|
Republic XF-103
The Republic XF-103 was an American project to develop a powerful missile-armed interceptor aircraft capable of destroying Soviet bombers while flying at speeds as high as Mach 3. Despite a prolonged development, it never progressed past the mockup stage. Development In 1949, the USAF issued a request for an advanced supersonic interceptor to equip the Air Defense Command. Known formally as Weapon System WS-201A, but better known informally as the 1954 interceptor, it called for a supersonic aircraft with all-weather capability, powerful airborne interception radar, and air-to-air missile armament. Republic was one of six companies to submit proposals. On 2 July 1951, three of the designs were selected for further development, Convair's scaled-up XF-92 that evolved into the F-102, a Lockheed design that led to the F-104, and Republic's AP-57. AP-57 was an advanced concept to be built almost entirely of titanium and capable of Mach 3 at altitudes of at least . A full-sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed F-104 Starfighter
The Lockheed F-104 Starfighter is an American single-engine, supersonic air superiority fighter which was extensively deployed as a fighter-bomber during the Cold War. Created as a day fighter by Lockheed as one of the "Century Series" of fighter aircraft for the United States Air Force (USAF), it was developed into an all-weather multirole aircraft in the early 1960s and produced by several other nations, seeing widespread service outside the United States. After a series of interviews with Korean War fighter pilots in 1951, Kelly Johnson, then lead designer at Lockheed, opted to reverse the trend of ever-larger and more complex fighters and produce a simple, lightweight aircraft with maximum altitude and climb performance. On 4 March 1954, the Lockheed XF-104 took to the skies for the first time, and on 26 February 1958 the production fighter was activated by the USAF. Only a few months later it was pressed into action during the Second Taiwan Strait Crisis, when it was de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Specific Fuel Consumption
Thrust-specific fuel consumption (TSFC) is the fuel efficiency of an engine design with respect to thrust output. TSFC may also be thought of as fuel consumption (grams/second) per unit of thrust (newtons, or N), hence ''thrust-specific''. This figure is inversely proportional to specific impulse, which is the amount of thrust produced per unit fuel consumed. TSFC or SFC for thrust engines (e.g. turbojets, turbofans, ramjets, rockets, etc.) is the mass of fuel needed to provide the net thrust for a given period e.g. lb/(h·lbf) (pounds of fuel per hour-pound of thrust) or g/(s·kN) (grams of fuel per second-kilonewton). Mass of fuel is used, rather than volume (gallons or litres) for the fuel measure, since it is independent of temperature. Specific fuel consumption of air-breathing jet engines at their maximum efficiency is more or less proportional to exhaust speed. The fuel consumption ''per mile'' or ''per kilometre'' is a more appropriate comparison for aircraft that travel a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed X-7
The Lockheed X-7 (dubbed the "Flying Stove Pipe") was an American unmanned test bed of the 1950s for ramjet engines and missile guidance technology. It was the basis for the later Lockheed AQM-60 Kingfisher, a system used to test American air defenses against nuclear missile attack. Early Development Development of the Kingfisher was first initiated in December 1946. The X-7 was called into production by the United States Air Force requirement for the development of an unmanned ramjet test plane with a top speed of at least . The X-7 project was developed under the AMC designator MX-883 and was given in the Lockheed in-house designation L-171. The L-171 was initially designated the PTV-A-1 by the USAF but was later designated the X-7 in 1951. Despite its first launch being a failure, after re-development of the original ramjet, following test flights were successful. A total of 130 X-7 flights were conducted from April 1951 to July 1960. Purpose The X-7 laid the foundation for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramjet
A ramjet, or athodyd (aero thermodynamic duct), is a form of airbreathing jet engine that uses the forward motion of the engine to produce thrust. Since it produces no thrust when stationary (no ram air) ramjet-powered vehicles require an assisted take-off like a rocket assist to accelerate it to a speed where it begins to produce thrust. Ramjets work most efficiently at supersonic speeds around and can operate up to speeds of . Ramjets can be particularly useful in applications requiring a small and simple mechanism for high-speed use, such as missiles. The US, Canada, and UK had widespread ramjet powered missile defenses during the 1960s onward, such as the CIM-10 Bomarc and Bloodhound. Weapon designers are looking to use ramjet technology in artillery shells to give added range; a 120 mm mortar shell, if assisted by a ramjet, is thought to be able to attain a range of . They have also been used successfully, though not efficiently, as tip jets on the ends of helicopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intake
An intake (also inlet) is an opening, structure or system through which a fluid is admitted to a space or machine as a consequence of a pressure differential between the outside and the inside. The pressure difference may be generated on the inside by a mechanism, or on the outside by ram pressure or hydrostatic pressure. Flow rate through the intake depends on pressure difference, fluid properties, and intake geometry. Intake refers to an opening, or area, together with its defining edge profile which has an associated entry loss, that captures pipe flow from a reservoir or storage tank. Intake refers to the capture area definition and attached ducting to an aircraft gas turbine engine or ramjet engine and, as such, an intake is followed by a compressor or combustion chamber. It may instead be referred to as a diffuser. For an automobile engine the components through which the air flows to the engine cylinders, are collectively known as an intake system and may include the inlet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
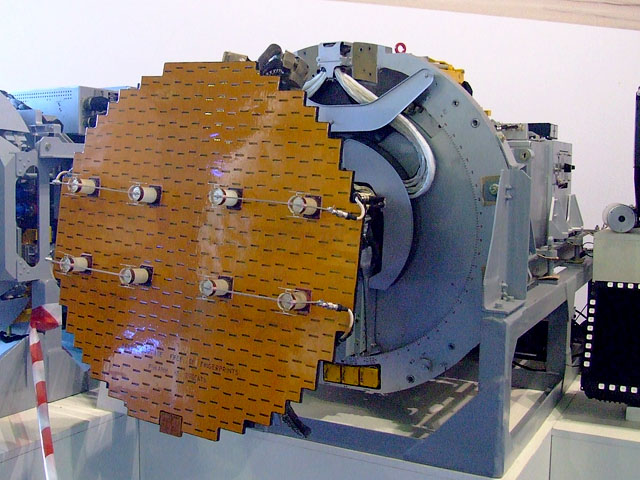
Republic XF-103 Mock-up
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th centuries, the term was used to imply a state with a democratic or representative constitution (constitutional republic), but more recently it has also been used of autocratic or dictatorial states not ruled by a monarch. It is now chiefly used to denote any non-monarchical state headed by an elected or appointed president. , 159 of the world's 206 sovereign states use the word "republic" as part of their official names. Not all of these are republics in the sense of having elected governments, nor is the word "republic" used in the names of all states with elected governments. The word ''republic'' comes from the Latin term ''res publica'', which literally means "public thing", "public matter", or "public affair" and was used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair B-58 Hustler
The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight. The B-58 was developed during the 1950s for the United States Air Force (USAF) Strategic Air Command (SAC). To achieve the high speeds desired, Convair chose a delta wing design used by contemporary fighters such as the Convair F-102. The bomber was powered by four General Electric J79 engines in underwing pods. It had no bomb bay: it carried a single nuclear weapon plus fuel in a combination bomb/fuel pod underneath the fuselage. Later, four external hardpoints were added, enabling it to carry up to five weapons. The B-58 entered service in March 1960, and flew for a decade with two SAC bomb wings: the 43rd Bombardment Wing and the 305th Bombardment Wing. It was considered difficult to fly, imposing a high workload upon its three-man crews. Designed to replace the subsonic Boeing B-47 Stratojet strategic bomber, the B-58 be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIM-47 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after its cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix. Development Development for XF-108 In the early 1950s, the United States Air Force developed requirements for a high speed, high performance interceptor aircraft, originally called the LRI-X. In 1957, Hughes won the contract to supply the weapons system for this aircraft. This system consisted of the GAR-X missile and the YX-1 radar and fire control system. The original missile design had a range of 15 to 25 miles (25 to 40 km), and could be equipped with a conventional warhead or a 0.25 kiloton version of the W42 nuclear warhead. When the North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes AN/ASG-18
The Hughes AN/ASG-18 Fire Control System was a prototype airborne fire control radar system for the planned North American XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft, and the Lockheed YF-12 for the United States Air Force. It was the US's first Pulse-Doppler radar, giving it look-down/shoot-down capability, and was also the first track while scan radar (could track one target at a time). This was paired with an infrared search and track (IRST) system. Range of the radar was estimated at between 200 and 300 miles (322 to 482 km), with reliable detection of bomber-sized targets at 100 miles. The installation itself was massive, weighing 2,100 lb (953 kg), and taking up most of the nose of the aircraft. The system was to be used with the Hughes AIM-47 Falcon missile, which also had a range of about 100 miles. While development work was done with the XF-108, the AN/ASG-18 and Falcon missiles were first tested on a highly modified Convair B-58 Hustler bomber. To fit the radar, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American XF-108 Rapier
The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would have cruised at speeds around with an unrefueled combat radius over , and was equipped with radar and missiles offering engagement ranges up to against bomber-sized targets. To limit development costs, the program shared engine development with the North American XB-70 Valkyrie strategic bomber program, and used a number of elements of earlier interceptor projects. The program had progressed only as far as the construction of a single wooden mockup when it was cancelled in 1959, due to a shortage of funds and the Soviets' adoption of ballistic missiles as their primary means of nuclear attack. Had it flown, the F-108 would have been the heaviest fighter of its era. Prior to the project's cancellation, U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower noted that rais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)