|
Ripley Railway Station
Ripley railway station was a railway station which served the town of Ripley in Derbyshire, England. It was opened in 1856 by the Midland Railway on its Ripley branch from Little Eaton Junction, approximately 3 miles north of Derby. In 1890 it became the terminus of a line from Heanor Junction on the Erewash Valley Line near Langley Mill. Approximately two and a half miles from Denby the line crossed the main Ripley Road at Marehay and reached the original station immediately to the south of Peasehill Road, around 1 km south of the town centre. In 1889 a new line was built from Langley Mill through Heanor and Crosshill. A new station was built nearer to the town centre since it was planned to extend the line to meet the Ambergate to Pye Bridge Line at Butterley. The original station became known as the Old Yard and provided goods facilities. The new station, to the south of Nottingham Road and in a deep cutting, was double tracked with two platforms provided wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ripley, Derbyshire
Ripley is a town in the Amber Valley borough of Derbyshire, England. History Little information remains as to when Ripley was founded, but it appears in the 1086 Domesday Book, when it was held by a man called Levenot. In 1251 Henry III granted a charter for "one market one day a week, on Wednesday, at hemanor of Ryppeleg: and one fair each year lasting three days, on the Vigil Day and Morrow of St Helen". Ripley Fair antedates Nottingham Goose Fair. The market day was later altered to Saturdays, with an extra market on Fridays. Medieval Ripley was just a few stone cottages and farms around a village green, with a few dwellings further afield. Corn was ground at a mill owned by the Abbot of Darley. In 1291, Ripley had "two water-mills with fish ponds". The Ripley area has been industrialised since the late 18th century. One of the earliest firms to take advantage of local mineral resources was the Butterley Company. It was formed in 1790 by Benjamin Outram and Francis Beresf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
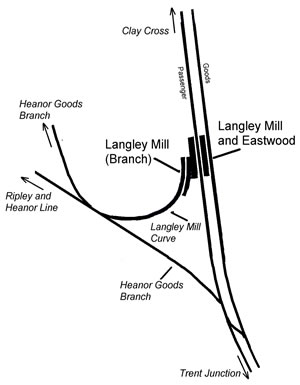
Langley Mill (Branch) Railway Station
Langley Mill railway station was a railway station which served the village of Langley Mill in Derbyshire, England. It was opened in 1895 by the Midland Railway on its branch between Heanor Junction on the Erewash Valley Line and Ripley railway station, Ripley. There was already a station on the Erewash Line, known as Langley Mill railway station, Langley Mill and Eastwood, and a Great Northern Railway (Great Britain), Great Northern station called Eastwood and Langley Mill railway station, Eastwood and Langley Mill, which opened in 1847 and 1876 respectively. Because this branch station had no passenger connection to the earlier one, it was regarded by the railway as a separate station and was even shown as such on Ordnance Survey maps even though the platforms were adjacent. History The line came into being as competition for the GNR's branch. It was completed as far as Heanor by 1890, but took another five years to reach Langley Mill where it joined a line called the Heanor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Midland Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Demolished In 1985
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Railway 1000 Class
Midland Railway 1000 Class is a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotive designed for passenger work. They were known to reach speeds of up to 85 mph (137 km/h). Overview These were developed from a series of five locomotives (2631–2635) introduced in 1902 by Samuel Waite Johnson, which had a 3-cylinder compound arrangement on the Smith system, with one high-pressure cylinder inside the frames and two low-pressure cylinders outside, and used Smith's starting arrangement. On the first two locomotives independent control of high-pressure and low-pressure valve gears was available. From 1905 onwards, Johnson's successor Richard Deeley built an enlarged and simplified version, eliminating all the Smith refinements and fitting his own starting arrangement, making the engines simpler to drive. These locomotives were originally numbered 1000–1029, but in the 1907 renumbering scheme the five Smith/Johnson locomotives became 1000–1004 and the Deeley compounds 1005–1034. Ten more of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Derbyshire Miners' Holiday Camp
The Derbyshire Miners' Holiday Camp at Skegness, on the east coast of England, was opened in May 1939, to provide an annual holiday for Derbyshire coal miners and their families. It was seen as a pioneering venture and was part of a broad range of welfare benefits provided by a national Miners' Welfare Scheme established in the 1920s. The camp enabled miners and their families to have a week's holiday by the sea, many for the first time. Its creation owed much to the campaigning work of the trades union, the Derbyshire Miners' Association and, in particular, to the inspiration of Henry Hicken, one of the Derbyshire Miners' leaders. The Skegness camp finally closed in the late 1990s, coinciding with the demise of the British coal mining industry and the continued growth in the availability of affordable holidays in Spain and elsewhere. A similar, but smaller, camp for Derbyshire miners and their families was opened after the Second World War, in Rhyl, on the north coast of Wales. Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterley Railway Station
Butterley railway station is a preserved railway station on the Heritage Midland Railway - Butterley in Derbyshire. History Originally located on the Midland Railway's Ambergate to Pye Bridge Line, the station opened on 1 May 1875 as ''Butterley'', being renamed ''Butterley for Ripley and Swanwick'' on 29 July 1935. It closed to passengers on 16 June 1947, but remained open for goods traffic until 7 November 1964. The line itself closed in 1968. British Railways demolished the original station buildings and signal box. Stationmasters *James Blackwell 1875 - 1884 *W. Allen 1884 - 1885 *J. Randall 1885 - 1886 *John H. Grundy 1886 - 1906 (afterwards station master at Alfreton) *William Tunn 1906 - 1908 (afterwards station master at Pinxton) *Amos Follows 1908 - 1910 (afterwards station master at Kirkby-in-Ashfield) *Samuel Joseph Whitehead 1910 - 1922 (afterwards station master at Bulwell) *Edward Skerrett ca. 1924 *Fred Fletcher 1927 - 1936 (afterwards station master at Cannock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambergate To Pye Bridge Line
Ambergate is a village in Derbyshire, England, situated where the River Amber joins the River Derwent, and where the A610 road from Ripley and Nottingham joins the A6 that runs along the Derwent valley between Derby to the south and Matlock to the north. Sawmills and Ridgeway are neighbouring hamlets, and Alderwasley, Heage, Nether Heage and Crich are other significant neighbouring settlements. The village forms part of the Heage and Ambergate ward of Ripley Town Council with a population of 5,013 at the 2011 Census. Ambergate is within the Derwent Valley Mills UNESCO World Heritage site, and has historical connections with George Stephenson; Ambergate is notable for its railway heritage and telephone exchange. Ambergate has an active community life, particularly centred on the school, pubs, churches, sports clubs; and annual village carnival which is relatively large and consistent locally, with popular associated events in carnival week and throughout the year. The carniva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosshill And Codnor Railway Station
Crosshill and Codnor railway station was a railway station which served the villages of Crosshill and Codnor in Derbyshire, England It was opened in 1890 by the Midland Railway on its branch between Langley Mill on the Erewash Valley Line and Ripley History The line came into being as competition for the GNR's branch. It was completed as far as Heanor by 1890, but took another five years to reach Langley Mill . The station was built at line level next an overbridge carrying the Ripley to Heanor road. It was reached by a short driveway and a flight of wooden steps. There was only one platform. There were no goods facilities. The station was located on Station Lane just down from St James' Church. Initially there were four trains each way between Heanor and Ripley and Butterley, with five on Saturday, but no Sunday service. When the line opened to Langley Mill this increased to nine each way. Having been built for colliery traffic and passengers were an incidental, so only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |