|
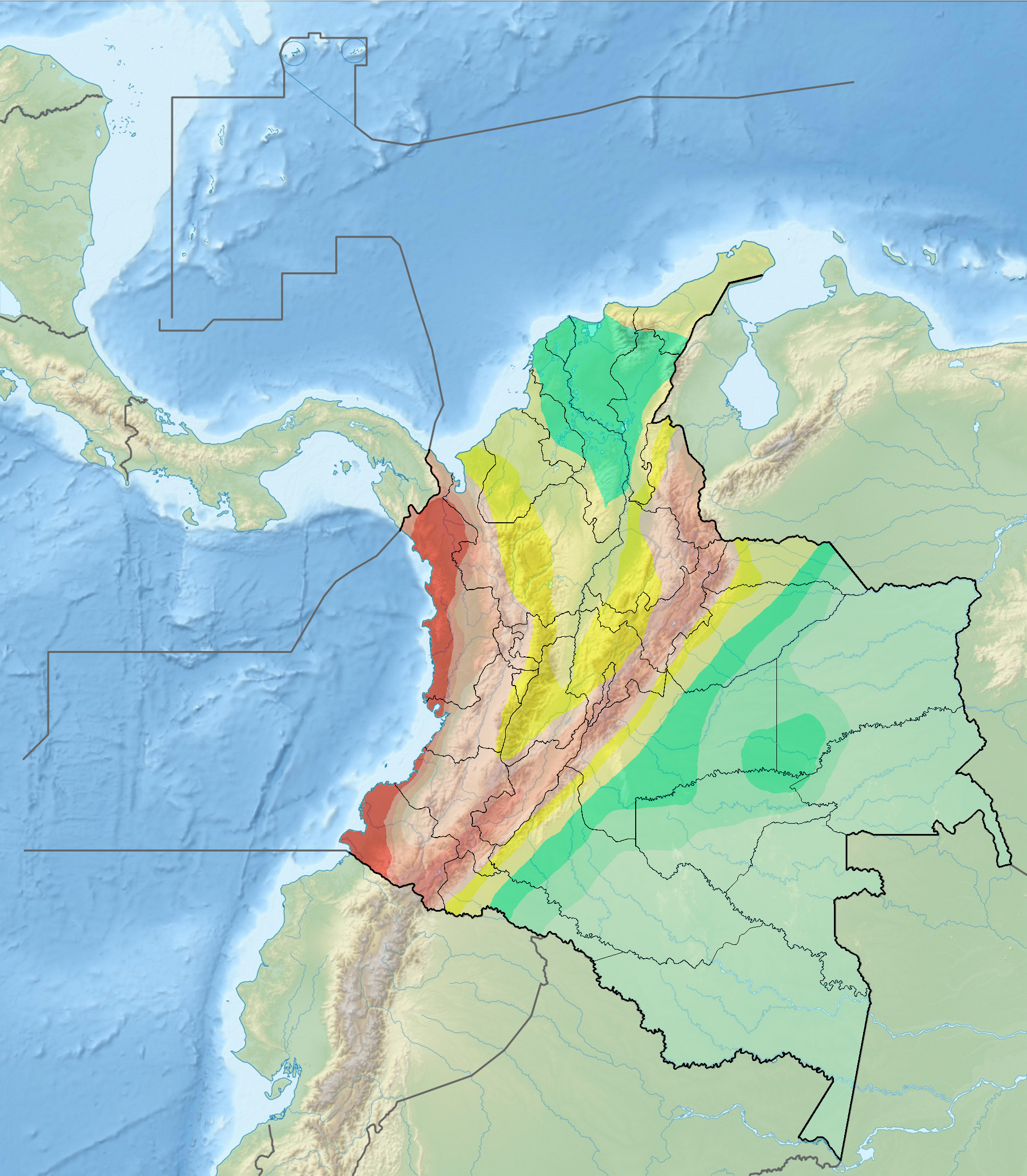
Remolino-El Charco Fault
The Remolino-El Charco Fault ( es, Falla de Remolino-El Charco) is a dextral strike-slip fault in the department of Nariño in Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 046.4 ± 6 in the Tumaco Basin along the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Etymology The fault is named after Remolino Grande and El Charco, Nariño.Paris et al., 2000a, p.55 Description The Remolino-El Charco Fault extends through the Pacific coastal lowlands and plains of Colombia to the east of the city of Tumaco. The fault begins in the southwesternmost point of Colombia and runs towards Guapi.Paris et al., 2000b It is close to and parallels the coast. It displaces alluvial fan sediments of the Patía, Mira, and Telembí Rivers and some Pleistocene marine terraces. The fault appears to be a southern continuation of the Naya-Micay Fault. The fault has a very well defined fault line on aerial photographs and satellite images. Pattern of deflection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Charco
El Charco is a town and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia. Climate El Charco has a tropical rainforest climate A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southea ... (Af) with heavy to very heavy rainfall year-round. References Municipalities of Nariño Department Road-inaccessible communities of Colombia {{Nariño-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where flow emerges from a confined channel and is free to spread out and infiltrate the surface. This reduces the carrying capacity of the flow and results in deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows or one or more ephemeral or perennial streams. Alluvial fans are common in the geologic record, such as in the Triassic basins of eastern North America and the New Red Sandstone of south Devon. Such fan deposits likely contain the largest accumulations of gravel in the geologic record. Alluvial fans have also been found on Mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Faults
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Faults Of Colombia
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpelo Plate
The Malpelo Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts west of Ecuador and Colombia. It is the 57th plate to be identified. It is named after Malpelo Island, the only emerged part of the plate. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos Plate, on the south by the Nazca Plate, on the east by the North Andes Plate, and on the north by the Coiba Plate, separated by the Coiba Transform Fault (CTF). This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca Plate. The Malpelo Plate borders three major faults of Pacific Colombia, the north to south striking Bahía Solano Fault in the north and the Naya-Micay and Remolino-El Charco Faults in the south. Description The Malpelo Plate was identified by a non-closure of the Nazca-Cocos-Pacific plate motion circuit, reported by Tuo Zhang and lead-researcher Richard G. Gordon et al. of Rice University in a paper published in August 2017.Zhang et al., 2017 The existence of the plate has been hypothesised be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romeral Fault System
The Romeral Fault System ( es, Sistema de Fallas (de) Romeral) is a megaregional system of major parallel and anastomosing faults in the Cordillera Central (Colombia), Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Cauca Basin, Cauca, Amagá Basin, Amagá, and Sinú-San Jacinto Basins. The system spans across ten departments of Colombia, departments of Colombia, from northeast to south Bolívar Department, Bolívar, Sucre Department, Sucre, Córdoba Department, Córdoba, Antioquia Department, Antioquia, Caldas Department, Caldas, Risaralda Department, Risaralda, Quindío Department, Quindío, Valle del Cauca Department, Valle del Cauca, Cauca Department, Cauca and Nariño Department, Nariño. The fault zone extends into Ecuador where it is known as the Peltetec Fault System. The in detail described part of the Romeral Fault System south of Córdoba has a total length of with a cumulative length of and runs along an average north to south strike (geology), strike of 017.6 ± 16, cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Colombia
This is a list of earthquakes in Colombia. Colombia is a seismically active country and has a large seismic risk in many areas of its territory due to its location at the boundaries of the Malpelo, Panama, Caribbean, North Andes (where most earthquakes occurred) and South American Plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The southeastern and extreme eastern portions of Colombia are not as seismically active as the rest of the country. The first historically registered earthquake felt in Colombia occurred on September 11, 1530, around 10:00 AM, probably with the epicentre near Cumaná, Venezuela. The earthquake was documented by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés in his work ''La Historia general de las Indias'' and by friar Bartolomé de las Casas in his book ''Historia de Las Indias''.Ramírez, 1975, p.63 The first documented earthquake with its epicentre in present-day Colombia territory took place in 1566,Ramírez, 1975, p.65 with the epicentre estimated around Santander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naya-Micay Fault
The Naya-Micay Fault ( es, Falla de Naya-Micay) is a dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Cauca and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 034.1 ± 12 in the Tumaco Basin along the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Etymology The fault is named after the Naya and Micay Rivers.Paris et al., 2000a, p.54 Description The Naya-Micay Fault runs parallel to and inland of the southwestern Pacific Coast of Colombia in the Cauca and Valle del Cauca departments from Guapi in the south to Buenaventura in the north.Paris et al., 2000b The fault displaces marine and non-marine Pliocene sedimentary rocks. It locally offsets undifferentiated Quaternary alluvial deposits. In general, there are uplifted Tertiary sediments on the east and Quaternary sediments on the western side of the fault. The fault appears to be a northern continuation of the Remolino-El Charco Fault. The fault controls drainage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telembí River
The Telembí River is a river of Colombia. It drains into the Pacific Ocean via the Patía River. See also *List of rivers of Colombia Atlantic Ocean Amazon River Basin * Amazon River ** Guainía River or Negro River *** Vaupés River or Uaupés River **** Papuri River **** Querary River *** Isana River or Içana River **** Cuiari River *** Aquio River ** Caquetá River o ... References *Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993. Rivers of Colombia {{Colombia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mira River (Ecuador And Colombia)
The Mira River originates in the Andes of Ecuador and flows to the Pacific Ocean in Colombia. For a few kilometers it forms the border between the two countries. The upper course of the Mira is called the Chota River and is notable for its Afro-Ecuadorian inhabitants, its bomba music, and the large number of internationally prominent soccer players it has produced. Course High Andes. The most distant source of the Mira River may be Puruanta Lake, located at an elevation of in the Cayambe Coca Ecological Reserve of northern Ecuador. The cities of Ibarra and Otavalo are in the upper drainage basin of the river which includes most of Imbabura and Carchi provinces. The borders of the two provinces run roughly along the course of the Mira. Chota River and Chota Valley. Several tributaries unite to form the Chota River north of the town of Pimampiro at an elevation of . The Chota valley, deep, but wide and fertile in places, extends along the river for about to the village of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |