|
Resonant Cavities
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical (including acoustic). Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency. A cavity resonator is one in which waves exist in a hollow space inside the device. In electronics and radio, microwave cavities consisting of hollow metal boxes are used in microwave transmitters, receivers and test equipment to control frequency, in place of the tuned circuits which are used at lower frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive coefficient, constant. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force (Damping ratio, damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction coefficient, the system can: * Oscillate with a frequency lower than in the Damping ratio, undamped case, and an amplitude decreasing with time (Damping ratio, underdamped oscillator). * Decay to the equilibrium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'', is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum of harmonically related frequencies, or the frequency of the difference between adjacent frequencies. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as 0, indicating the lowest frequency counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as 1, the first harmonic. (The second harmonic is then 2 = 2⋅1, etc. In this context, the zeroth harmonic would be 0 Hz.) According to Benward's and Saker's ''Music: In Theory and Practice'': Explanation All sinusoidal and many non-sinusoidal waveforms repeat exactly over time – they are periodic. The period of a waveform is the smallest value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and wind instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Modes
A normal mode of a dynamical system is a pattern of motion in which all parts of the system move sinusoidally with the same frequency and with a fixed phase relation. The free motion described by the normal modes takes place at fixed frequencies. These fixed frequencies of the normal modes of a system are known as its natural frequencies or resonant frequencies. A physical object, such as a building, bridge, or molecule, has a set of normal modes and their natural frequencies that depend on its structure, materials and boundary conditions. The most general motion of a system is a superposition of its normal modes. The modes are normal in the sense that they can move independently, that is to say that an excitation of one mode will never cause motion of a different mode. In mathematical terms, normal modes are orthogonal to each other. General definitions Mode In the wave theory of physics and engineering, a mode in a dynamical system is a standing wave state of exci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
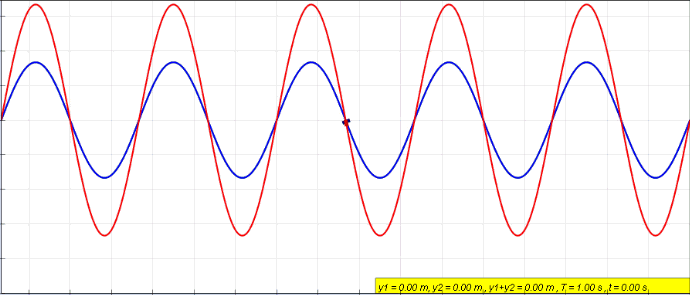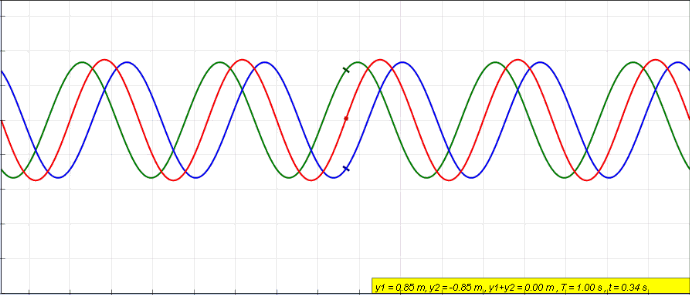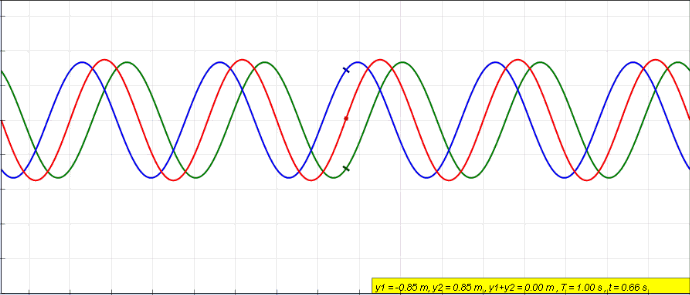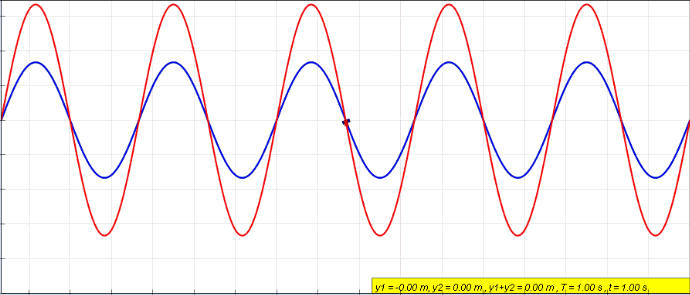
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', ''ordinary frequency'', the ''number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', ''angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, ''phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to be shifted in time by the amount ''φ''/''ω'' seconds. A negative value rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase of a periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is denoted \phi(t) and expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \phi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \phi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly scans the same range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (physics)
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Lattice
In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after , is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by : \mathbf = n_1 \mathbf_1 + n_2 \mathbf_2 + n_3 \mathbf_3, where the ''ni'' are any integers, and a''i'' are ''primitive translation vectors'', or ''primitive vectors'', which lie in different directions (not necessarily mutually perpendicular) and span the lattice. The choice of primitive vectors for a given Bravais lattice is not unique. A fundamental aspect of any Bravais lattice is that, for any choice of direction, the lattice appears exactly the same from each of the discrete lattice points when looking in that chosen direction. The Bravais lattice concept is used to formally define a ''crystalline arrangement'' and its (finite) frontiers. A crystal is made up of one or more atoms, called the ''basis'' or ''motif'', at each lattice point. The ''basis'' may consist of atoms, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signal-processing circuits. Since the invention of the first constant-potential transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Pendulum
In physics and mathematics, in the area of dynamical systems, a double pendulum also known as a chaos pendulum is a pendulum with another pendulum attached to its end, forming a simple physical system that exhibits rich dynamic behavior with a strong sensitivity to initial conditions. The motion of a double pendulum is governed by a set of coupled ordinary differential equations and is chaotic. Analysis and interpretation Several variants of the double pendulum may be considered; the two limbs may be of equal or unequal lengths and masses, they may be simple pendulums or compound pendulums (also called complex pendulums) and the motion may be in three dimensions or restricted to the vertical plane. In the following analysis, the limbs are taken to be identical compound pendulums of length and mass , and the motion is restricted to two dimensions. In a compound pendulum, the mass is distributed along its length. If the mass is evenly distributed, then the center of mass o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |