|
René François Rohrbacher
Réné François Rohrbacher (27 September 1789, Langatte – 17 January 1856, Paris) was an ecclesiastical historian. He studied for several months at Sarrebourg and Phalsbourg (Pfalzburg) and at the age of seventeen had completed his Classical studies. He taught for three years at the college of Phalsbourg; entered in 1810 the ecclesiastical seminary at Nancy; and was ordained priest in 1812. Appointed assistant priest at Insming, he was transferred after six months to Lunéville. A mission which he preached in 1821 at Flavigny led to the organization of a diocesan mission band. Several years later he became a member of the Congregation of St. Peter founded by Félicité and Jean-Marie de Lamennais, and from 1827 to 1835 directed the philosophical and theological studies of young ecclesiastics who wished to become the assistants of the two brothers in their religious undertakings. When Felicite de La Mennais refused to submit to the condemnation pronounced against him by Rome, Rohr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langatte
Langatte (; ; Lorraine Franconian ''Lan(g)d'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. In 1805 it was the site of the Battle of Landbach between the French and the anti French coalition. Langatte is located in Southeastern Moselle near Sarrebourg. It is one of the communes who share the Étang du Stock (a pond) with Kerprich-aux-Bois, Diane-Capelle, Rhodes and Fribourg. A leisure centre and a campsite have been installed near of the pond. The new LGV Est part connecting Baudrecourt (where the High Speed Line ended before 2016) and Vendenheim has been built in Southern Moselle including Langatte and since 2016, TGV trains pass by here every day to connect Strasbourg, Paris and other destinations around France and Germany. Notable people * René François Rohrbacher See also * Communes of the Moselle department The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, Fashion capital, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called Caput Mundi#Paris, the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarrebourg
Sarrebourg (; also , ; Lorraine Franconian: ; older la, Pons Saravi) is a commune of northeastern France. In 1895 a Mithraeum was discovered at Sarrebourg at the mouth of the pass leading from the Vosges Mountains. Geography Sarrebourg is located in the department of Moselle, Lorraine, administrative region of Grand Est. It lies in on the upper course of the river Saar. The Vosges mountains are located about 10 kilometers south of the locality. To the northwest, the Oberwald forest massif - where the state forest of the municipality is located. It is 54 km away from Strasbourg, 64 km from Nancy, 77 km from Metz and 345 km from Paris ( orthodromic distance). The lines of communication and transport Sarrebourg station has rail connections to Paris, Strasbourg, Metz and Nancy. The commune is on the route of the Route nationale 4. Sarrebourg is the departure point of several departmental roads: D 27 to Morhange, D 43 to Sarre-Union, D 44 to Le D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
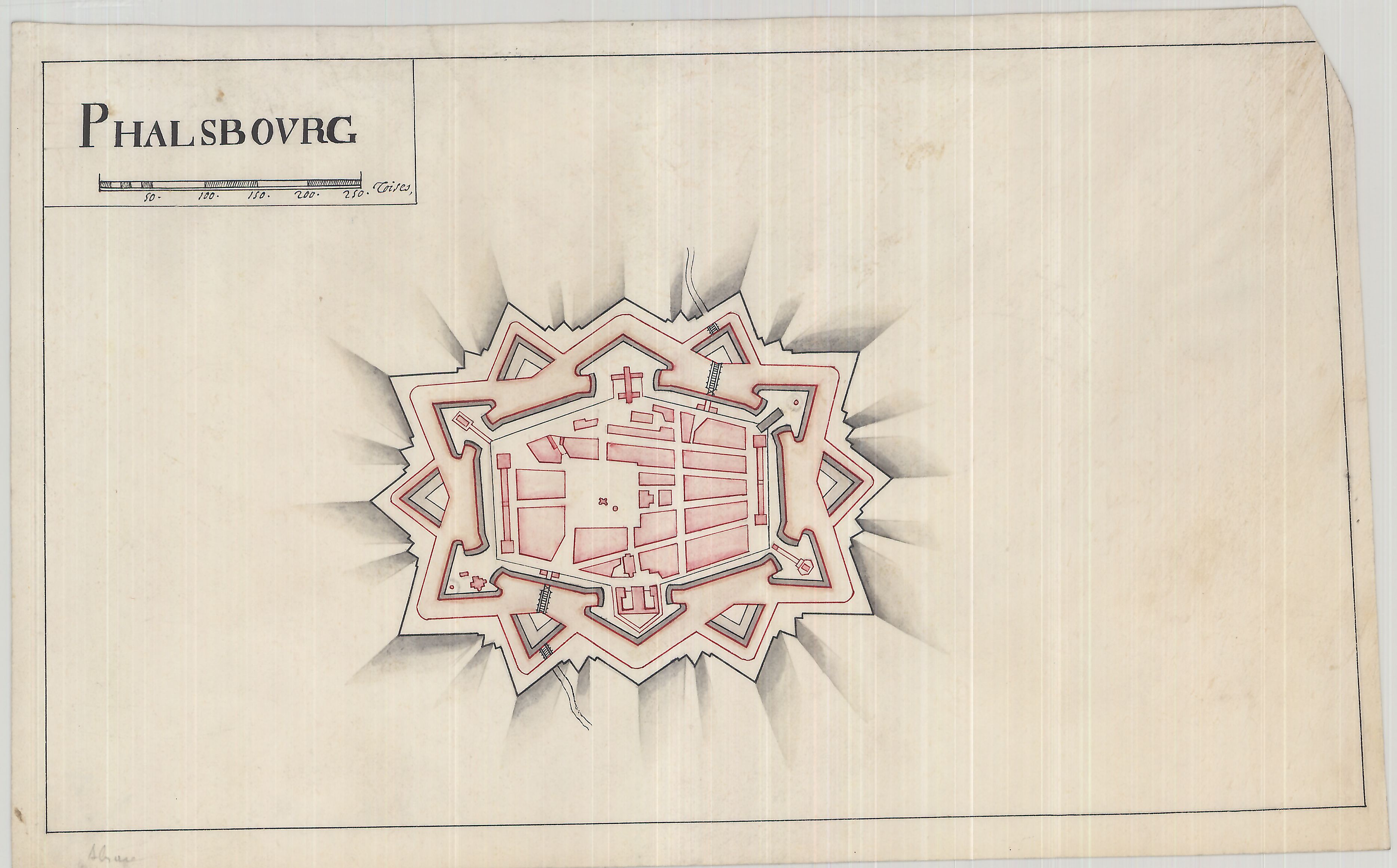
Phalsbourg
Phalsbourg (; ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Phalsburch'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France, with a population of about 5,000. It lies high on the west slopes of the Vosges, northwest of Strasbourg by rail. In 1911, it contained an Evangelical and a Roman Catholic church, a synagogue and a teachers' seminary. Its industries then included the manufacture of gloves, straw hats and liqueurs, and quarrying. History The area of the city of Phalsbourg, originally Pfalzburg, was originally part of the principality of Lützelstein, under the overlordship of Luxembourg, then the bishops of Metz and of Strasbourg, before becoming possessed by the Dukes of Palantine Veldenz, all within the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. In 1570, Duke Georg Johann I of Palantine Veldenz founded the town of Pfalzburg as a refuge for Reformed Protestants expelled from of the Duchy of Lorraine, and as an administrative center of his holdings. But the cost f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy, France
Nancy ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Nanzisch'' is the prefecture of the northeastern French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle. It was the capital of the Duchy of Lorraine, which was annexed by France under King Louis XV in 1766 and replaced by a province, with Nancy maintained as capital. Following its rise to prominence in the Age of Enlightenment, it was nicknamed the "capital of Eastern France" in the late 19th century. The metropolitan area of Nancy had a population of 511,257 inhabitants at the 2018 census, making it the 16th-largest functional urban area in France and Lorraine's largest. The population of the city of Nancy proper is 104,885. The motto of the city is , —a reference to the thistle, which is a symbol of Lorraine. Place Stanislas, a large square built between 1752 and 1756 by architect Emmanuel Héré under the direction of Stanislaus I of Poland to link the medieval old town of Nancy and the new city built under Charles III, Duke of Lorraine in the 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insming
Insming (; ) is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. Geography It is situated about 60 km southeast of Metz, about 80 km northeast of Nancy, and about 100 km northwest of Strasbourg. Its altitude is 215 meters minimum and 273 meters maximum. It is part of the canton d'Albestroff, which is part of the "arrondissement" of Château-Salins. History Since the eighth century, Insming has been known under different names: ''Asmengia'' (1106), ''Asmingiam'' (1152), ''Amanges'' (1296), ''Esminga'' and ''Einsminga'' (1299), ''Einsmingen'' (1456), ''Amangen'' and ''Enssmingen'' (1594). It is the oldest village of the canton of Albestroff. In the 12th century, it was the headquarters of a priesthood dependent on Saint-Mihiel Abbey, which was founded at the end of the 11th century. Insming was a small dependence of Counts de Ferrettes and de Montbeliard. After World War II, Insming saw an economic boom, mainly thanks to Fernand Lam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunéville
Lunéville ( ; German, obsolete: ''Lünstadt'' ) is a commune in the northeastern French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle. It is a subprefecture of the department and lies on the river Meurthe at its confluence with the Vezouze. History Lunéville was a renowned resort in the 18th century, known as the capital of Lorraine. The grand Château de Lunéville, built in 1702 for Leopold, Duke of Lorraine to replace an older palace, was the residence of the duke of Lorraine until the duchy was annexed by France in 1766. The château was designed in the style of Versailles to satisfy Leopold's wife, Élisabeth Charlotte d'Orléans, the niece of Louis XIV, and became known as the "Versailles of Lorraine". It includes a chapel designed by Germain Boffrand. Leopold and his wife were the parents of Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor (through him they were the grandparents of Marie Antoinette). The last duke of Lorraine was Stanislaus I, the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Felicité Robert De Lamennais
Hughes may refer to: People * Hughes (surname) * Hughes (given name) Places Antarctica * Hughes Range (Antarctica), Ross Dependency * Mount Hughes, Oates Land * Hughes Basin, Oates Land * Hughes Bay, Graham Land * Hughes Bluff, Victoria Land * Hughes Glacier, Victoria Land * Hughes Island, Victoria Land * Hughes Peninsula, Ellsworth Land * Hughes Point, Ellsworth Land Australia * Division of Hughes, an electoral district * Hughes, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra * Hughes, Northern Territory, a rural locality United States * Hughes, Alaska, a city * Hughes, Arkansas, a city * Hughes, Iowa, a ghost town * Hughes, Wisconsin, a town * Hughes County, Oklahoma * Hughes County, South Dakota * Hughes Lake (California) * Hughes Mountain, Missouri * Hughes River (Virginia) * Hughes River (West Virginia) Other * Hughes, Santa Fe, Argentina, a town * Hughes Range (British Columbia), Canada * Hughes Reef, South China Sea * 1878 Hughes, an asteroid Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Marie De Lamennais
Jean-Marie Robert de La Mennais, FICP (or de Lamennais; 1780–1860) was a Breton Catholic priest and brother of the philosopher Felicité Robert de Lamennais, whom he influenced in their youth. He was a leading figure in the revival of the Catholic Church in France after the French Revolution, involved in founding three religious institutes as part of this effort. Pope Paul VI proclaimed him to be Venerable in 1966 and his cause of canonization is ongoing. Life Early life Jean-Marie wwwwas born at Saint-Malo, then in the ancient Province of Brittany, on 8 September 1780, in . He is one of the sons of Robert de Lamennais, a wealthy merchant who had recently received a coat of arms from the king, and Marie des Saudrais. He was five years old when his mother died, and as a result, he and his younger brother were sent for education to an uncle, Robert des Saudrais, at La Chênaie, an estate near Saint-Malo. During the period of the Revolution, the family sheltered non-juring p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallicanism
Gallicanism is the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by the monarch's or the state's authority—over the Catholic Church is comparable to that of the Pope. Gallicanism is a rejection of ultramontanism; it has something in common with Anglicanism, but is nuanced, in that it plays down the authority of the Pope in church without denying that there are some authoritative elements to the office associated with being ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals). Other terms for the same or similar doctrines include Erastianism, Febronianism, and Josephinism. University of Notre Dame professor John McGreevy defines it as "the notion that national customs might trump Roman (Catholic Church) regulations."''Catholicism and American Freedom,'' John McGreevy Norton and Co., New York 2003, p. 26. The doctrine originated in France (the term derives from ''Gallia'', Gaul). In the 18th century it spread to the Low Countries, especially the Netherlands. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1789 Births
Events January–March * January – Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès publishes the pamphlet '' What Is the Third Estate?'' ('), influential on the French Revolution. * January 7 – The 1788-89 United States presidential election and House of Representatives elections are held. * January 9 – Treaty of Fort Harmar: The terms of the Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1784) and the Treaty of Fort McIntosh, between the United States Government and certain native American tribes, are reaffirmed, with some minor changes. * January 21 – The first American novel, ''The Power of Sympathy or the Triumph of Nature Founded in Truth'', is printed in Boston, Massachusetts. The anonymous author is William Hill Brown. * January 23 – Georgetown University is founded in Georgetown, Maryland (today part of Washington, D.C.), as the first Roman Catholic college in the United States. * January 29 – In Vietnam, Emperor Quang Trung crushes the Chinese Qing forces in Ng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1856 Deaths
Events January–March * January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California. * January 23 – American paddle steamer SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatlantic voyage on which she will be lost with all 186 on board. * January 24 – U.S. President Franklin Pierce declares the new Free-State Topeka government in " Bleeding Kansas" to be in rebellion. * January 26 – First Battle of Seattle: Marines from the suppress an indigenous uprising, in response to Governor Stevens' declaration of a "war of extermination" on Native communities. * January 29 ** The 223-mile North Carolina Railroad is completed from Goldsboro through Raleigh and Salisbury to Charlotte. ** Queen Victoria institutes the Victoria Cross as a British military decoration. * February ** The Tintic War breaks out in Utah. ** The National Dress Reform Association is founded in the United States to promote "rational" dress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |