|
Reptiles Of New Zealand
For the reptiles of New Zealand, see: * Dinosaurs and other Mesozoic reptiles of New Zealand *Geckos of New Zealand *''Oligosoma'', a genus of skinks *Tuatara, incorrectly referred to as a "living dinosaur". The New Zealand mosasaur has been named ''Moanasaurus'', and was one of the largest mosasaurs in the world. The New Zealand plesiosaur has been named ''Mauisaurus''. See also *Fauna of New Zealand The animals of New Zealand, part of its biota, have an unusual history because, before the arrival of humans, less than 900 years ago, the country was mostly free of mammals, except those that could swim there (seals, sea lions, and, off-shore, ... External links Conservation Status of New Zealand Reptiles, 2021New Zealand reptiles and frogs Department of Conservation {{New Zealand Reptiles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauisaurus BW
''Mauisaurus'' ("Māui lizard") is a dubious genus of plesiosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now New Zealand. Numerous specimens have been attributed to this genus in the past, but a 2017 paper restricts ''Mauisaurus'' to the lectotype and declares it a ''nomen dubium''. Description Little can be said about the appearance of ''Mauisaurus'' as the only known material is an undiagnostic, fragmentary pelvic area and flippers. The lectotype material shows some features that may indicate aristonectine affinities, but simultaneously possesses anatomical features more consistent with non-aristonectine elasmosaurs. Etymology ''Mauisaurus'' gets its name from the New Zealand Māori mythological demigod, Māui. Māui is said to have pulled New Zealand up from the seabed using a fish hook, thus creating the country. Thus, ''Mauisaurus'' means "''Māui lizard''". ''Mauisaurus'' gets its scientific last name from its original finder, Julius von Haast, who found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dinosaurs And Other Mesozoic Reptiles Of New Zealand
__NOTOC__ Although the evidence is rare, fossils reveal that there were dinosaurs in New Zealand. Possibly because it lacks the right conditions for fossilisation, only fragments of bone and a few vertebrae have been found there. Because these fossils are only a single bone or a piece of a bone, the dinosaurs' species cannot be identified, but by comparing the fossils with others it can be seen which family or order a given fossil belonged to. Marine fossils are more common than fossils of land animals in New Zealand because dead animals and plants are easily preserved in sand and mud. Therefore, some fossils of large marine reptiles are nearly complete, and so can be identified to species. Species list So far, there have been fossils found in New Zealand that have been identified as coming from: Non-avian dinosaurs Dinosaurs that lived in the Ross Dependency, a part of Antarctica within the Realm of New Zealand, include the tetanuran ''Cryolophosaurus''. The Ross Dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geckos Of New Zealand
Dozens of species of geckos are found in New Zealand. The number of species is unknown – as of 2021 there are 48 species in 7 genera, but more species are being studied. All of them are native to New Zealand and are endemic (found in no other country). They are all in the Diplodactylidae family of geckoes, which is found in Australia, New Caledonia and New Zealand. New Zealand's geckos are highly unusual in that they are viviparous, giving birth to live young, typically twins, rather than laying eggs. Two species of rough-snouted giant geckos from New Caledonia are the only other viviparous geckos in the world. New Zealand geckos are omnivorous – their diet is primarily insectivorous in nature – flies, spiders, moths etc., but they will supplement it with fruit (i.e. from mahoe) and nectar (i.e. from flax flowers) when it is available. Geckos are often a target for wildlife smugglers. Species As at 2021 the taxonomically described species are as follows: *'' Dactylocnemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligosoma
''Oligosoma'' is a genus of small to medium-sized skinks (family Scincidae) found only in New Zealand, Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. ''Oligosoma'' had previously been found to belong to the ''Eugongylus'' group of genera in the subfamily Lygosominae; the Australian genus ''Bassiana'' appears to be fairly closely related. Species The currently described species are: *'' Oligosoma acrinasum'' – Fiordland skink *'' Oligosoma aeneum'' – copper skink *'' Oligosoma alani'' – Alan's skink, robust skink *''Oligosoma albornense'' – Alborn skink *'' Oligosoma auroraense'' – Hawke's Bay skink, eastern speckled skink *'' Oligosoma awakopaka'' – Awakopaka skink *'' Oligosoma burganae'' – Burgan skink *'' Oligosoma chloronoton'' – green skink *'' Oligosoma elium'' – Marlborough spotted skink *'' Oligosoma fallai'' – Falla's skink, Three Kings skink *'' Oligosoma grande'' – grand skink *'' Oligosoma hardyi'' – Hardy's skink *'' Oligosoma homalonotum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skink
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions. Description Skinks look like lizards of the family Lacertidae (sometimes called ''true lizards''), but most species of skinks have no pronounced neck and relatively small legs. Several genera (e.g., ''Typhlosaurus'') have no limbs at all. This is not true for all skinks, however, as some species such as the red-eyed crocodile skink have a head that is very distinguished from the body. These lizards also have legs that are relatively small proportional to their body size. Skinks' skulls are covered by substantial bony scales, usually matching up in shape and size, while overlapping. Other gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
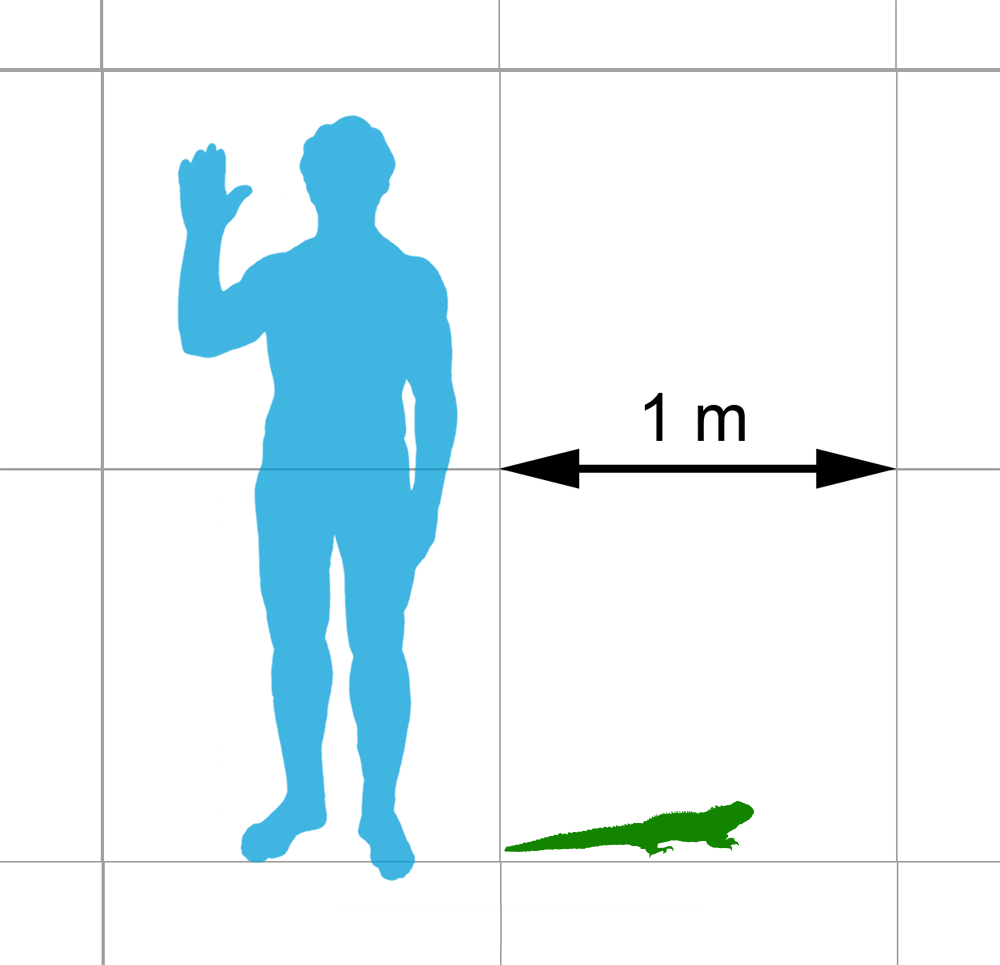
Tuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moanasaurus
''Moanasaurus'' (From Māori ''moana'' "sea" and Greek ''sauros'' "lizard"; meaning "Sea Lizard") was a genus of mosasaur from the Late Cretaceous period. Its fossil remains have been discovered in the North Island of New Zealand. ''Moanasaurus'' was a very large mosasaurine known originally from a disarticulated skull, vertebrae, ribs and flipper bones. The skull measures in length, which shows that ''Moanasaurus'' was one of the largest in the subfamily of Mosasaurinae. Researchers argue that some Antarctic '' Mosasaurus'' remains (including a "large, fragmentaery skull") may be attributed to this genus. Gregory S. Paul Gregory Scott Paul (born December 24, 1954) is an American freelance researcher, author and illustrator who works in paleontology, and more recently has examined sociology and theology. He is best known for his work and research on theropod dino ... estimated its maximum adult size at in length and in body mass. See also * List of dinosaurs and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauisaurus
''Mauisaurus'' ("Māui lizard") is a dubious genus of plesiosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now New Zealand. Numerous specimens have been attributed to this genus in the past, but a 2017 paper restricts ''Mauisaurus'' to the lectotype and declares it a ''nomen dubium''. Description Little can be said about the appearance of ''Mauisaurus'' as the only known material is an undiagnostic, fragmentary pelvic area and flippers. The lectotype material shows some features that may indicate aristonectine affinities, but simultaneously possesses anatomical features more consistent with non-aristonectine elasmosaurs. Etymology ''Mauisaurus'' gets its name from the New Zealand Māori mythological demigod, Māui. Māui is said to have pulled New Zealand up from the seabed using a fish hook, thus creating the country. Thus, ''Mauisaurus'' means "''Māui lizard''". ''Mauisaurus'' gets its scientific last name from its original finder, Julius von Haast, who fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of New Zealand
The animals of New Zealand, part of its biota, have an unusual history because, before the arrival of humans, less than 900 years ago, the country was mostly free of mammals, except those that could swim there (seals, sea lions, and, off-shore, whales and dolphins) or fly there (bats), though as recently as the Miocene, it was home to the terrestrial Saint Bathans mammal, implying that mammals had been present since the island had broken away from other landmasses. The absence of mammals meant that all of the ecological niches occupied by mammals elsewhere were occupied instead by either insects or birds, leading to an unusually large number of flightless birds, including the kiwi, the weka, the moa (now extinct), the takahē, and the kakapo. Because of the lack of predators, even bats spend most of their time on the ground. There are also about 60 species of lizard (30 each of gecko and skink), four species of frog (all rare and endangered), and the tuatara (reptiles resemblin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |