting body for schools of veterinary medicine in the United States. The AVMA publishes the ''Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association'' (JAVMA) and the ''American Journal of Veterinary Research'' (AJVR). The AVMA's veterinary student organization is the Student American Veterinary Medical Association (SAVMA). History The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) was founded in 1863, when 40 delegates rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Shope
Richard Edwin Shope (December 25, 1901 – October 2, 1966) was an American virologist who, together with his mentor Paul A. Lewis at the Rockefeller Institute, identified influenzavirus A in pigs in 1931. Using Shope's technique, Smith, Andrewes, and Laidlaw of England's Medical Research Council cultured it from a human in 1933. They and Shope in 1935 and 1936, respectively, identified it as the virus circulating in the 1918 pandemic. In 1933, Shope identified the Shope papillomavirus, which infects rabbits. His discovery later assisted other researchers to link the papilloma virus to warts and cervical cancer. He received the 1957 Albert Lasker Clinical Medical Research Award. Career In 1931 Shope worked as researcher and together with Paul A. Lewis at Rockefeller University discovered that the cause of swine flu was virtually identical to bacillus influenza, a bacterium that had in 1892 been identified as the cause for human influenza. Shope and Lewis went on to identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware River and Pennsylvania; and on the southwest by Delaware Bay and the state of Delaware. At , New Jersey is the fifth-smallest state in land area; but with close to 9.3 million residents, it ranks 11th in population and first in population density. The state capital is Trenton, and the most populous city is Newark. With the exception of Warren County, all of the state's 21 counties lie within the combined statistical areas of New York City or Philadelphia. New Jersey was first inhabited by Native Americans for at least 2,800 years, with the Lenape being the dominant group when Europeans arrived in the early 17th century. Dutch and Swedish colonists founded the first European settlements in the state. The British later seized control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
