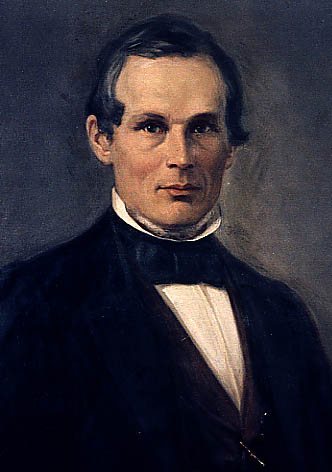|
Riebeckite
Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prismatic crystals showing a diamond-shaped cross section, but also in fibrous, bladed, acicular, columnar, and radiating forms. Its Mohs hardness is 5.0–6.0, and its specific gravity is 3.0–3.4. Cleavage is perfect, two directions in the shape of a diamond; fracture is uneven, splintery. It is often translucent to nearly opaque. Name and discovery Riebeckite was first described in 1888 for an occurrence on Socotra Island, Aden Governorate, Yemen, and named for German explorer Emil Riebeck (1853–1885). The mineral is also known as crocidolite. Occurrence Riebeckite typically forms dark-blue elongated to fibrous crystals in highly alkali granites, syenites, rarely in felsic volcanics, granite pegmatites and schist. It occurs in banded i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibole
Amphibole () is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is Amp. Amphiboles can be green, black, colorless, white, yellow, blue, or brown. The International Mineralogical Association currently classifies amphiboles as a mineral supergroup, within which are two groups and several subgroups. Mineralogy Amphiboles crystallize into two crystal systems, monoclinic and orthorhombic. In chemical composition and general characteristics they are similar to the pyroxenes. The chief differences from pyroxenes are that (i) amphiboles contain essential hydroxyl (OH) or halogen (F, Cl) and (ii) the basic structure is a double chain of tetrahedra (as opposed to the single chain structure of pyroxene). Most apparent, in hand specimens, is that amphiboles form oblique cleavage planes (at around 120 degrees), whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and ferro-actinolite. Pure magnesium tremolite is creamy white, but the color grades to dark green with increasing iron content. It has a hardness on Mohs scale of 5 to 6. Nephrite, one of the two minerals of the gemstone jade, is a green variety of tremolite. The fibrous form of tremolite is one of the six recognised types of asbestos. This material is toxic, and inhaling the fibers can lead to asbestosis, lung cancer and both pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma. Fibrous tremolite is sometimes found as a contaminant in vermiculite, chrysotile (itself a type of asbestos) and talc. Occurrence Tremolite is an indicator of metamorphic grade since at high temperatures it converts to diopside. Tremolite occurs as a result of contact metam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or '' granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arfvedsonite
Arfvedsonite () is a sodium amphibole mineral with composition: aNa2] Fe2+)4Fe3+(OH)2, Si8O22]. It crystallizes in the monoclinic prismatic crystal system and typically occurs as greenish black to bluish grey fibrous to radiating or stellate prisms. It is a rather rare mineral occurring in nepheline syenite intrusions and agpaitic (peralkaline) pegmatites and granites as the Golden Horn batholith in Okanogan County, Washington (type locality for zektzerite). Occurrences include Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada; the Ilímaussaq complex in Southern Greenland; and in pegmatites of the Kola Peninsula, Russia. Its mineral association includes nepheline, albite, aegirine, riebeckite, katophorite and quartz. Arfvedsonite was discovered in 1823 and named for the Swedish chemist Johan August Arfwedson (1792–1841). See also * List of minerals * List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition follows name. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegirine
Aegirine is a member of the clinopyroxene group of inosilicate minerals. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula Na Fe Si2 O6 in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augite series the sodium is variably replaced by calcium with iron(II) and magnesium replacing the iron(III) to balance the charge. Aluminium also substitutes for the iron(III). Acmite is a fibrous, green-colored variety. Aegirine occurs as dark green monoclinic prismatic crystals. It has a glassy luster and perfect cleavage. Its Mohs hardness varies from 5 to 6, and its specific gravity is between 3.2 and 3.4. This mineral commonly occurs in alkalic igneous rocks, nepheline syenites, carbonatites and pegmatites. It also appears in regionally metamorphosed schists, gneisses, and iron formations; in blueschist facies rocks, and from sodium metasomatism in granulites. It may occur as an authigenic mineral in shales and marls. It occurs in asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere by abrasion and other processes. Inhalation of asbestos fibres can lead to various dangerous lung conditions, including mesothelioma, asbestosis, and lung cancer, so it is now notorious as a serious health and safety hazard. Archaeological studies have found evidence of asbestos being used as far back as the Stone Age to strengthen ceramic pots, but large-scale mining began at the end of the 19th century when manufacturers and builders began using asbestos for its desirable physical properties. Asbestos is an excellent electrical insulator and is highly fire-resistant, so for much of the 20th century it was very commonly used across the world as a building material, until its adverse effects on human health were more widely acknowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asbestiform
Asbestiform is a crystal habit. It describes a mineral that grows in a fibrous aggregate of high tensile strength, flexible, long, and thin crystals that readily separate.Committee on Asbestos: Selected Health Effects, 2006, ''Asbestos: Selected Cancers,'' National Academies Press, The most common asbestiform mineral is chrysotile, commonly called "white asbestos", a magnesium phyllosilicate part of the serpentine group. Other asbestiform minerals include riebeckite, an amphibole whose fibrous form is known as crocidolite or "blue asbestos", and brown asbestos, a cummingtonite-grunerite solid solution series. The United States Environmental Protection Agency explains that, "In general, exposure may occur only when the asbestos-containing material is disturbed or damaged in some way to release particles and fibers into the air." "Mountain leather" is an old-fashioned term for flexible, sheet-like natural formations of asbestiform minerals which resemble leather. Asbestos-containi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil Riebeck
Emil Riebeck (11 June 1853 – 22 June 1885) was a German explorer, mineralogist, ethnologist, and naturalist. He was born in Preusslitz to Carl Adolf Riebeck, an industrial magnate. He traveled to North Africa and Arabia several times, and in 1881 travelled with Georg Schweinfurth on an expedition to Socotra. He traveled with Adolf Bastian to the hills of Chittagong in 1882. In 1884, he financed Gottlob Krause’s expedition to the Niger River, Benue River, and Lake Chad. Riebeck amassed an extensive collection of artifacts from Eastern Asia, India, Arabia and Africa. The mineral riebeckite is named after him. Also, a species of Socotran lizard, ''Haemodracon riebeckii ''Haemodracon riebeckii'' is a species of lizard in the family Phyllodactylidae. The species is endemic to Yemen. Etymology The specific name, ''riebeckii'', is in honor of German ethnologist Emil Riebeck. Beolens B, Watkins M, Grayson M ...'', is named in his honor.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prism (geometry)
In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an polygon base, a second base which is a translated copy (rigidly moved without rotation) of the first, and other faces, necessarily all parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the bases are translations of the bases. Prisms are named after their bases, e.g. a prism with a pentagonal base is called a pentagonal prism. Prisms are a subclass of prismatoids. Like many basic geometric terms, the word ''prism'' () was first used in Euclid's Elements. Euclid defined the term in Book XI as “a solid figure contained by two opposite, equal and parallel planes, while the rest are parallelograms”. However, this definition has been criticized for not being specific enough in relation to the nature of the bases, which caused confusion among later geometry writers. Oblique prism An oblique prism is a prism in which the joining edges and faces are ''not perpendicular'' to the bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic composition to granite. However, rarer intermediate composition and mafic pegmatites are known. Many of the world's largest crystals are found within pegmatites. These include crystals of microcline, quartz, mica, spodumene, beryl, and tourmaline. Some individual crystals are over long. Most pegmatites are thought to form from the last fluid fraction of a large crystallizing magma body. This residual fluid is highly enriched in volatiles and trace elements, and its very low viscosity allows molecules to migrate rapidly to join an existing crystal rather than coming together to form new crystals. This allows a few very large crystals to form. While most pegmatites have a simple composition of minerals common in ordinary igneous rock, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/angstrom. (, ; , ) or ångström is a metric unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth ( US) of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre,Entry "angstrom" in the Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1986). Retrieved on 2021-11-22 from https://www.oed.com/oed2/00008552. 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. Its symbol is Å, a letter of the Swedish alphabet. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–1874). The angstrom is often used in the natural sciences and technology to express sizes of atoms, molecules, microscopic biological structures, and lengths of chemical bonds, arrangement of atoms in crystals,Arturas Vailionis (2015):Geometry of Crystals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)