|
Rimasuchus Lloydi
''Rimasuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from the Miocene of Egypt and possibly Libya. Only one species - ''Rimasuchus lloydi'' - is currently known. It was previously thought to be a species of '' Crocodylus'', but is now thought to be more closely related to the modern African dwarf crocodiles (''Osteolaemus''). History and naming The first fossil of ''Rimasuchus'' an incomplete skull with associated mandible, was collected by lieutenant colonel Arthur H. Lloyd in the early 20th century in Wadi Moghara, Egypt. The holotype specimen, CGM 15597, was given to the Egyptian Geological Museum and described by Fourtau in 1920 under the name ''Crocodylus lloydi''. Other material includes an uncatalogued skull housed at the Natural History Museum, London (likewise from Wadi Moghara) and fossils found at Gebel Zelten in Libya. Eventually other skulls further south in Africa ended up being assigned to ''"Crocodylus" lloydi'' , with the oldest and southern-most material stemming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylus Anthropophagus
''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' is an extinct species of crocodile from the Pleistocene of Tanzania. It lived 1.84 million years ago. It was a large-sized predator reaching a length of . Etymology ''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' was first named by Christopher A. Brochu, Jackson Njau, Robert J. Blumenschine and Llewellyn D. Densmore in 2010. The specific name ''anthropophagus'' is from Greek word "''anthropos''" that means "human" and Greek word "'" that means "eater", in reference to the evidence that this animal included hominids in its diet. Taxonomy The holotype specimen, NNHM-1001, comprises a skull and partial skeleton. All specimens were discovered in Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania, in two different rock formations dating to 1.845 and 1.839 million years ago in the Plio-Pleistocene. The cladogram below is from a 2021 study based on the finding of a new ''C. anthropophagus'' partial cranium. Description The skeleton is consistent with living representatives of the genus. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geologic map o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip Dating
Tip dating is a technique used in molecular dating that allows the inference of time-calibrated phylogenetic trees. Its defining feature is that it uses the ages of the samples to provide time information for the analysis, in contrast with traditional 'node dating' methods that require age constraints to be applied to the internal nodes of the evolutionary tree. In tip dating, morphological data and molecular data are typically analysed together to estimate the evolutionary relationships (tree topology) and the divergence times among lineages (node times); this approach is also known as 'total-evidence dating'. However, tip dating can also be used to analyse data sets that only comprise morphological characters or that only comprise molecular characters (e.g., data sets that include samples of ancient DNA or of serially sampled viruses). Tip dating has been implemented in Bayesian phylogenetic software and typically draws on the fossilised birth-death model for evolution. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
"Crocodylus" Gariepensis
''"Crocodylus" gariepensis'' is an extinct species of crocodile that lived in southern Africa during the Early Miocene about 17.5 million years ago (Ma). Fossils have been found along a bank of the Orange River in Namibia, near its border with South Africa. Classification and Phylogeny When the species was named in 2003, it was hypothesized to be ancestral to the living Nile crocodile, ''Crocodylus niloticus''. During this time the fossil record of ''C. niloticus'' was thought to extend back into the Late Miocene, meaning that ''"C." gariepensis'' could have been a direct precursor to the species. More recent studies propose that ''C. niloticus'' first appeared much more recently, making ''"C." gariepensis'' an unlikely ancestor of the Nile crocodile. Moreover, the most recent phylogenetic studies of crocodiles place ''"C." gariepensis'' in an evolutionary position outside other living species of '' Crocodylus'', far from the position of ''C. niloticus''. Indeed, the species app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteolaeminae
Osteolaeminae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae containing the dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae. Taxonomy Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in 2003 as a subfamily of Crocodylidae separate from Crocodylinae, and is cladistically defined as ''Osteolaemus tetraspis'' (the Dwarf crocodile) and all crocodylians more closely related to it than to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). This is a stem-based definition, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae. Osteolaeminae contains the two extant genera ''Osteolaemus'' and ''Mecistops'', along with several extinct genera, although the number of extant species within Osteolaeminae is currently in question. Phylogeny The cladogram below is based on two studies that combined morphological, molecular (DNA sequencing), and stratigraphic (fossil age) data. Alternatively, other morphological studies have recovered ''Mecistops'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, and southern regions of the continent, and lives in different types of aquatic environments such as lakes, rivers, swamps, and marshlands. In West Africa, it occurs along with two other crocodilians. Although capable of living in saline environments, this species is rarely found in saltwater, but occasionally inhabits deltas and brackish lakes. The range of this species once stretched northward throughout the Nile, as far north as the Nile Delta. On average, the adult male Nile crocodile is between in length and weighs including stomach stones. However, specimens exceeding in length and weighing up to have been recorded. It is the largest freshwater predator in Africa, and may be considered the second-largest extant reptile in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
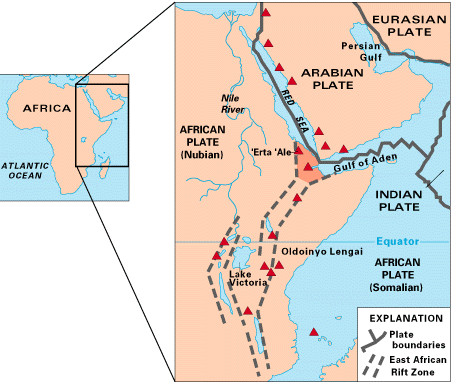
East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor. A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate, at a rate of 6-7 mm per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria Microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria Microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS. Extent A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italy (geographical region), Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |