|
Richard Tomlinson
Richard John Charles Tomlinson (born 13 January 1963) is a former officer of the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6). He argued that he was subjected to unfair dismissal from MI6 in 1995, and attempted to take his former employer to a tribunal. MI6 refused, arguing that to do so would breach state security. Tomlinson was imprisoned under the Official Secrets Act 1989 in 1997 after he gave a synopsis of a proposed book detailing his career with MI6 to an Australian publisher. He served six months of a twelve-month sentence before being given parole, whereupon he left the country. The book, named ''The Big Breach,'' was published in Moscow in 2001 (and later in Edinburgh), and was subsequently serialised by ''The Sunday Times''. The book detailed various aspects of MI6 operations, alleging that it employed a mole in the German Bundesbank and that it had a "licence to kill", the latter later confirmed by the head of MI6 at a public hearing. Tomlinson then attempted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligence Officer
An intelligence officer is a person employed by an organization to collect, compile or analyze information (known as intelligence) which is of use to that organization. The word of ''officer'' is a working title, not a rank, used in the same way a "police officer" can also be a sergeant, or in the military, in which non-commissioned personnel may serve as intelligence officers. Organizations which employ intelligence officers include armed forces, police, and customs agencies. Sources of intelligence Intelligence officers make use of a variety of sources of information, including ; Communications intelligence (COMINT): Eavesdropping and interception of communications (e.g., by wiretapping) including signals intelligence (SIGINT) and electronic intelligence (ELINT). ; Financial intelligence (FININT): The gathering of information about the financial affairs of entities of interest. ; Human intelligence (HUMINT): Derived from covert human intelligence sources ( Covert Human Intellige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević (, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the president of Serbia within Yugoslavia from 1989 to 1997 (originally the Socialist Republic of Serbia, a constituent republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, from 1989 to 1992) and president of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1997 to 2000. Formerly a high-ranking member of the League of Communists of Serbia (SKS) during the 1980s, he led the Socialist Party of Serbia from its foundation in 1990 until 2003. Born in Požarevac, he studied law at the University of Belgrade Faculty of Law and joined the League of Socialist Youth of Yugoslavia as a student. During the 1960s he served as an advisor to mayor of Belgrade Branko Pešić, and was later appointed chairman of Tehnogas and Beobanka, roles which he served until the 1980s. Milošević rose to power in 1987 by promoting populist and nationalist views, arguing for the reduction of power of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Roberts (historian)
Andrew Roberts, Baron Roberts of Belgravia (born 13 January 1963) is an English historian and journalist. He is a visiting professor at the Department of War Studies, King's College London, a Roger and Martha Mertz Visiting Research Fellow at the Hoover Institution at Stanford University, and a Lehrman Institute Distinguished Lecturer at the New-York Historical Society. He was a trustee of the National Portrait Gallery, London from 2013 to 2021. Roberts' public commentary has appeared in several periodicals such as ''The Daily Telegraph'' and ''The Spectator''. He is well known internationally for his 2009 non-fiction work '' The Storm of War'', which covers historical factors of the Second World War such as Adolf Hitler's rise to power and the organisation of Nazi Germany. The book has been lauded by several publications, notably ''The Economist'', and it additionally received the British Army Military Book of the Year Award for 2010. Much of Roberts' work, including his 2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
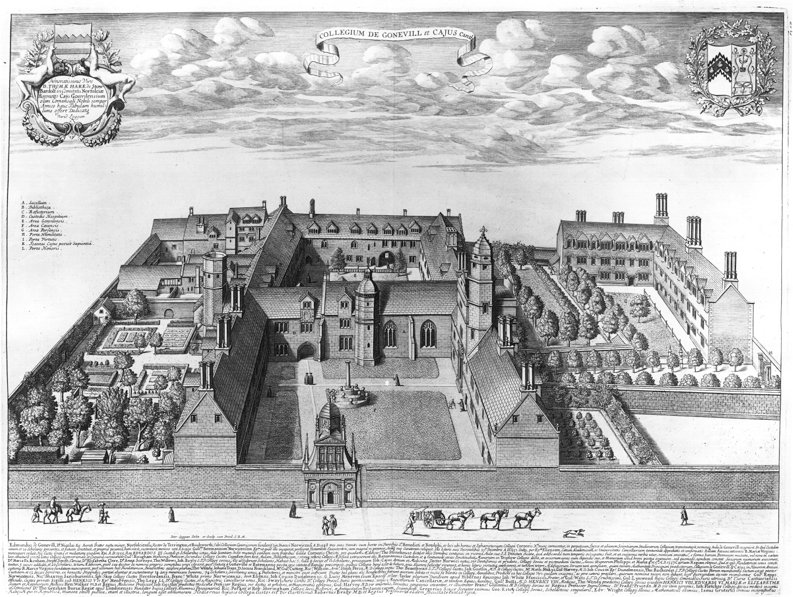
Gonville And Caius College
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Chadwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rob Andrew
Christopher Robert Andrew (born 18 February 1963) is a former English Rugby Union player and was, until April 2016, Professional Rugby Director at the RFU. He was formerly the Director of Rugby of Newcastle Falcons and has been Chief Executive of Sussex County Cricket Club since January 2017.Rob Andrew: Sussex name ex-England rugby player as chief executive '''', 23 November 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2016. As a player, Andrew was assured in his kicking and defensive skills off both feet. Andrew also had a brief career in |
Rory Underwood
Rory Underwood, (born 19 June 1963) is an English former rugby union player, he is 's record international try scorer with 49 tries in 85 internationals between 1984 and 1996. Underwood's principal position was wing and he played 236 games for Leicester Tigers between 1983 and 1997, he also played for Middlesbrough, Bedford Blues and the Royal Air Force. Underwood toured with the British and Irish Lions in 1989 and 1993 playing in six tests and scoring one try. In 1992 Underwood played for England alongside his younger brother Tony Underwood, becoming the first brothers to play together for England since 1937. Playing during the amateur era his profession was as a Royal Air Force pilot. Early life Underwood was born in Middlesbrough, England, of Chinese-English parentage. His father was a Yorkshire engineer who worked in Malaysia where he met and married Underwood's Chinese-Malaysian mother. Underwood was educated at Barnard Castle School (with fellow rugby international Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnard Castle School
Barnard Castle School (colloquially Barney School or locally the County School) is a co-educational Independent school (United Kingdom), independent day and boarding school in the market town of Barnard Castle, County Durham, in the North East England, North East of England. It is a member of The Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference (HMC). It was founded in 1883 with funding from a 13th-century Financial endowment, endowment of John I de Balliol and the bequest of the local industrialist Benjamin Flounders. The ambition was to create a school of the quality of the ancient Public school (United Kingdom), public schools at a more reasonable cost, whilst accepting pupils regardless of their faith. Originally the ''North Eastern County School'', the name was changed in 1924, but is still generally known locally as the "County School". The school is set in its own grounds in Teesdale, within the North Pennines, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. An on-site Preparatory School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts ( Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness (Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland ( Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by area. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armathwaite
Armathwaite is a village in the English ceremonial county of Cumbria. Historically within the county of Cumberland, Armathwaite lies on the River Eden, forms part of Eden district and is served by Armathwaite railway station. The majority of the village is in Hesket civil parish but with some buildings in the parish of Ainstable and others on the outskirts of the village located in the parish of Wetheral, within the City of Carlisle district. The castle on the west bank of the river was originally a pele tower with a large but undistinguished Edwardian extension. The parish church of Christ and St Mary was formerly a chapel-of-ease in the parish of Hesket-in-the-Forest and is one of the smallest parish churches in England. By the 17th century the original chapel had become ruinous but it was rebuilt before 1688 by Richard Skelton of Armathwaite Castle. It consists of a chancel and nave with a wooden roof and a small western bell turret. The town of Armathwaite in Fentress Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle University
Newcastle University (legally the University of Newcastle upon Tyne) is a UK public university, public research university based in Newcastle upon Tyne, North East England. It has overseas campuses in Singapore and Malaysia. The university is a red brick university and a member of the Russell Group, an association of research-intensive UK universities. The university finds its roots in the School of Medicine and Surgery (later the College of Medicine), established in 1834, and the Edward Fenwick Boyd#College of Physical Science, College of Physical Science (later renamed Armstrong College), founded in 1871. These two colleges came to form the larger division of the federal University of Durham, with the Durham Colleges forming the other. The Newcastle colleges merged to form King's College in 1937. In 1963, following an Act of Parliament, King's College became the University of Newcastle upon Tyne. The university subdivides into three faculties: the Faculty of Humanities and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Agriculture And Forestry (New Zealand)
The Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (in Māori, ''Te Manatu Ahuwhenua, Ngāherehere'') was a state sector organisation of New Zealand which dealt with matters relating to agriculture, forestry and biosecurity. It was commonly known by its acronym, "MAF". In April 2012, it became part of the newly formed Ministry for Primary Industries. History The New Zealand Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry was formerly known as the ''Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries'', but in 1995 responsibilities for fisheries were passed to the newly formed Ministry of Fisheries. However, the government of New Zealand decided that, despite the loss of Fisheries, the newly created ''Ministry of Agriculture'' should continue to be known by the acronym "MAF", and should still use the same logo, because of the high recognition and regard for the name and logo amongst the country's overseas trading partners. In 1998, this Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Forestry merged to become the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |