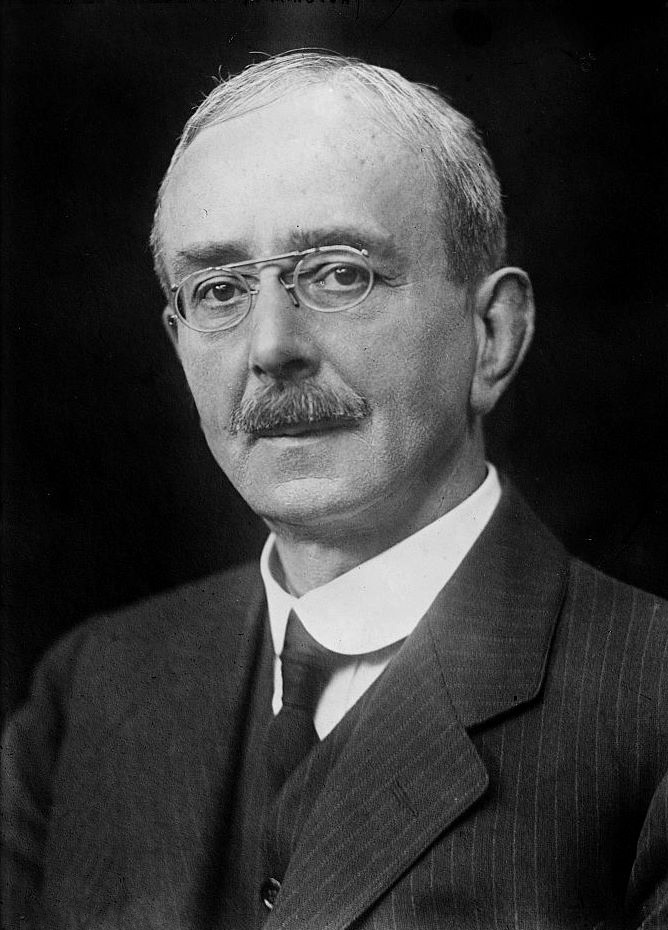|
Revue Neurologique
The ''Revue neurologique'' (''Neurological Review'') is a French neurological and psychiatric medical journal. It was established in 1893 with Jean-Martin Charcot as adviser. Today it is the official journal of the Société Française de Neurologie (French Neurology Society). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2016 impact factor of 1.039. The monthly journal became the main periodical in France devoted to psychiatry and nervous diseases. It was made the official journal of the Société de Neurologie de Paris when the society was founded in 1899. It gradually displaced the quarterly ''Archives de Neurologie'', publishing original articles by prominent French neurologists such as Charcot, Joseph Jules Dejerine, Édouard Brissaud and Fulgence Raymond, as well as work from foreign researchers including Charles Scott Sherrington of Great Britain, Alexander E. Scherbak of Russia, and João Baptista de Lacerda of Argentine. In November 1901 the ''Revue N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Brissaud
Édouard Brissaud (15 April 1852, Besançon – 20 December 1909) was a French physician and pathologist. He was taught by Jean Martin Charcot at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital. He had interests in a number of medical disciplines including motion disturbances, anatomy, neurology and psychiatry. He died of a brain tumour, aged 57. He has been awarded a large number of eponyms many of which are now rarely used and some were not the dominant eponym in use. *Bourneville-Brissaud disease – tuberous sclerosis. He studied one of the earliest diagnosed cases with Désiré-Magloire Bourneville in 1881. *Brissaud's scoliosis – a form of scoliosis giving "a list of the lumbar part of the spine away from the affected side in sciatica" (Dorland's Medical Dictionary). Described in 1895. *Brissaud's disease – Tourette syndrome. He gave a detailed description in 1896. *Brissaud's infantilism – infantile myxedema (hypothyroidism). Described in 1907. * Brissaud's reflex – a contraction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Established In 1893
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2010-05-10.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other audio-visual content, including paper ( |
French-language Journals
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the ''Organisation internationale de la Francophonie'' (O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology Journals
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical specialty, its corresponding surgical specialty is neurosurgery. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akathisia
Akathisia is a movement disorder characterized by a subjective feeling of inner restlessness accompanied by mental distress and an inability to sit still. Usually, the legs are most prominently affected. Those affected may fidget, rock back and forth, or pace, while some may just have an uneasy feeling in their body. The most severe cases may result in aggression, violence, and/or suicidal thoughts. Akathisia is also associated with threatening behaviour and physical aggression that is greatest in patients with mild akathisia, and diminishing with increasing severity of akathisia. Antipsychotic medication, particularly the first generation antipsychotics, are a leading cause. Other agents commonly responsible for this side-effect may also include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, metoclopramide, and reserpine, though any medication listing agitation as a side effect may trigger it. It may also occur upon stopping antipsychotics. The underlying mechanism is believed to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
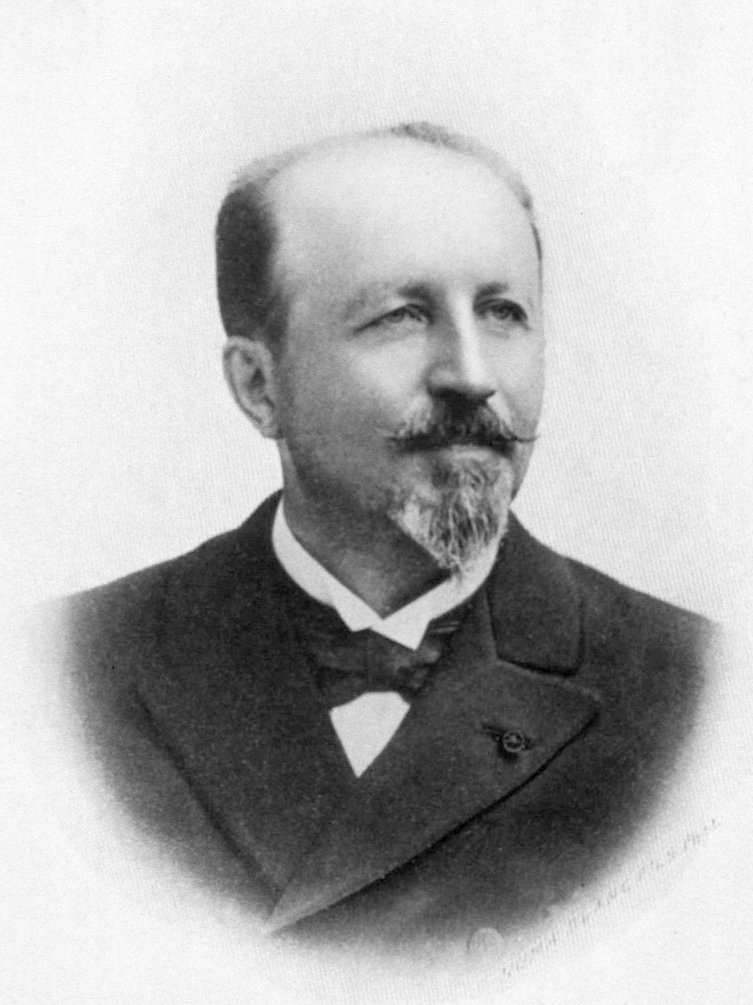
Ladislav Haškovec
Ladislav Haškovec (May 18, 1866 – January 16, 1944) was a Czech neuropsychiatrist, eugenicist, and physician, professor of neuropathology at the Charles University in Prague. In November 1901 he coined the term " akathisia" in the journal ''Revue neurologique'', and with Jean-Martin Charcot provided an initial demonstration to the Paris Neurological Society after noting that two patients were unable to remain seated. In 1905 he founded the first neurological department in the area of today's Czech Republic. He is considered one of the founders of the Czechoslovak neurology. Biography Born in Bechyně, Haškovec studied at the gymnasium in Jindřichův Hradec, and later continued at the Medical Faculty of Charles University in Prague, graduating in 1891. He started medical practice in the laboratory of the National Museum, where he focused on craniology – the science dealing with the morphological description of the skull. From 1890 to 1891 he worked in the Pathological-An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
João Baptista De Lacerda
João Batista de Lacerda (12 July 1846 – 6 August 1915), was a physician and one of the pioneering Brazilian biomedical scientists in the fields of experimental physiology and pharmacology. Biography Born in Campos dos Goytacazes in 1846, João Baptista de Lacerda graduated in medicine from the Medical School of Rio de Janeiro and returned to Campos to open a private practice. Soon after, he was invited by the Minister of Agriculture to be the associate director of the section of anthropology, zoology and paleontology of the recently created National Museum of Natural History of Rio de Janeiro, by Emperor D. Pedro II. Later, he assumed also the associate directorship of the Laboratory of Experimental Physiology, under the French physiologist Louis Couty, who had been invited to the post. In this position, Lacerda carried out successfully a number of experimental investigations on curare and the poisons of Brazilian snakes, frogs and lizards. One of his important discoveri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander E
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre (given name), Alexandre, Aleks (given name), Aleks, Aleksa (given name), Aleksa and Sander (name), Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria (given name), Alexandria, and Sasha (name), Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genetive, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy shield wall, battle line. The earliest Attested langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Scott Sherrington
Sir Charles Scott Sherrington (27 November 1857 – 4 March 1952) was an eminent English neurophysiologist. His experimental research established many aspects of contemporary neuroscience, including the concept of the spinal reflex as a system involving connected neurons (the "neuron doctrine"), and the ways in which signal transmission between neurons can be potentiated or depotentiated. Sherrington himself coined the word "synapse" to define the connection between two neurons. His book ''The Integrative Action of the Nervous System'' (1906) is a synthesis of this work, in recognition of which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1932 (along with Edgar Adrian). In addition to his work in physiology, Sherrington did research in histology, bacteriology, and pathology. He was president of the Royal Society in the early 1920s. Biography Early years and education Official biographies claim Charles Scott Sherrington was born in Islington, London, England, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulgence Raymond
Fulgence Raymond (29 September 1844 – 28 September 1910) was a French neurologist born in Saint-Christophe-sur-le-Nais, Indre-et-Loire. Originally trained as a veterinarian, he later studied human medicine under Alfred Vulpian (1826–1887) in Paris. In 1877 he was ''chef de clinique'' under Germain Sée (1818–1896), becoming ''médecin des hôpitaux'' during the following year, and receiving his habilitation in 1880. In 1894 he succeeded Jean Martin Charcot (1825–1893) as chair of neurology at the Faculty of Medicine; a position he held until his death in 1910. During his career he worked with several famous physicians, including Joseph Babinski (1857–1932), Gheorghe Marinescu, Georges Marinesco (1863–1938) and Pierre Marie (1853–1940). Radiologist Jean-Athanase Sicard (1872–1929) was a prominent student of his. Raymond made contributions in research of syringomyelia, neurasthenia, poliomyelitis, tabes dorsalis and diseases of the cauda equina, to name a few. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Jules Dejerine
Joseph Jules Dejerine (3 August 1849 – 26 February 1917), was a French neurologist. Biography Joseph Jules Dejerine was born to French parents in Geneva, Switzerland, where his father was a carriage proprietor. During the Franco-Prussian War (1870) Dejerine worked as a volunteer in a Geneva Hospital and in the spring of 1871 decided to pursue his medicine studies in Paris. In France, he was introduced to and subsequently became a pupil of Alfred Vulpian, a notable neurologist. Following qualification he achieved the academic ranks and gained several awards. In 1877 he was appointed to the Hôpital Bicêtre, where he organized a pathological laboratory. He became ''professeur agrégé'' in 1886, and he found the opportunity to concentrate his efforts on neurology. He worked at the Hôpital Salpêtrière from 1895, became professor of the history of medicine in 1901 and received a senior appointment at the Salpêtrière in 1911 as professor of neurology at the University of Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |