|
Naya-Micay Fault
The Naya-Micay Fault ( es, Falla de Naya-Micay) is a dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Cauca and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 034.1 ± 12 in the Tumaco Basin along the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Etymology The fault is named after the Naya and Micay Rivers.Paris et al., 2000a, p.54 Description The Naya-Micay Fault runs parallel to and inland of the southwestern Pacific Coast of Colombia in the Cauca and Valle del Cauca departments from Guapi in the south to Buenaventura in the north.Paris et al., 2000b The fault displaces marine and non-marine Pliocene sedimentary rocks. It locally offsets undifferentiated Quaternary alluvial deposits. In general, there are uplifted Tertiary sediments on the east and Quaternary sediments on the western side of the fault. The fault appears to be a northern continuation of the Remolino-El Charco Fault. The fault controls drainage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naya River
The Naya River ( es, Río Naya) is a river in Colombia that flows into the Pacific Ocean. The Naya forms the southern boundary of the Farallones de Cali National Park. The river is long, and is one of the main rivers of the Pacific slope and the Cauca The river rises in the Cerro Naya range, and runs through the municipality of Buenos Aires, Cauca. Lower down it serves as a boundary between the departments of Valle del Cauca and Cauca. The municipality of Buenaventura, Valle del Cauca is on its left bank, and the municipality of López de Micay López de Micay () is a town and municipality in the Cauca Department, Colombia. The Colombian meteorological service IDEAM reports an average annual precipitation of , potentially making it the wettest inhabited place in the world; however, som ..., Cauca on its right bank. Tributaries include the Agua Clara river and the Canayero River. The river divides into two branches near the ocean, and forms Ají Island between its two mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenaventura, Colombia
Buenaventura is a coastal seaport city in the department of Valle del Cauca, Colombia (South America). Buenaventura (Spanish for "good fortune") is the main port of Colombia in the Pacific Ocean. Buenaventura is a city with a population of 333,194 as of the 2005 census. Most city development lies on Cascajal Island. Most of the city's land is rural with scattered small villages. It is served by the Gerardo Tobar López Airport. The city is part of the UNESCO Creative Cities Network after it was named "City of Gastronomy" in 2017. History The city was founded on July 14, 1540, by Juan de Ladrilleros through orders from Pascual de Andagoya. At that time it was inhabited by the Buscajas. The city was destroyed by Native Americans before 1600; it was later rebuilt. Buenaventura thrived after the opening of the Panama Canal in 1914; and in the 1950s became a regular stopover for the 'international jet set'. Today, the city is crucial for sending raw materials to nearby areas; this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Faults
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Faults
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
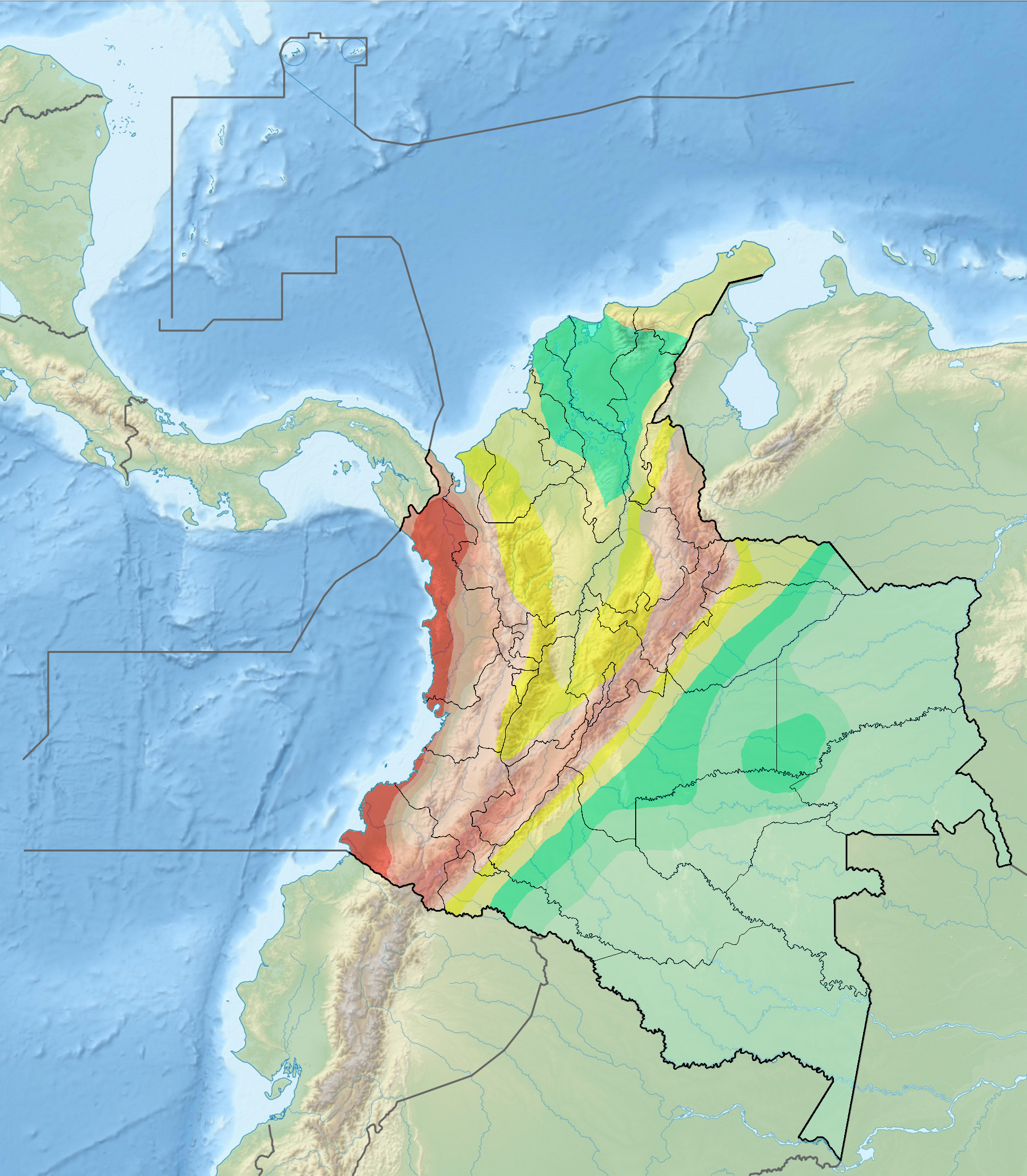
Seismic Faults Of Colombia
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpelo Plate
The Malpelo Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts west of Ecuador and Colombia. It is the 57th plate to be identified. It is named after Malpelo Island, the only emerged part of the plate. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos Plate, on the south by the Nazca Plate, on the east by the North Andes Plate, and on the north by the Coiba Plate, separated by the Coiba Transform Fault (CTF). This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca Plate. The Malpelo Plate borders three major faults of Pacific Colombia, the north to south striking Bahía Solano Fault in the north and the Naya-Micay and Remolino-El Charco Faults in the south. Description The Malpelo Plate was identified by a non-closure of the Nazca-Cocos-Pacific plate motion circuit, reported by Tuo Zhang and lead-researcher Richard G. Gordon et al. of Rice University in a paper published in August 2017.Zhang et al., 2017 The existence of the plate has been hypothesised be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romeral Fault System
The Romeral Fault System ( es, Sistema de Fallas (de) Romeral) is a megaregional system of major parallel and anastomosing faults in the Cordillera Central (Colombia), Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Cauca Basin, Cauca, Amagá Basin, Amagá, and Sinú-San Jacinto Basins. The system spans across ten departments of Colombia, departments of Colombia, from northeast to south Bolívar Department, Bolívar, Sucre Department, Sucre, Córdoba Department, Córdoba, Antioquia Department, Antioquia, Caldas Department, Caldas, Risaralda Department, Risaralda, Quindío Department, Quindío, Valle del Cauca Department, Valle del Cauca, Cauca Department, Cauca and Nariño Department, Nariño. The fault zone extends into Ecuador where it is known as the Peltetec Fault System. The in detail described part of the Romeral Fault System south of Córdoba has a total length of with a cumulative length of and runs along an average north to south strike (geology), strike of 017.6 ± 16, cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Colombia
This is a list of earthquakes in Colombia. Colombia is a seismically active country and has a large seismic risk in many areas of its territory due to its location at the boundaries of the Malpelo, Panama, Caribbean, North Andes (where most earthquakes occurred) and South American Plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The southeastern and extreme eastern portions of Colombia are not as seismically active as the rest of the country. The first historically registered earthquake felt in Colombia occurred on September 11, 1530, around 10:00 AM, probably with the epicentre near Cumaná, Venezuela. The earthquake was documented by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés in his work ''La Historia general de las Indias'' and by friar Bartolomé de las Casas in his book ''Historia de Las Indias''.Ramírez, 1975, p.63 The first documented earthquake with its epicentre in present-day Colombia territory took place in 1566,Ramírez, 1975, p.65 with the epicentre estimated around Santander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guapi River
The Guapi River ( es, Río Guapi) is a river of Colombia that flows into the Pacific Ocean near the town of Guapi, Cauca. The mouth of the river has extensive stands of mangroves, part of the Esmeraldes-Pacific Colombia mangroves ecoregion. See also *List of rivers of Colombia Atlantic Ocean Amazon River Basin * Amazon River ** Guainía River or Negro River *** Vaupés River or Uaupés River **** Papuri River **** Querary River *** Isana River or Içana River **** Cuiari River *** Aquio River ** Caquetá River o ... References Sources * Rivers of Colombia {{Colombia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remolino-El Charco Fault
The Remolino-El Charco Fault ( es, Falla de Remolino-El Charco) is a dextral strike-slip fault in the department of Nariño in Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 046.4 ± 6 in the Tumaco Basin along the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Etymology The fault is named after Remolino Grande and El Charco, Nariño.Paris et al., 2000a, p.55 Description The Remolino-El Charco Fault extends through the Pacific coastal lowlands and plains of Colombia to the east of the city of Tumaco. The fault begins in the southwesternmost point of Colombia and runs towards Guapi.Paris et al., 2000b It is close to and parallels the coast. It displaces alluvial fan sediments of the Patía, Mira, and Telembí Rivers and some Pleistocene marine terraces. The fault appears to be a southern continuation of the Naya-Micay Fault. The fault has a very well defined fault line on aerial photographs and satellite images. Pattern of deflection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the merged Paleogene and Neogene periods, which are informally called the Early Tertiary and the Late Tertiary, respectively. The Tertiary established the Antarctic as an icy island continent. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |