|
Reva, South Dakota
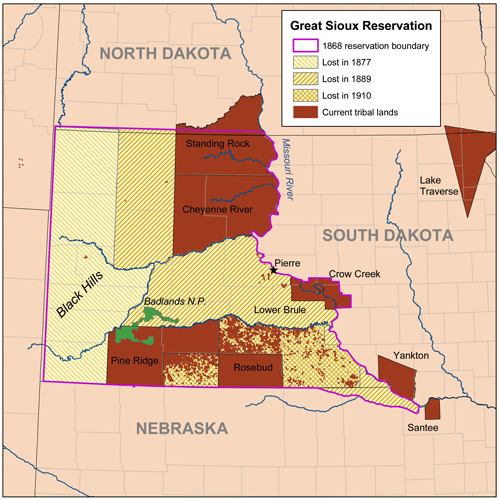
Reva is an unincorporated community in Harding County, South Dakota, United States. Although not tracked by the Census Bureau, Reva has been assigned the ZIP code of 57651. The community has the name of Reva Bonniwell, the daughter of a first settler. It is the location of the annual Reva Turtle Races. History The Battle of Slim Buttes occurred here on September 9–10, 1876, in the Great Sioux Reservation between the United States Army and Miniconjou Sioux during the Great Sioux War of 1876. It marked the first significant victory for the Army since the stunning defeat of General George Custer at the Battle of Little Bighorn in June. One hundred fifty troopers led by Captain Anson Mills from the 3rd U.S. Cavalry surrounded the village of thirty-seven lodges and attacked it the next morning, shooting anyone who resisted. Taken by surprise, the Native Americans fled, with a mortally wounded Chief American Horse the elder and fifteen women and children hiding in a nearby ravine/dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unincorporated Area
An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have no unincorporated areas at all or these are very rare: typically remote, outlying, sparsely populated or List of uninhabited regions, uninhabited areas. By country Argentina In Argentina, the provinces of Chubut Province, Chubut, Córdoba Province (Argentina), Córdoba, Entre Ríos Province, Entre Ríos, Formosa Province, Formosa, Neuquén Province, Neuquén, Río Negro Province, Río Negro, San Luis Province, San Luis, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, Santa Cruz, Santiago del Estero Province, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina, Tierra del Fuego, and Tucumán Province, Tucumán have areas that are outside any municipality or commune. Australia Unlike many other countries, Australia has only local government in Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniconjou
The Miniconjou (Lakota: Mnikowoju, Hokwoju – ‘Plants by the Water’) are a Native American people constituting a subdivision of the Lakota people, who formerly inhabited an area in western present-day South Dakota from the Black Hills in to the Platte River. The contemporary population lives mostly in west-central South Dakota. Perhaps the most famous Miniconjou chief was Touch the Clouds. Historic Miniconjou thiyóšpaye or bands Together with the Sans Arc (''Itázipčho'', ''Itazipcola'', ''Hazipco'' - ‘Those who hunt without bows’) and Two Kettles (''Oóhe Núŋpa'', ''Oóhenuŋpa'', ''Oohenonpa'' - ‘Two Boiling’ or ‘Two Kettles’) they were often referred to as ''Central Lakota'' and divided into several ''bands'' or ''thiyóšpaye'': * Unkche yuta (‘Dung Eaters’) * Glaglaheca (‘Untidy’, ‘Slovenly’, ‘Shiftless’) * Shunka Yute Shni (‘Eat No Dogs’, split off from the ''Wanhin Wega'') * Nige Tanka (‘Big Belly’) * Wakpokinyan (‘Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
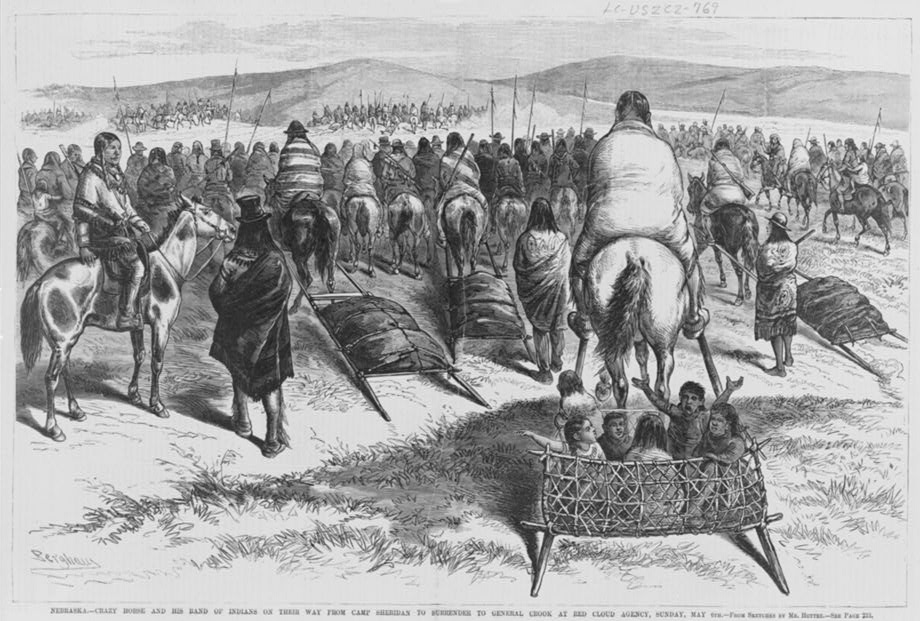
Crazy Horse
Crazy Horse ( lkt, Tȟašúŋke Witkó, italic=no, , ; 1840 – September 5, 1877) was a Lakota war leader of the Oglala band in the 19th century. He took up arms against the United States federal government to fight against encroachment by white American settlers on Native American territory and to preserve the traditional way of life of the Lakota people. His participation in several famous battles of the Black Hills War on the northern Great Plains, among them the Fetterman Fight in 1866, in which he acted as a decoy, and the Battle of the Little Bighorn in 1876, in which he led a war party to victory, earned him great respect from both his enemies and his own people. In September 1877, four months after surrendering to U.S. troops under General George Crook, Crazy Horse was fatally wounded by a bayonet-wielding military guard while allegedly resisting imprisonment at Camp Robinson in present-day Nebraska. He was honored by the U.S. Postal Service in 1982 with a 13¢ Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheyenne People
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian languages, Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized tribe, federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes in Oklahoma, and the Northern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation in Montana. The Cheyenne comprise two Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o (more commonly spelled as Suhtai or Sutaio) and the Tsétsêhéstâhese (also spelled Tsitsistas, The term for the Cheyenne homeland is ''Tsiihistano''. Language The Cheyenne of Montana and Oklahoma speak the Cheyenne language, known as ''Tsêhésenêstsestôtse'' (common spelling: Tsisinstsistots). Approximately 800 people speak Cheyenne in Oklahoma. There are only a handful of vocabulary d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brulé
The Brulé are one of the seven branches or bands (sometimes called "sub-tribes") of the Teton (Titonwan) Lakota American Indian people. They are known as Sičhą́ǧu Oyáte (in Lakȟóta) —Sicangu Oyate—, ''Sicangu Lakota, o''r "Burnt Thighs Nation". Learning the meaning of their name, the French called them the ''Brûlé'' (literally, "burnt"). The name may have derived from an incident where they were fleeing through a grass fire on the plains. Distribution Many Sičhą́ǧu people live on the Rosebud Indian Reservation in southwestern South Dakota and are enrolled in the federally recognized Rosebud Sioux Tribe, also known in Lakȟóta as the ''Sičhą́ǧu Oyáte.'' A smaller population lives on the Lower Brule Indian Reservation, on the west bank of the Missouri River in central South Dakota, and on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, also in South Dakota, directly west of the Rosebud Indian Reservation. The different federally recognized tribes are politically inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sans Arc
The Sans Arc, or Itázipčho (''Itazipcola'', ''Hazipco'' - ‘Those who hunt without bows’) in Lakota, are a subdivision of the Lakota people. Sans Arc is the French translation of the Lakota name which means, "Without bows." The translator of '' Wooden Leg: A Warrior Who Fought Custer'' renders the name as Arrows all Gone. They live in the Cheyenne River Reservation. One of the many etymologies of the ''Lakota'' name tells the following story: The true meaning of ''Itazipacola'' is "no markings". This referred to the fact that the ''Itazipco'' were so generous they did not mark their arrows (they were usually marked so that braves could claim the bison they killed, etc.), that way everyone could share the meat of the hunt. This is why when the Creator wanted to give the pipe to the ''Lakota'', the White Buffalo Woman ''Wopi'' brought it to the ''Itazipco'', because they would always be willing to share it. Historic Itázipčho thiyóšpaye or bands Together with the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Horse (elder)
American Horse (Oglala Lakota: ''Wašíčuŋ Tȟašúŋke'' in Standard Lakota Orthography) (a/k/a "American Horse the Elder") (1830–September 9, 1876) was an Oglala Lakota warrior chief renowned for courage and honor. American Horse is notable in American history as one of the principal war chiefs allied with Crazy Horse during Red Cloud's War (1866–1868) and the Battle of the Little Bighorn during the Great Sioux War of 1876–1877. Chief American Horse was a son of Old Chief Smoke, an Oglala Lakota head chief and one of the last great Shirt Wearers, a highly prestigious Lakota warrior society. He was a signatory to the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868, along with his brothers Chief Red Cloud and Chief Blue Horse. A month or so after the Treaty, American Horse was chosen a ''"Ogle Tanka Un"'' (Shirt Wearer, or war leader) along with Crazy Horse, Young-Man-Afraid-of-His-Horses and Man That Owns a Sword. On September 9, 1876, American Horse was mortally wounded in the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd U
Third or 3rd may refer to: Numbers * 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3 * , a fraction of one third * 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute'' Places * 3rd Street (other) * Third Avenue (other) * Highway 3 Music Music theory *Interval number of three in a musical interval **major third, a third spanning four semitones **minor third, a third encompassing three half steps, or semitones **neutral third, wider than a minor third but narrower than a major third **augmented third, an interval of five semitones **diminished third, produced by narrowing a minor third by a chromatic semitone *Third (chord), chord member a third above the root *Degree (music), three away from tonic **mediant, third degree of the diatonic scale **submediant, sixth degree of the diatonic scale – three steps below the tonic **chromatic mediant, chromatic relationship by thirds *Ladder of thirds, similar to the circle of fifths Albums *''Third/Sister Lovers'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anson Mills
Anson Mills (August 31, 1834 – November 5, 1924) was a United States Army officer, surveyor, inventor, and entrepreneur. Engaged in south Texas as a land surveyor and civil engineer, he both named and laid out the city of El Paso, Texas. Mills also invented a woven cartridge belt which late in life made his fortune. Biography Mills was born on a farm near Thorntown, Indiana, the first of nine children to a father and mother of Quaker ancestry but with no particular interest in religion. As a young man, Mills worked on the farm but also became a practiced carpenter and weaver. In 1855, he entered West Point but in 1857 was dismissed for "deficiency in mathematics." Too embarrassed to return home, he taught school in McKinney, Texas and then moved on to El Paso to work as a surveyor, which included drawing up the original plat of the town. When the Civil War broke out in 1861, he accepted a commission as a first lieutenant in the regular 18th Infantry regiment of the U.S. Army. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Little Bighorn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota people, Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and also commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes and the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army. The battle, which resulted in the defeat of U.S. forces, was the most significant action of the Great Sioux War of 1876. It took place on June 25–26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River in the Crow Indian Reservation in southeastern Montana Territory. Most battles in the Great Sioux War, including the Battle of the Little Bighorn (14 on the map to the right), "were on lands those Indians had taken from other tribes since 1851". The Lakotas were there without consent from the local Crow tribe, which had treaty on the area. Already in 1873, Crow chief Blackfoot had called for U.S. military actions against the Indian intruders. The stead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars. Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, but as the Civil War was just starting, trained officers were in immediate demand. He worked closely with General George B. McClellan and the future General Alfred Pleasonton, both of whom recognized his qualities as a cavalry leader, and he was promoted to brigadier general of volunteers at age 23. Only a few days after his promotion, he fought at the Battle of Gettysburg, where he commanded the Michigan Cavalry Brigade and despite being outnumbered, defeated J. E. B. Stuart's attack at what is now known as the East Cavalry Field. In 1864, he served in the Overland Campaign and in Philip Sheridan's army in the Shenandoah Valley, defeating Jubal Early at Cedar Creek. His division blocked the Army of Northern Virginia's final retreat an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sioux War Of 1876
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the desire of the US government to obtain ownership of the Black Hills. Gold had been discovered in the Black Hills, settlers began to encroach onto Native American lands, and the Sioux and the Cheyenne refused to cede ownership. Traditionally, American military and historians place the Lakota at the center of the story, especially because of their numbers, but some Native Americans believe the Cheyenne were the primary target of the American campaign. Among the many battles and skirmishes of the war was the Battle of the Little Bighorn; often known as Custer's Last Stand, it is the most storied of the many encounters between the US Army and mounted Plains Indians. Despite the Indian victory, the Americans leveraged national resources to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)