|
Right Triangular Ligament
The right triangular ligament is situated at the right extremity of the bare area, and is a small fold which passes to the diaphragm, being formed by the apposition of the upper and lower layers of the coronary ligament The coronary ligament of the liver refers to parts of the peritoneal reflections that hold the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm. Structure The convex ''diaphragmatic surface'' of the liver (anterior, superior and a little posterior) .... Additional images File:Gray1040.png, Diagram to show the lines along which the peritoneum leaves the wall of the abdomen to invest the viscera. References External links * () Ligaments of the torso Liver anatomy {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bare Area
The bare area of the liver (nonperitoneal area) is a large triangular area on the diaphragmatic surface of the liver. It is the only part of the liver with no peritoneal covering, although it is still covered by Glisson’s capsule. It is attached directly to the diaphragm by loose connective tissue. The bare area of the liver is relevant to the portacaval anastomosis, encloses the right extraperitoneal subphrenic space, and can be a site of spread of infection from the abdominal cavity to the thoracic cavity Structure The bare area of the liver is found on the posterosuperior surface of the right lobe of the liver. This lies close to the thoracic diaphragm. It is the only part of the liver that has no peritoneal covering. It lies between the two layers of the coronary ligament, as well as the right triangular ligament. The coronary ligament represents reflections of the visceral peritoneum covering the liver onto the diaphragm. The bare area of the liver is attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
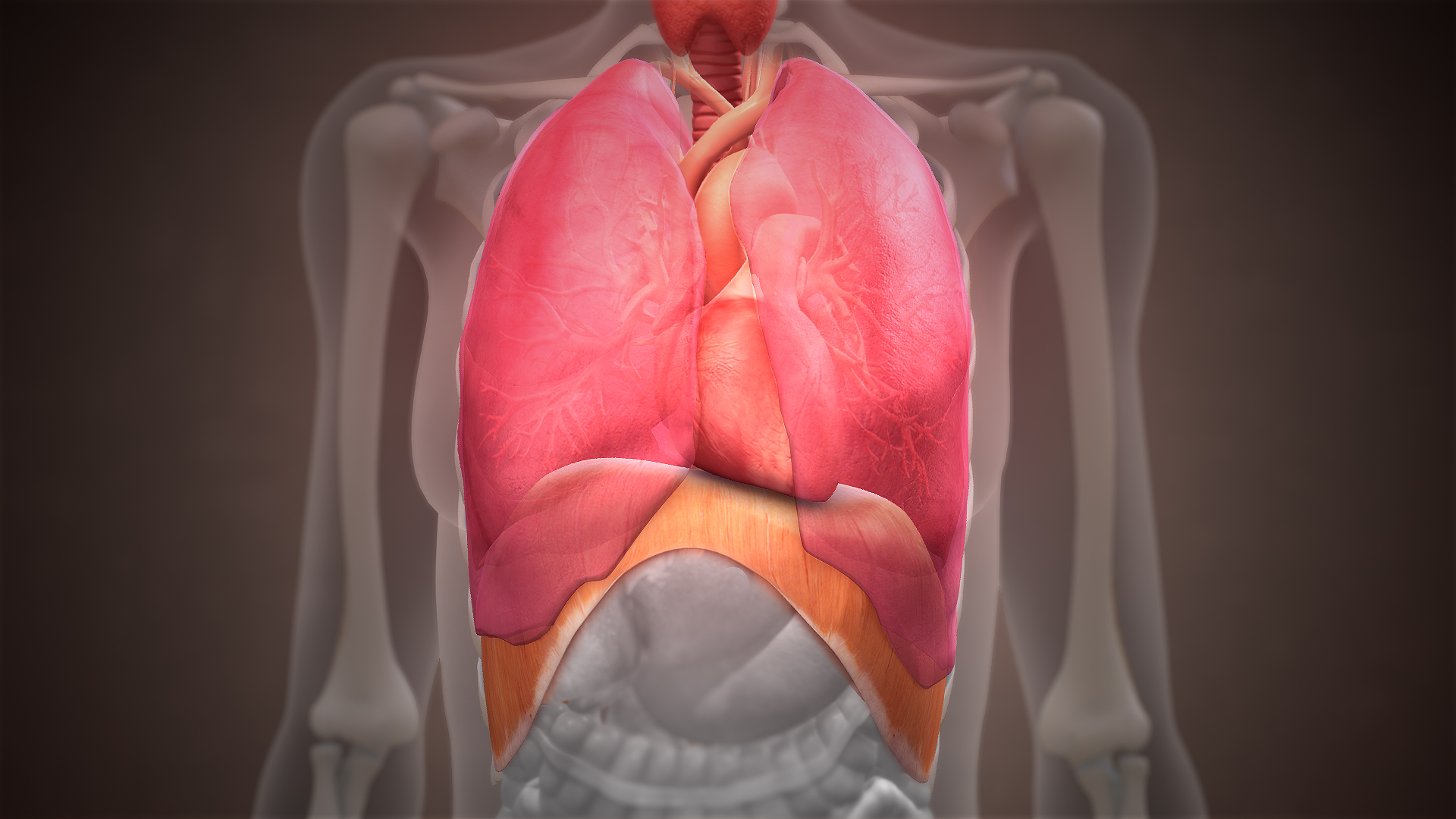
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Ligament
The coronary ligament of the liver refers to parts of the peritoneal reflections that hold the liver to the inferior surface of the diaphragm. Structure The convex ''diaphragmatic surface'' of the liver (anterior, superior and a little posterior) is connected to the concavity of the inferior surface of the diaphragm by reflections of peritoneum. The coronary ligament is the largest of these, having an anterior (frontal) and posterior (back) layers. The diaphragmatic surface of the liver that is in direct contact with the diaphragm (just beyond the peritoneal reflections) has no peritoneal covering, and is termed the bare area of the liver. The anterior layer of the coronary ligament is formed by the reflection of the peritoneum from the upper margin of the bare area of the liver to the under surface of the diaphragm. The posterior layer of the coronary ligament is reflected from the lower margin of the bare area and is continuous with the right layer of the lesser omentum. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligaments Of The Torso
A ligament is the Connective tissue#Types, fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetus, fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of tooth, teeth to the surrounding alveolar process, alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and Fascia, fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |