|
RevCen
RevCen is a family of non-coding RNA found in ''Schizosaccharomyces''. It is a megastructure containing several siRNA which use the RNAi pathway to regulate heterochromatin formation. The long RNA transcript forms a secondary structure with several stem-loops which are processed by dicer into siRNA. This siRNA then initiate the formation of heterochromatin at the centromeres of fission yeast. Northern blot analysis confirmed the siRNAs were produced from the large RNA structure RevCen ''in vivo''. As with all siRNAs, the enzyme dicer is responsible for dissecting dsRNA into the 21 nt stretch of double-stranded RNA. Human recombinant dicer enzyme processed the RevCen structure ''in vitro'', though the same activity by yeast Dcr1 has not been confirmed. This is a different mechanism to that involving the well-understood RITS (RNA-induced initiation of transcriptional gene silencing Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals. Facultative hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the :wikt:anaerobic, absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugar in wine, sugars of the fruit into ethanol, alcohol and carbon dioxide throu ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
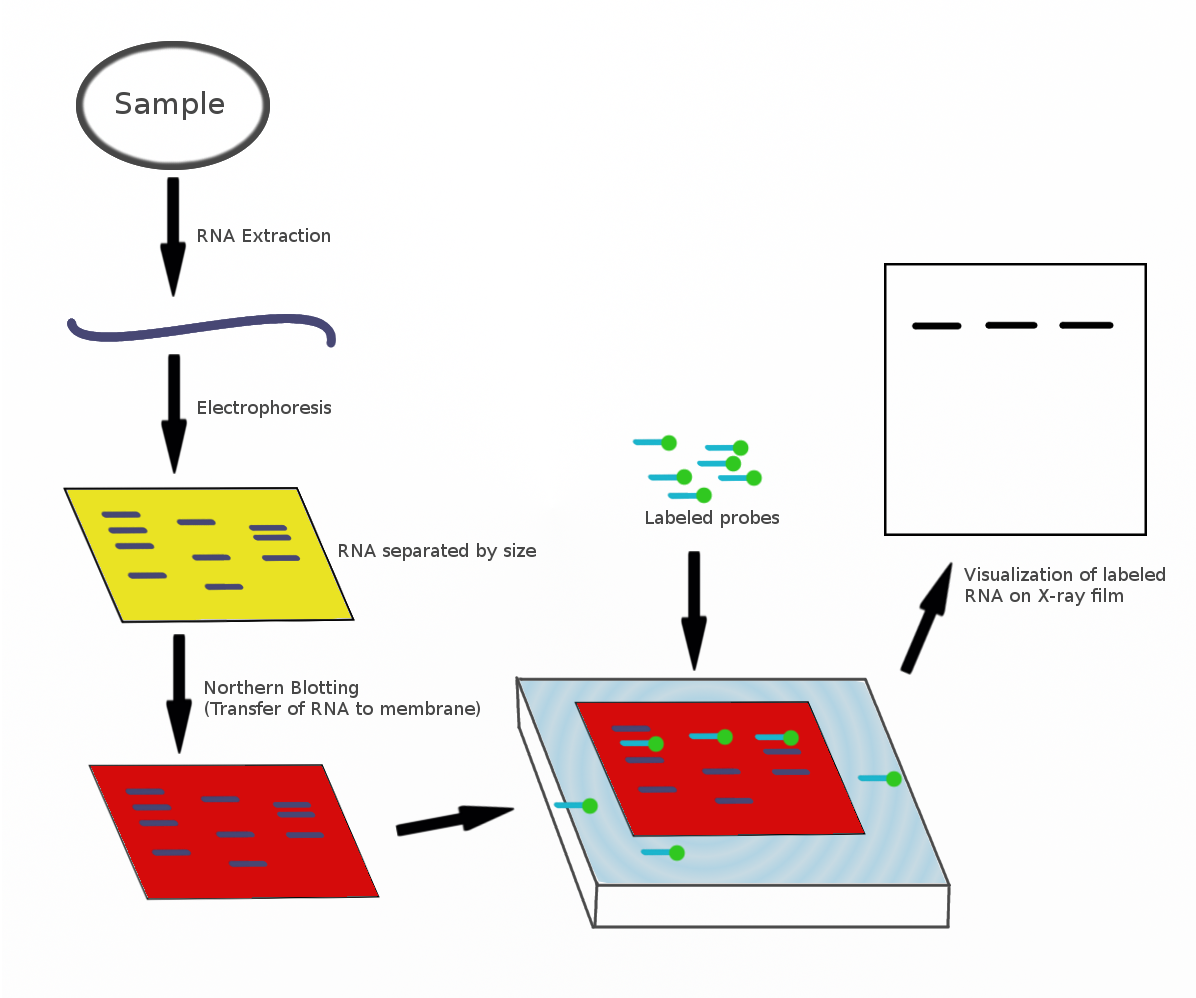
Northern Blot
The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.Kevil, C. G., Walsh, L., Laroux, F. S., Kalogeris, T., Grisham, M. B., Alexander, J. S. (1997) An Improved, Rapid Northern Protocol. Biochem. and Biophys. Research Comm. 238:277–279. With northern blotting it is possible to observe cellular control over structure and function by determining the particular gene expression rates during differentiation and morphogenesis, as well as in abnormal or diseased conditions. Northern blotting involves the use of electrophoresis to separate RNA samples by size, and detection with a hybridization probe complementary to part of or the entire target sequence. Strictly speaking, the term 'northern blot' refers specifically to the capillary transfer of RNA from the electrophoresis gel to the blotting m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caister Academic Press
Caister Academic Press is an independent academic publishing company that produces books and ebooks on microbiology and molecular biology. The address for the editorial offices is in Poole, UK with worldwide sales and distribution through the Ingram Content Group. Published books include review volumes, practical manuals and reference texts aimed at the post-graduate, research and professional market. Aims and scope Caister Academic Press aims to provide the scientific community with authoritative texts on topical areas of microbiology and molecular biology Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi .... There is a focus on current research and emerging trends. Volumes on related technology and applications are also published. History The academic publishing company was fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Silencing
Gene silencing is the regulation of gene expression in a cell to prevent the expression of a certain gene. Gene silencing can occur during either transcription or translation and is often used in research. In particular, methods used to silence genes are being increasingly used to produce therapeutics to combat cancer and other diseases, such as infectious diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. Gene silencing is often considered the same as gene knockdown. When genes are silenced, their expression is reduced. In contrast, when genes are knocked out, they are completely erased from the organism's genome and, thus, have no expression. Gene silencing is considered a gene knockdown mechanism since the methods used to silence genes, such as RNAi, CRISPR, or siRNA, generally reduce the expression of a gene by at least 70% but do not eliminate it. Methods using gene silencing are often considered better than gene knockouts since they allow researchers to study essential genes that are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RITS Complex
RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS) is a form of RNA interference by which short RNA molecules – such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) – trigger the downregulation of transcription of a particular gene or genomic region. This is usually accomplished by posttranslational modification of histone tails (e.g. methylation of lysine 9 of histone H3) which target the genomic region for heterochromatin formation. The protein complex that binds to siRNAs and interacts with the methylated lysine 9 residue of histones H3 is the RITS complex. RITS was discovered in the fission yeast '' Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', and has been shown to be involved in the initiation and spreading of heterochromatin in the mating-type region and in centromere formation. The RITS complex in ''S. pombe'' contains at least a piwi domain-containing RNase H-like argonaute, a chromodomain protein Chp1, and an argonaute interacting protein Tas3 which can also bind to Chp1, while heterochromatin fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centromere if pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fission Yeast
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function. There is no consensus in the literature on how much of non-coding transcription is functional. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional (sometimes referred to as "junk RNA"), spurious transcriptions. Others, however, disagree, arguing instead that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicer
Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into short double-stranded RNA fragments called small interfering RNA and microRNA, respectively. These fragments are approximately 20–25 base pairs long with a two-base overhang on the 3′-end. Dicer facilitates the activation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is essential for RNA interference. RISC has a catalytic component Argonaute, which is an endonuclease capable of degrading messenger RNA (mRNA). Discovery Dicer was given its name in 2001 by Stony Brook PhD student Emily Bernstein while conducting research in Gregory Hannon's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Bernstein sought to discover the enzyme responsible for generating small RNA fragments from double-stranded RNA. Dicer's ability to generate around 22 nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |